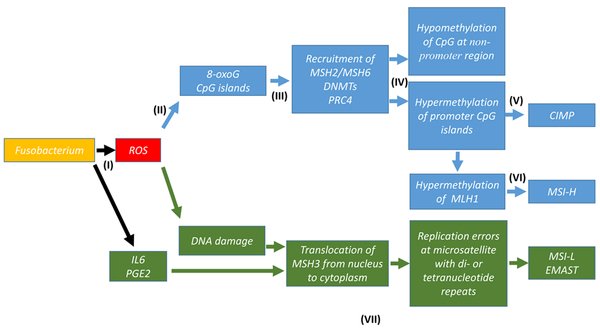
Fig. 1:
Hypothetical Pathways of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations in CRC induced by Chronic Fusobacterium Infection
(I): Chronic infection of colon mucosa by Fusobacterium induces ROS and other pro-inflammatory factors including IL6 and PGE2 (references 5,50).
(II): ROS generates clustered 8-oxoG lesions at promoter CpG island.
(III): MSH2/MSH6, DNMT1, DMNT3B and PRC4 are recruited from whole genome and enriched at damaged promoter CpG islands.
(IV): non-promoter CpG sites become DNMT-poor, leading to hypomethylation.
(V): Recruited DNMT1 and DMNT3B methylate promote CpGs to enhance DNA repair by MSH2/MSH6, leading to hypermethylation of CpG islands (CIMP) (references 53–56).
(VI): hypermethylation of the hMLH1 promoter CpG island leads to MSH-H.
(VII): DNA damage (8-oxoG) or IL6/PGE2 induces translocation of MSH3 from nucleus to cytoplasm, leading to MSI-L/EMAST (references 37,39).
Blue arrows and boxes represent the pathway to CIMP/MSI-H triggered by Fn infection.
Green arrows and boxes represent the pathway to MSI-L/EMAST triggered by Fn infection.