Figure 1.
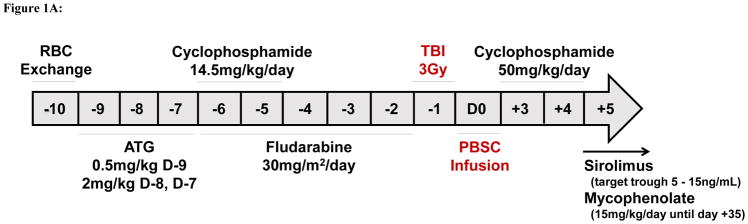
Figure 1A: Regimen for haploidentical transplantation in adult patients with sickle cell disease.
Figure 1B: Screening process for haploidentical transplantation in adult patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). Of 50 patients referred to the SCD transplant clinic, 41 proceeded with HLA typing. 25 (61%) had a suitable HLA-haploidentical donor with 4 (10%) lacking an available HLA-haploidentical relative and 12 (29%) having donor-specific HLA antibodies. In addition, 10 (20%) were denied by insurance and 14 (34%) declined or deferred transplantation.
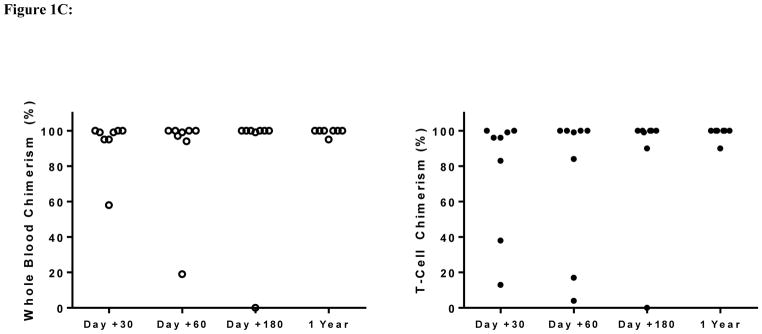
Figure 1C: Stable whole blood and CD3+ T-cell engraftment after haploidentical transplantation in adult patients with sickle cell disease.
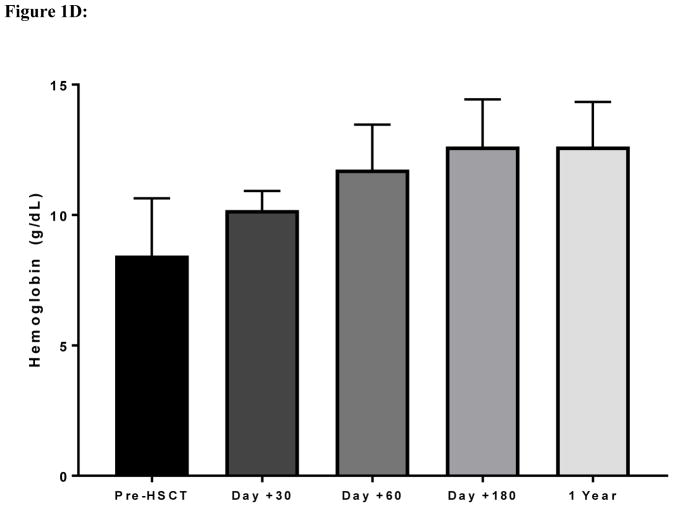
Figure 1D: Improvements in hemoglobin concentration after haploidentical transplantation in adult patients with sickle cell disease.