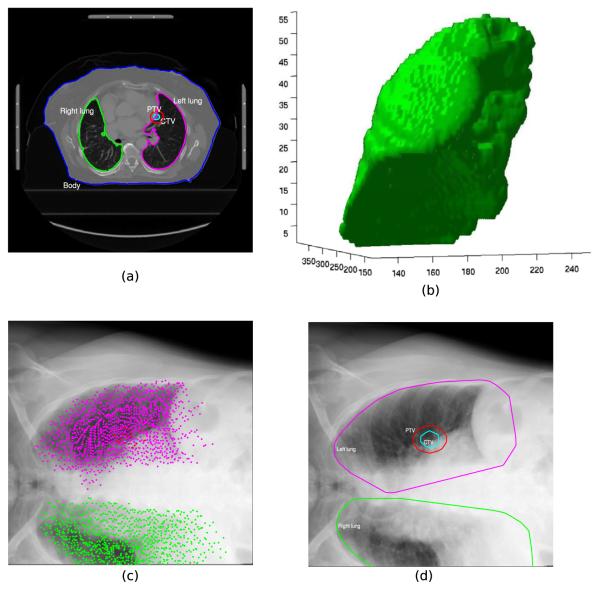
Fig. 1.
Illustration of the method used to define the ROI for the clinical patient data sets. The contours of the planning CT from DICOM-RT data (a) were used to derive a 3D surface model of the organs, PTV and CTV (b, only the 3D model of the right lung is shown); the points that define the vertices of the 3D surface model were projected into the 2D X-ray imaging plane using the first transformation matrix Tinit (c). The convex hull that enclosed all points of the organs is shown in (d). The convex hull of the PTV was used as the ROI for the 2D/3D registration.