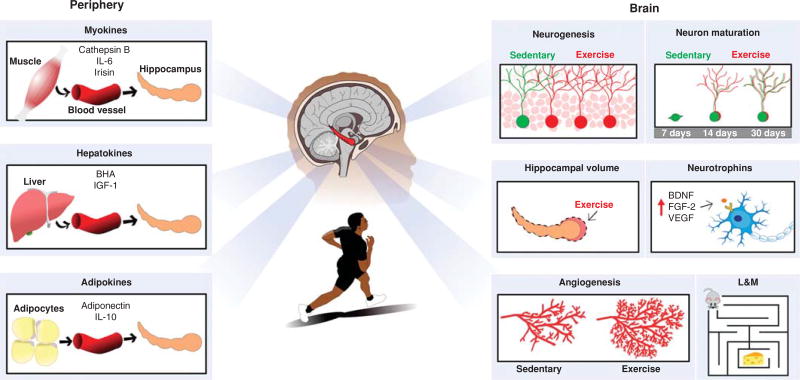
Figure 1.
Running induces structural and functional plasticity in the hippocampus. Illustration summarizing how running enhances neurogenesis, accelerates new neuron maturation, augments hippocampal volume (in humans), and promotes angiogenesis. Enhanced neural plasticity and improved memory function may be supported by central and peripheral factors. Increased levels of growth factors in the brain may result, in part, from systemic factors secreted by muscle (myokines), liver (hepatokines), and fat cells (adipokines). BHA, β-Hydroxybutyrate; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; FGF-2, fibroblast growth factor 2; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-10, interleukin 10; L&M, learning and memory; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.