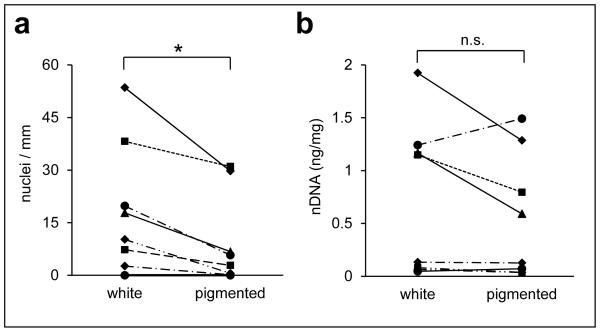
Fig. 2.
The influence of pigmentation on the detection of nuclear DNA remnants in hair. Hairs of 8 individuals were separated in pigmented (brown or black) and non-pigmented (white) hairs. In a fraction of hairs from each group, DNA was labeled in situ and nuclei were counted under the microscope (a). In another batch of hairs from each group, DNA was extracted amplified by quantitative PCR with primers specific for nuclear DNA (b). Lines connect results of samples from black and white hair of the same individual. The significance of differences was determined with a paired t-test. Asterisk, p < 0.05; n.s., not significant