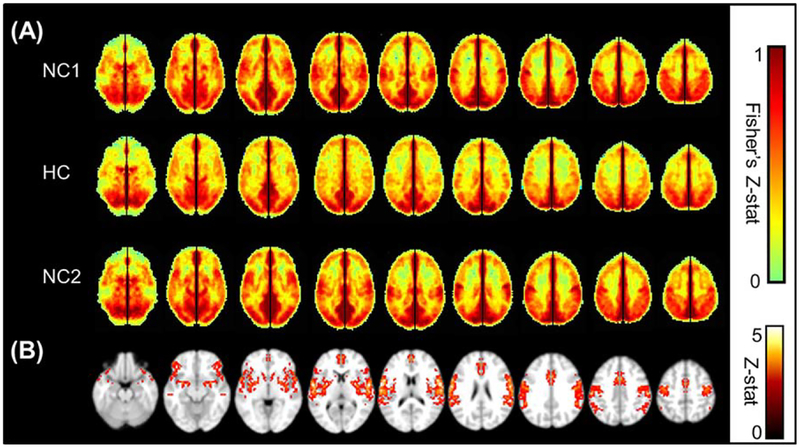
Figure 2.
(A) Average VMHC maps showing Fisher Z-transformed correlation, restricted to GM only, of the first normocapnic run (NC1), the hypercapnic run (HC), and the second normocapnic run (NC2). Enough time (at least 2 min) was given each time the delivered air was switched between normocapnia and hypercapnia, to allow end tidal CO2 to return to a steady state. A global decrease in VMHC is seen under hypercapnia, which is restored to the original magnitude in the final normocapnia run. The color bar shows the limits of the Z-score values. (B) Significant group decrease from NC1 to HC shown as a result of a voxel by voxel pairwise comparison of the Fisher’s Z-transformed VMHC maps, performed in FSL/FEAT (minimum Z > 2.3; cluster level, P < 0.05, corrected). [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]