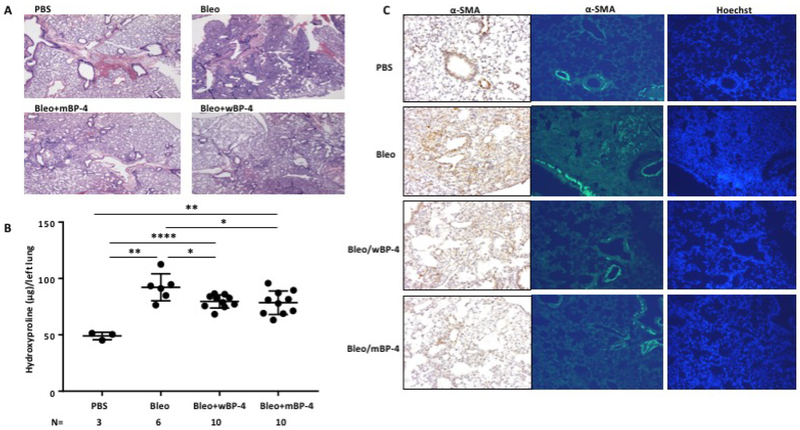
Figure 4: IGFBP-4 attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis and α-SMA levels in vivo independently of IGF-1.
A. IGFBP-4 attenuates bleomycin induced lung fibrosis in mice. Purified recombinant wild type (wBP-4) and IGFBP-4 with a mutated IGF-binding domain (mBP-4) were intratracheally administered to mice (10 μg/dose for a total of 3 doses on days 0, 3 and 6). Mice were euthanized after 21 days. Histologic assessment of H&E-stained sections shows that both wild type and mutant IGFBP-4 reduced lung fibrosis. Images are representative of 3–4 mice/group. B. IGFBP-4 reduces total collagen deposition as measured with hydroxyproline assay. Mice were treated as in A, and the left lung was used for measuring hydroxyproline levels. Both wBP4 and mBP4 significantly reduced hydroxyproline levels (number of mice/group is as indicated in the figure). C. IGFBP-4 reduces α-SMA levels in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Mice were treated as in A. The right lung was used for immunohistochemistry (left panel) and immunofluorescence (right panel) to detect α-SMA, Hoechst was used to detect nuclei. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.