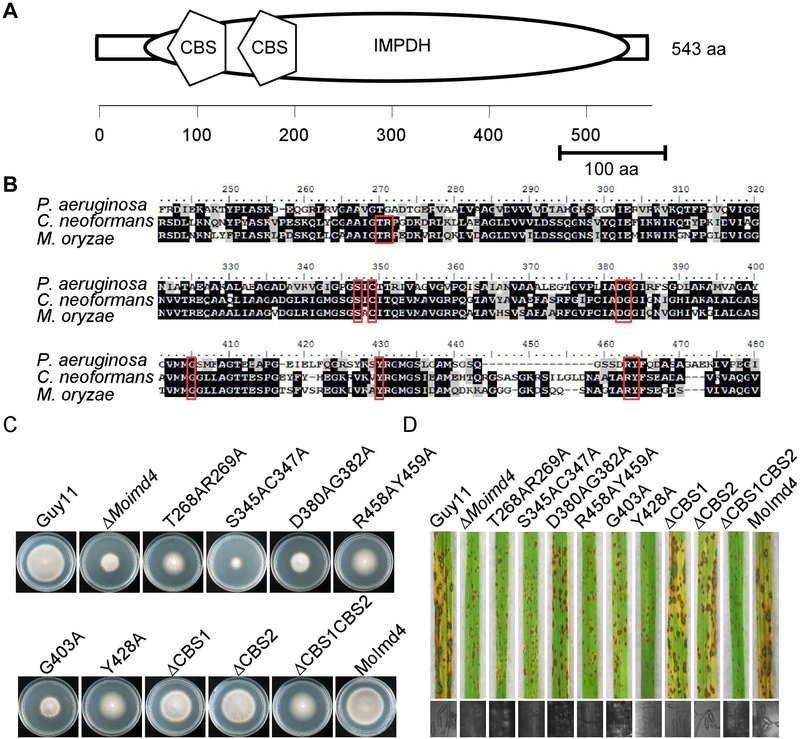
Fig. 5.
Functional characterization of CBS domains and reaction sites of MoImd4. (A) Schematic representation of MoImd4 IMPDH domain (oval) and tandem CBS subdomains (pentagon). Domains were predicted using the SMART program (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/). (B) Multiple alignments of P. aeruginosa, C. neoformans, and M. oryzae IMPDH proteins. Red boxes represent conservative functional sites involved in the interaction with the substrates. The amino acid identity of IMPDH was 37% between M. oryzae and P. aeruginosa, and 63% between M. oryzae and C. neoformans. (C) The wild type Guy11, ΔMoimd4, the complement strains, predicted sites mutation mutants, and CBS domain deletion mutants were incubated on CM media at 28˚C in the dark and photographed after 7 days incubation. (D) Pathogenicity test on rice seedlings of the indicated strains. Infected rice leaves were illuminated under the fluorescent light for 24 h to produce conidia. The lesions were observed under a light microscope.