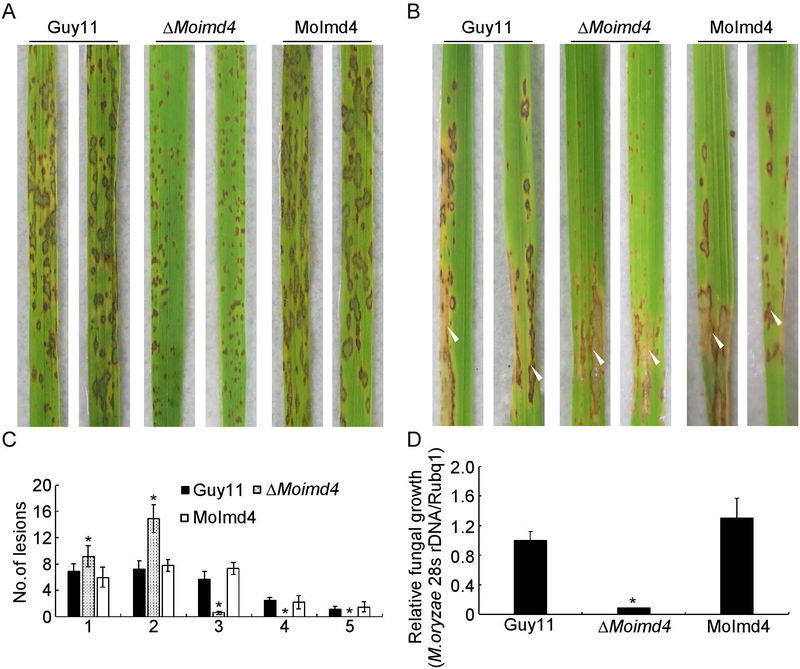
Fig. 2.
MoImd4 is required for pathogenicity. (A) Conidial suspensions (5 × 104 spores/ml) of Guy11, ΔMoimd4, and the complement strains were sprayed onto 11-day rice seedlings and photography were made 7 days after inoculation. (B) Conidial suspensions (15 × 104 spores/ml) were injected into 18-day old rice sheaths and photography were made 5 days post inoculation (dpi). (C) Lesions type statistical analysis. (0, no lesion; 1, pinhead-sized brown specks; 2, 1.5 mm brown spots; 3, 2–3 mm grey spots with brown margins; 4, many elliptical grey spots longer than 3 mm; 5, coalesced lesions infecting 50% or more of the leaf area). Lesions were photographed and were measured after 7 dpi. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. Asterisk represents significant differences (Duncan’s new multiple range test, p<0.01). (D) Severity of lesions was analyzed by quantifying M. oryzae genomic 28S rDNA relative to rice genomic Rubq1 DNA. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. Error bars represent the standard deviations and asterisk represents significant difference (Duncan’s new multiple range test, p<0.01).