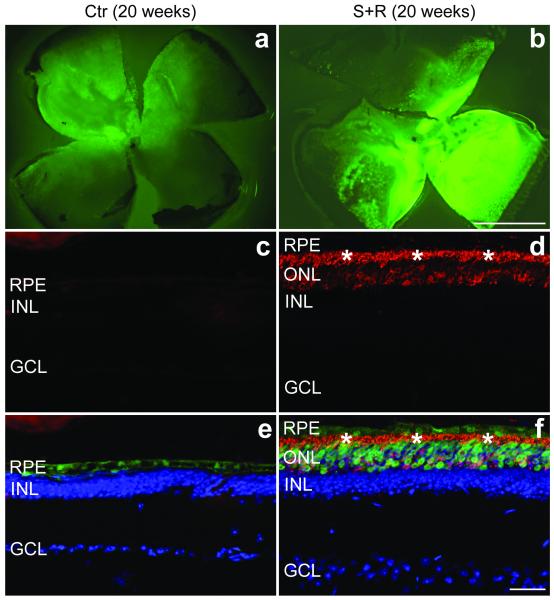
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemical analysis of rhodopsin expression following combined suppression and replacement therapy twenty weeks post-injection.
The right eyes of P5 P347S mice were subretinally injected with a mixture of 6.0×108 vp AAV-S (b, d and f) and 1.8×1010 vp AAV-R while the left eyes were injected with 6.0×108 vp AAV-C (a, c and e). Note that AAV-S and AAV-C co-express EGFP. Eyes were fixed (n=5), whole mounted for imaging, then cryosectioned (12 μm) and processed for immunocytochemistry using rhodopsin primary and Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. a and b: representative whole mounts. c and d: representative sections show rhodopsin labelling (red). e and f: rhodopsin (red), EGFP (green) and nuclear DAPI (blue) signals overlaid. *: photoreceptor segment layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; GCL: ganglion cell layer; RPE: retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bars: 1 mm (a and b) and 25 μm (c–f).