Figure 6.
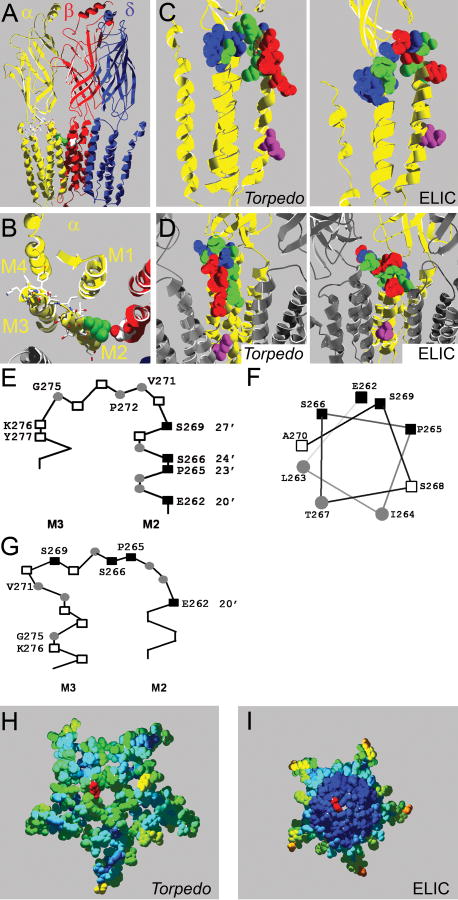
Homology models of the mouse muscle nAChR. A, Side view of homology model based on the Torpedo nAChR structure, one α-subunit and the γ-subunit are omitted for clarity. The intracellular domain - most of which was not resolved in the Torpedo nAChR structure - is not shown. Residue αL263 is in green, other residues mutated to Cys in α-subunits in stick representation and CPK colors, βD268 is shown in space filling representation and CPK colors. B, Same model as in A but viewed from the extracellular side focusing on the α-subunit (yellow). Only the slice of the receptor in the M2M3 loop area that we investigated is shown, the extracellular domain is not shown. C, Rate of MTSEA modification indicated in homology models of the nAChR α subunit based on the Torpedo (left) and ELIC (right) structures. The rate of MTSEA reaction is color coded: red = fast reacting (>10,000 M-1s-1), green = slow reacting (<1,000 M-1s-1), blue = non reactive, pink = 9′ Leu, viewed from the side, and D, same models as in panel C except viewed from the channel lumen with two neighboring subunits in grey for orientation purposes. E, Schematic representation of the residues we studied based on Unwin's structure, positions with fast modification rates (■), slow rates (●), and residues where MTSEA application did not cause an effect (□) viewed from the side, and F, M2 positions studied plotted on an α-helical wheel viewed from the extracellular side. G. Same as in E, except based on the ELIC structure. H, Computed overall water accessibility of the Torpedo and I, ELIC structures of a topview slice of the receptors encompassing the investigated area. One 20′ αE262 residue for orientation in red. Otherwise color coding of investigated amino acids as per accessibility of a 1.4 Å sphere. Scale is red to blue where red is highly accessible and dark blue is inaccessible. Note that in contrast to the Torpedo structure the center of the ELIC structure consists entirely of water inaccessible (dark blue) residues which in general indicated higher compactness.