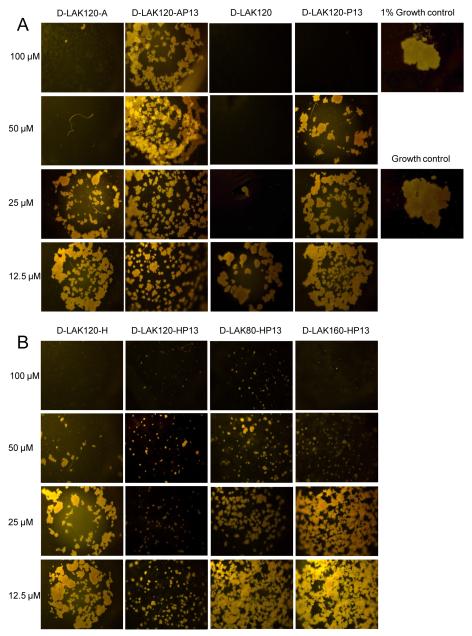
Figure 1.
The ability of eight D-LAK peptides to inhibit the growth of M. tuberculosis H37Ra is shown and compared with a positive growth control (1 × 106 CFU/ml) and a 1% growth control (1 × 104 CFU/ml). When histidine free peptides are compared (A), a reduction of antibacterial activity is observed when proline is incorporated. For histidine containing peptides (B), incorporation of proline increases antibacterial activity. Altering the angle subtended by the lysine residues to either 80 or 160° diminishes peptide potency.