Figure 3.
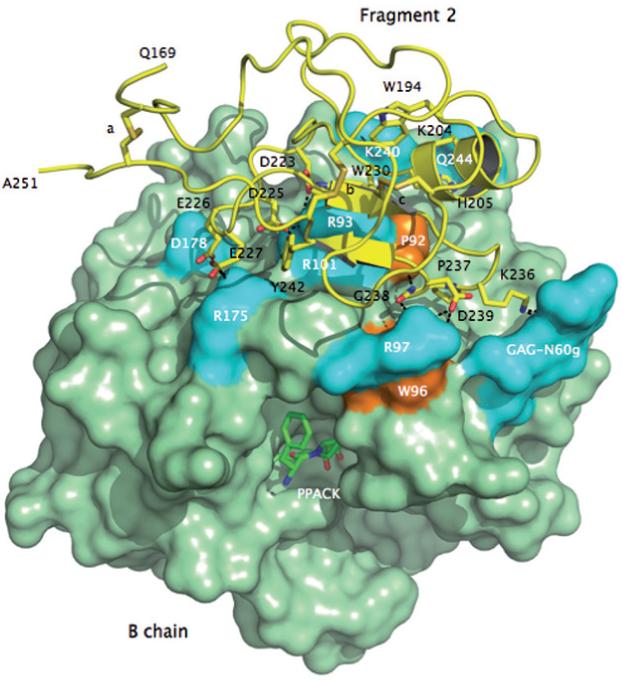
Crystal structure of meizoIIRRΔF1 at 2.1 Å resolution showing the architecture of fragment 2 (ribbon and sticks in yellow) and its docking on the surface of the B chain (green). Three disulfide bonds stabilizing the kringle domain of fragment 2 are indicated with letters a (C170-C248), b (C219-C243) and c (C191-C231). Shown are the residues of fragment 2 that make direct interactions with the B chain. The anionic cluster DGDEE (residues 223-227), corresponding to the Lys-binding center of other kringles in plasminogen and tissue-type plasminogen activator, makes extensive ionic interactions (cyan) with R93, R101 and R175. R93 and R101 are critical residues for the binding of heparin [66] and the γ’-peptide of fibrinogen [67]. Other ionic interactions involve D239 with R97 of the B chain, K236 with the GAG moiety linked to N60g of the 60-loop and Q206 with K240. The only relevant hydrophobic interactions (orange) of fragment 2 with the B chain involve the environment of P92 and W96 with P237 and G238. W194 and W230 are in stacking interaction with each other and presumably function as a single fluorophore. Perturbation of W96 and the presence of W194 and W230 may be responsible for the different fluorescence response to Na+ binding observed in meizoIIRRΔF1 compared to thrombin (see Fig. 4).
