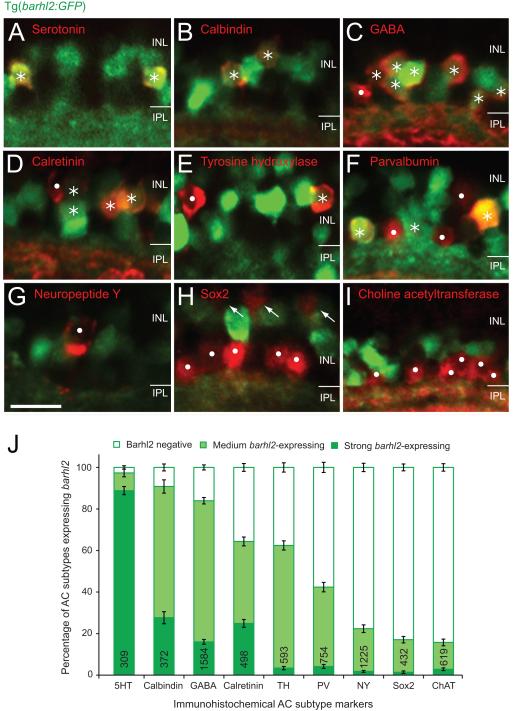
Figure 2.
Amacrine markers reveal distinct subtypes expressing barhl2. Micrographs of 120 hpf Tg(barhl2:GFP) embryos immunohistochemically labelled with markers (red). (A – C) Serotonin (5HT, A), calbindin (B) and GABA (C) immunoreactive AC types primarily co-label with Barhl2:GFP. (D – F) Calretinin (D), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, E) and parvalbumin (PV, F) labelled populations show varying degree and intensities of Barhl2:GFP co-labelling. (G – I) Neuropeptide Y (NY, G), Sox2 (H) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT, I) label ACs that do not co-label with Barhl2:GFP. Sox2 additionally labels Müller glia cells (arrows, H). Asterisks indicate ACs (red) that co-localise with GFP; dots mark cells that do not express GFP. (J) Quantification of the percentage of different markers co-labelled with Tg(barhl2:GFP), n = 21 – 220 eyes, 309 – 1584 cells. ACs labelled by 5-HT, calbindin and GABA primarily arise from barhl2-expressing cells. ACs labelled by NY, Sox2 and ChAT primarily come from Barhl2-negative or weakly barhl2-expressing cells. ACs labelled with calretinin, TH or PV include both, cells that do and do not arise from barhl2-expressing cells. AC: amacrine cell. Numbers in each bar indicate the number of labelled cells analyzed. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. INL: inner nuclear layer; IPL: inner plexiform layer. Scale bar G (for A – I) = 20 μm.