Figure 4.
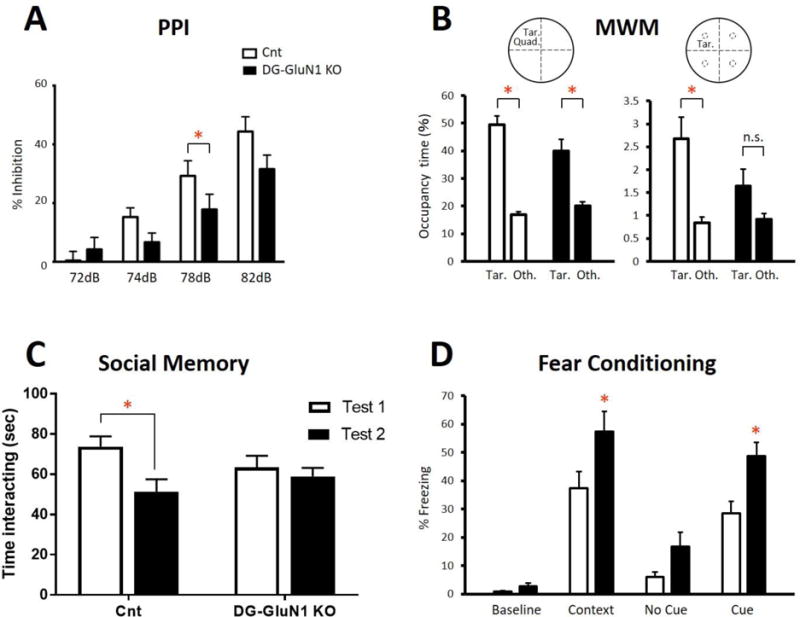
(A) Prepulse inhibition (PPI) was reduced in DG-GluN1 KO mice compared with cont littermates. Two way ANOVA (genotype × dB level): F(3,108)=3.299, * p=0.0232. Decible level: F(3, 108)=55.15, p<0.0001; Genotype: F(3,108) 2.127, p=0.1534. Post hoc test at 78 dB, *p=0.039 and a trend for significance at 76 dB, p=0.066.
(B) Morris water maze. Number of crossings of the target quadrant (left) vs the mean of the other non-target quadrants (right) on Day 13 probe test. The cont mice (left, white) remembered where the platform was located (target quadrant relative to average of the other quadrants: t=9.715, df1,38, p<0.0001 or platform area relative to average of the parallel areas in the other quadrants: t=3.792, df1,38, p=0.0005); whereas, DG-GLuN1 KO mice (right, black) failed to remember accurately where the target was located (target quadrant relative to average of the other quadrants: t=4.370, df1,34, p<0.0001; platform area relative to average of the corresponding areas in the other quadrants: t=1.831, df1,34, p=0.0758). Platform vs other.
(C) Social memory (SM). In contrast to cont mice (t=2.81, df1,24, p=0.02), DG-GluN1 KO mice showed no decrease in interaction time upon re-exposure to a juvenile mouse 24 hours following initial exposure (t=0.62, df1,24, p=0.79). (D) Fear conditioning: The unconditioned DG-GluN1 KO mice did not show elevated freezing in a new context (t=1.37, df1,28, p=0.18). However, when analyzing genotype × situation with 2-way ANOVA, there was a significant effect of situation (F(2,28)=34.43, p<0.0001) and genotype (F(1,14)=20, p=0.0005) (interaction genotype × situation: F(2,28)=0.4838, p=0.6215). Post hoc tests showed a significant increase in freezing in the same context (p=0.0160) and in the cued context (p=0.0147) without difference in the new context (p=0.1792).
