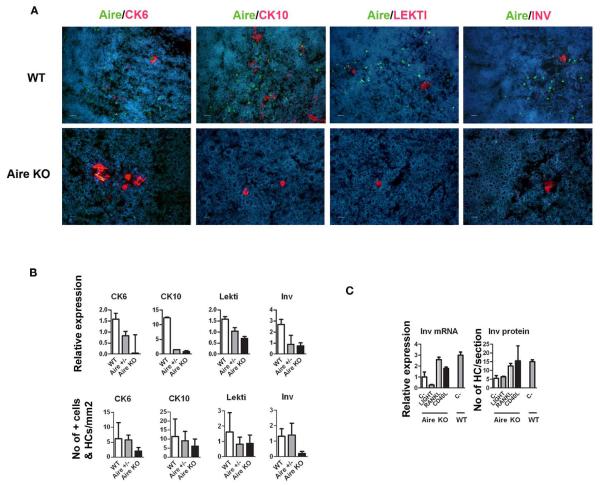
FIGURE 2. Effect of Aire on the expression of epidermal differentiation markers and the effect of TNFRSF ligands on the expression of involucrin.
(A) Thymi from 6-week-old WT or Aire KO mice were stained for Aire and four epidermal differentiation markers CK6, CK10, LEKTI, involucrin by immunofluorescence. In the WT mice, Aire showed green dots in the nuclei of medullary thymic epithelial-like cells. CK6, CK10, LEKTI, and involucrin showed staining mainly in the outer layer of HCs. There was some co-staining for Aire and CK6 or CK10, whereas Aire and LEKTI or involucrin never co-localized. In the Aire KO thymus, there was no staining for Aire, while CK6, CK10, LEKTI, and involucrin showed some staining in the outer layers of HCs. This relatively rare positive staining is depicted on the panels of the Aire KO mice, whereas for the WT mice typical representative medullary stainings of at least three experiments are shown. DAPI was used for nuclear staining. Bars correspond to 20 μm. (B) Relative gene and protein expression of epidermal differentiation markers in wild-type (WT), heterozygous (Aire+/−), and Aire KO mouse. Whole thymi were collected for RNA purification and analyzed by qPCR or stained for CK6, CK10, LEKTI, and involucrin. In the Aire KO mouse, there was a statistically significant reduction of all four epidermal differentiation markers at the mRNA level and of CK6 and involucrin at the protein level (p < 0.05 as compared with WT, Student’s t-test, n = 3), whereas the protein signals for CK10 and Lekti did not reach statistical significance (p > 0.05). Values are mean ± SEM of triplicate experiments. (C) Relative gene and protein expression of involucrin in Aire KO thymus after treatment with LIGHT, RANKL, or CD40L. Thymi from Aire KO or WT mice were treated ex vivo for 24 (for mRNA) or 48 h (protein) and analyzed thereafter for involucrin expression by qPCR or immunofluorescence. The TNFRSF ligands RANKL and CD40L increased the gene and protein expression of involucrin in the Aire KO mice (p < 0.05, Student’s t-test, n = 3). Values are mean ± SEM of triplicate experiments.