Figure 3. Delirium over time.
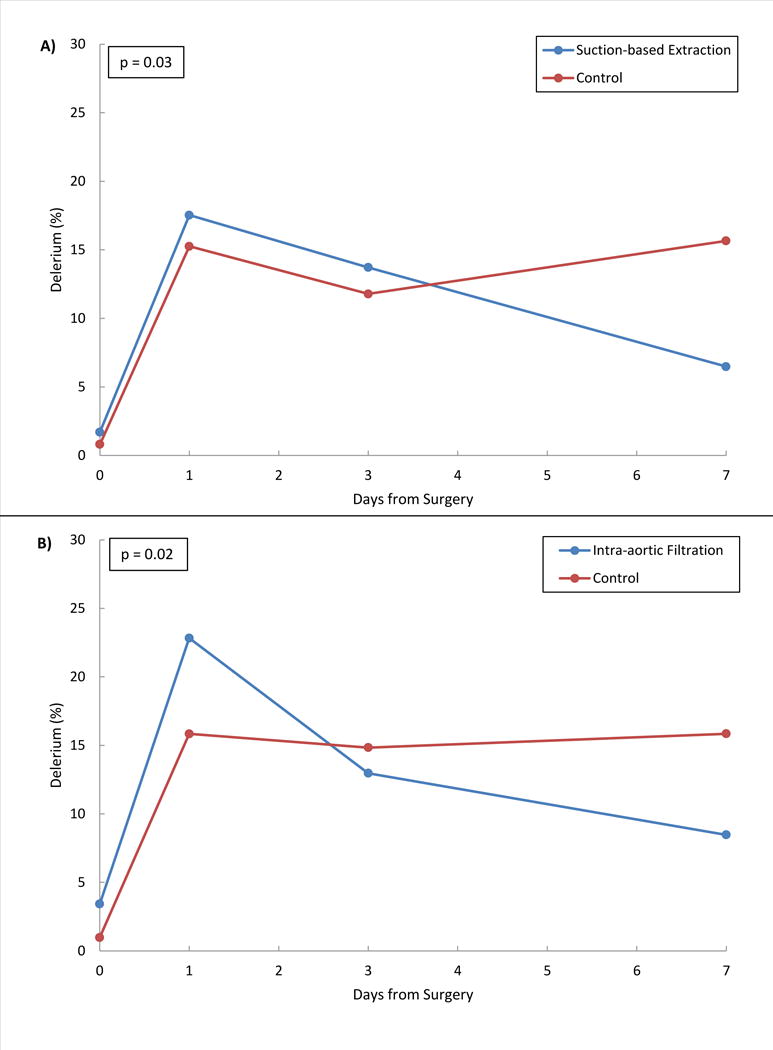
Delirium was measured by CAM assessment at baseline, days 1, 3 and 7. For both treatment devices vs. controls, the probability of delirium over time was modeled using GEE. Panel A gives the model estimated incidence of delirium at baseline, days 1, 3 and 7 for the suction-based extraction device vs. control and panel B gives estimates for the intra-aortic filtration device vs. control. In both models, the interaction term between days from surgery and randomization group was statistically significant (p<0.05) indicating that the incidence of delirium over time was significantly different between treatment interventions and their controls.
