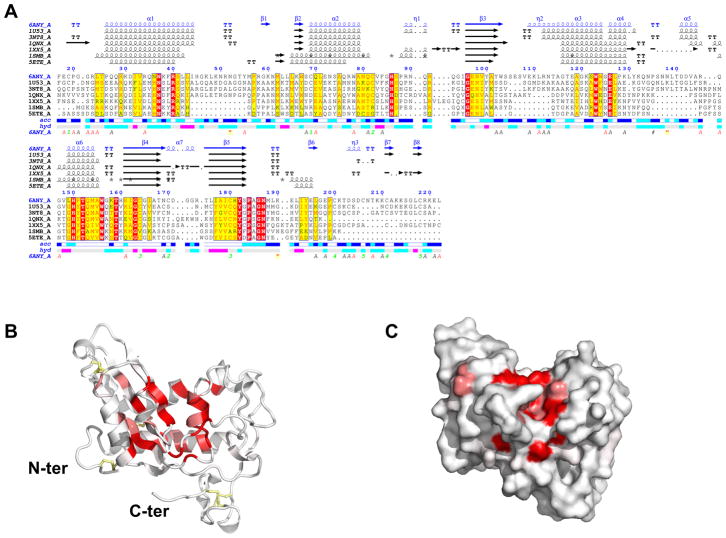
Fig. 3.
Structural alignment of Brugia malayi venom allergen-like protein 1 (BmVAL-1) with selected SCP/TAPS (Sperm-coating protein/Tpx/antigen 5/pathogenesis related-1/Sc7) proteins. (A) ENDscript (Robert and Gouet, 2014) alignment identifies conserved residues in CRISP-type SCP/TAPS proteins. Amino acid numbering corresponds to full-length BmVAL-1. Also shown are vector-derived C-ter amino acid residues. Identical and conserved residues are highlighted in red and yellow, respectively. The different secondary structure elements shown are alpha helices (α), 310-helices (η), beta strands (β), and beta turns (TT). The representative structural models with their respective protein data bank codes are Na-ASP-2 (1U53); Na-ASP-1 (3NT8); GAPR-1 (1SMB) (van Galen et al., 2012); a major allergen from Vespula vulgaris venom, Ves v 5, (1QNX), (Henriksen et al., 2001); the snake venom protein natrin, 1XX5, (Wang et al., 2006); and Pry1 CAP domain 5ETE (Darwiche et al., 2016). Solvent accessibility (acc) and hydropathy scales per residue (hyd) are also indicated. (B) Ribbon and (C) surface plots of BmVAL-1 reveal that identical residues cluster mostly around the central cavity. Identical residues are shown in red while conserved are shown in pink, and disulfide bridges are shown in yellow.