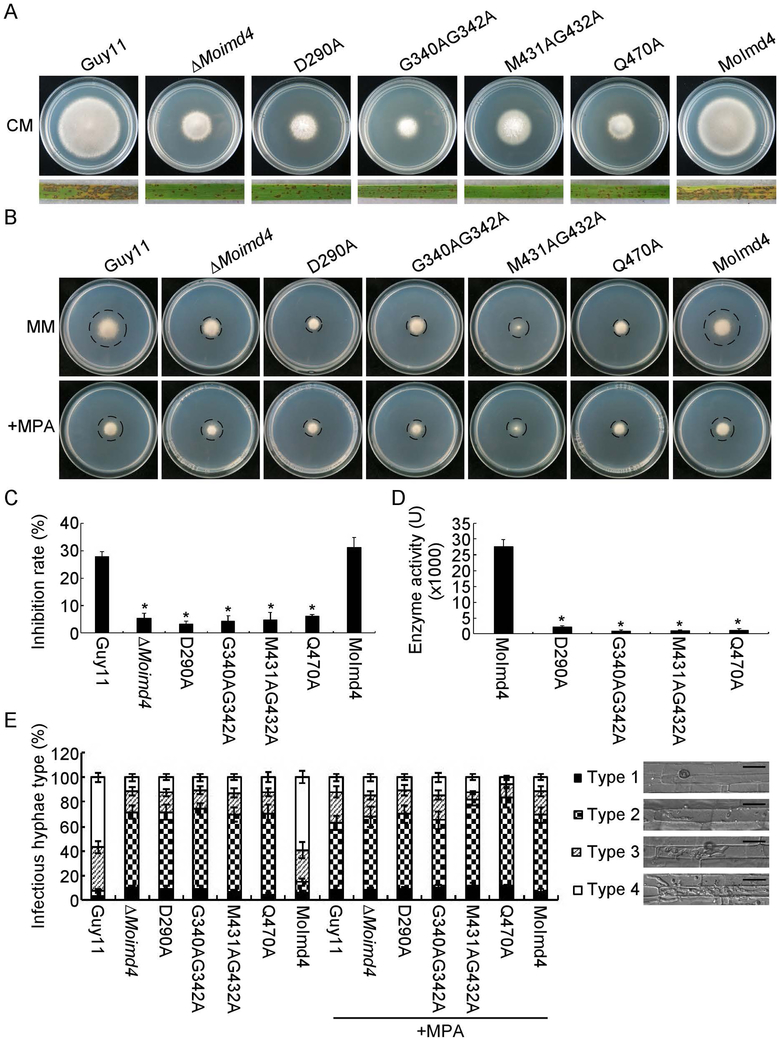
Fig. 4.
Inactivation of MPA binding sites leads to attenuation of MoImd4 activities. (A) Vegetative growth of Guy11, ΔMoimd4, D290A, G340AG342A, M431AG432A, Q470A mutants, and the complement strains on CM media at 7 days in the darkness. Conidial suspensions (5 × 104 spores/ml) of the indicated strains were sprayed onto 11-day old rice seedlings. Photographs were taken 7 days after inoculation. (B) Vegetative growth of Guy11, ΔMoimd4, D290A, G340AG342A, M431AG432A, Q470A and the complement strains on MM media treated with or without 10 μg/ml MPA. (C) Inhibition rates of the indicated strains on MM media treated with or without 10 μg/ml MPA. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. The error bars indicate standard deviation of three replicates. Asterisk indicates statistically significant differences (Duncan’s new multiple range test, p<0.01). (D) Detection of enzymatic activities of the indicated strains in vitro. Target proteins were expressed in E. coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3) cells. We defined that the production of 1 mM XMP per milligram of protein per minute as one unit of enzyme activity (U). Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. The error bars indicate standard deviations of three replicates. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (Duncan’s new multiple range test, p<0.01). (E) Statistical analysis of IH of the indicated strains with or without 10 μg/ml MPA after 48 hpi, approximate 100 IH were counted and the experiments were repeated three times. The error bars indicate standard deviations of three replicates. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (Duncan’s new multiple range test, p<0.01). Four type grading standards as in Figure 3E. Bar = 10 μm.