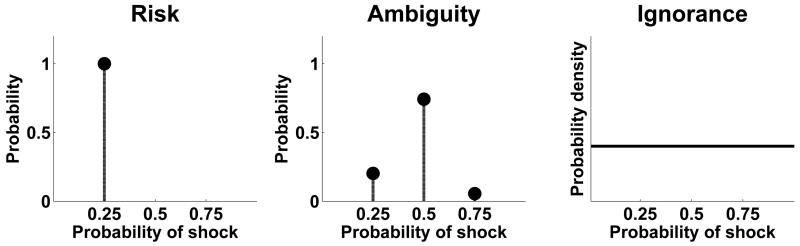
Figure 1.
Examples for outcome prediction after risky, ambiguous or ignorance cues, visualised by a second order distribution of outcome probabilities. In the risk condition, prediction of outcome probability corresponds to a point estimate (left). In ambiguous trials, outcome probabilities can be predicted using a second-order distribution, thus rendering outcome predictions probabilistic. Ignorance cues convey no information about outcomes, the outcome probability could therefore have any value, and its prediction corresponds to a uniform distribution.