Figure 15.
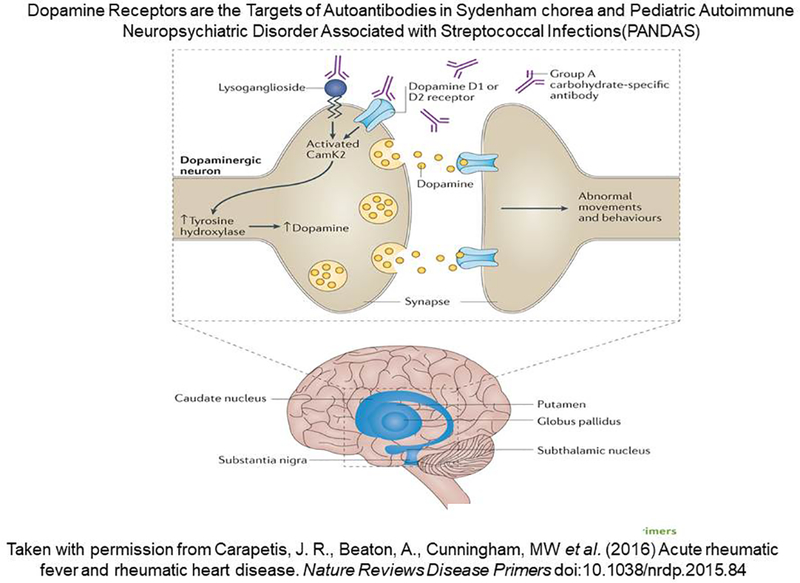
Diagram of proposed events leading to the group A streptococcal sequelae Sydenham chorea and Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorder Associated with Streptococcal Infections (PANDAS). Autoantibodies against brain tissues in Sydenham chorea and PANDAS with pianoplaying choreiform movements cross-react with the group A streptococcal carbohydrate, lysoganglioside, and dopamine receptors D1R and D2R. The antibodies in Sydenham chorea and PANDAS react with the surface of neuronal cells and trigger cell signaling events leading to upregulation of calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and excess dopamine release that leads to the involuntary movements in Sydenham chorea or PANDAS with pianoplaying choreiform movements. Both Sydenham chorea and PANDAS are likely to be a dopamine receptor encephalitis based on our data (194, 210) and those of Dale et al (202, 203).
