Figure 6. Inequality and envy.
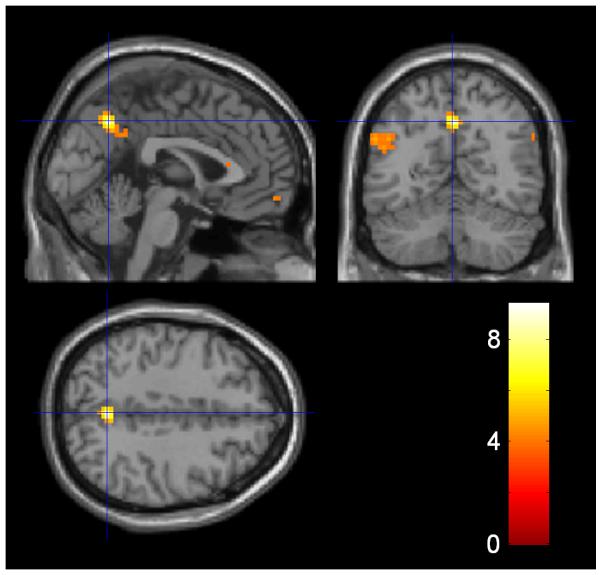
For each subject we calculated an α (envy) parameter by fitting an inequality aversion model to behavioural data of the Responder. In this economic model, utility is the offer amount minus inequality (defined as amount to other minus amount to self) and inequality is weighted by α. Given their close relationship, the envy parameter was used as a second level covariate on the main effect of inequality. Areas highlighted are those that correlate between subjects with the degree to which the Responder cared about how much money the other person stood to gain relative to themselves. Activation surviving whole brain correction at the voxel level (P<0.05 FWE) was seen in precuneus (x=0, y=−60, z=42) and L frontopolar cortex (x=−18, y=60, z=18), whilst activation surviving cluster level correction (P<0.05 FWE corrected; threshold of P<0.005 used to define the clusters) is seen in the L angular gyrus (inferior parietal cortex) (x=−54, y=−60, z=30). The data are displayed at P<0.001 (uncorrected) at the peak voxel of the precuneus activation.
