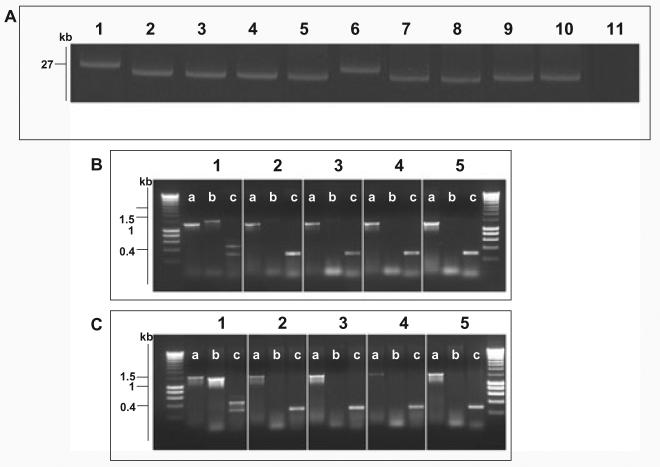
Fig. 4.
Molecular basis of fljB z66 to fliC phase change.
A. Agarose gel electrophoresis of alkaline lysis plasmid preparation from S. Typhi strains pre- and post-phase switch. Lane 1, S. Typhi 403ty-fliC(j) (j); Lane 2, 403tya; Lane 3, 403tyb; Lane 4, 403tyc; Lane 5, 403tyd; Lane 6, S. Typhi 404ty-fliC(d); Lane 7, 404tya; Lane 8, 404tyb; Lane 4, 404tyc; Lane 5, 404tyd. Sizes are estimated with respect to pBSSB1 (27, 037 kbp) isolated from S. Typhi 403ty(j) and S. Typhi 404ty-fliC(d).
B. Agarose gel of PCR amplicons produced to identify the nature of the deletion produced post phase change in strains derived from S. Typhi 403ty-fliC(j). The target for the PCR primers are; (i) fliC, primers fliC_F/R; (ii) fljB z66, primers z66flag_F/R; (iii) terminal inverted repeat (tir), primers tir_a, tir_d and tir_e. Each panel represents template genomic DNA from: 1, S. Typhi 403ty-fliC(j); 2, 403tya; 3, 403tyb; 4, 403tyc and 5, 403tyd. Sizes are compared with migration of Hyperladder I (Bioline).
C. PCR amplifications as B using genomic template DNA from: 1, S. Typhi 404ty-fliC(d); 2, 404tya; 3, 404tyb; 4, 404tyc and 5, 404tyd.