Fig 1.
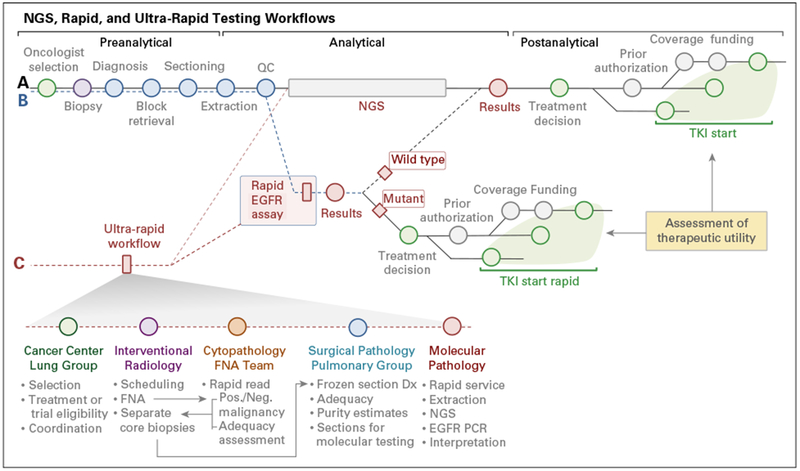
Rapid EGFR testing approach. We implemented rapid EGFR testing in parallel to genotyping using next-generation sequencing (NGS; compare pathway A v B). As a result of differences in reporting times, detection of an actionable EGFR mutation with rapid testing might lead to a treatment decision before NGS results are obtained. Note that there is a (variable) delay from reporting to treatment decision and initiation of therapy because of cost-coverage determination, preauthorization requirements, etc. The ultra-rapid EGFR testing pathway (pathway C) is a multidisciplinary workflow designed to improve turnaround time using fresh tissue (frozen sections) to extract nucleic acids. Note that ultra-rapid testing combines preanalytical improvements with the optimized rapid workflow and allows coupling with NGS (Data Supplement). Dx, diagnosis; FNA, fine-needle aspiration; Neg, negative; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; Pos, positive QC, quality control; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
