Figure 3. Role of the tandem C2 domain and PH domain of CAPRI.
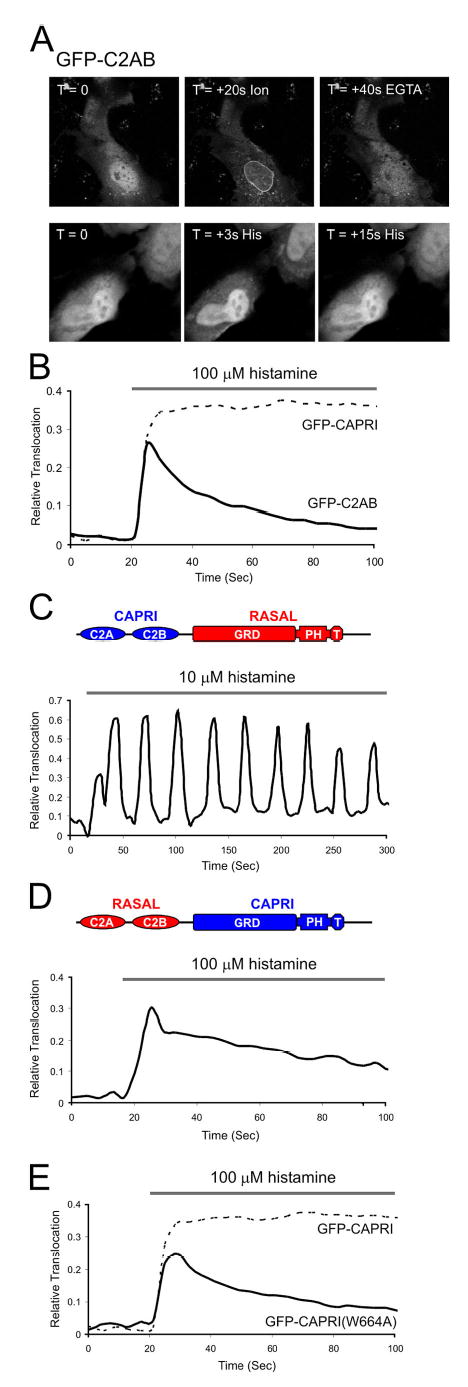
(A) Top: 5 μM ionomycin is sufficient to drive GFP-C2AB CAPRI to the HeLa inner nuclear membrane (+ ion = 20 s after stimulation). Translocation is Ca2+-dependent (+ EGTA = 40 s after 5 mM EGTA-containing media). Bottom: GFP-C2AB plasma membrane translocation induced by histamine. (B) GFP-C2AB translocation in HeLa cells stimulated with 100 μM histamine. Bold trace is GFP-C2AB (average n = 7 cell, n = 3 experiments) compared with average GFP-CAPRI translocation (dotted trace) under similar conditions (see Fig. 1 B). (C) Representative response of GFP-CAPRI/ RASAL chimera to 10 μM histamine. (D) Response of GFP-RASAL/CAPRI chimera to 100 μM histamine (average n = 6 cells, n = 2 experiments). (E) Response of GFP-CAPRI (W664A) to 100 μM histamine (average n = 12 cells, n = 3 experiments).
