Fig. 1.
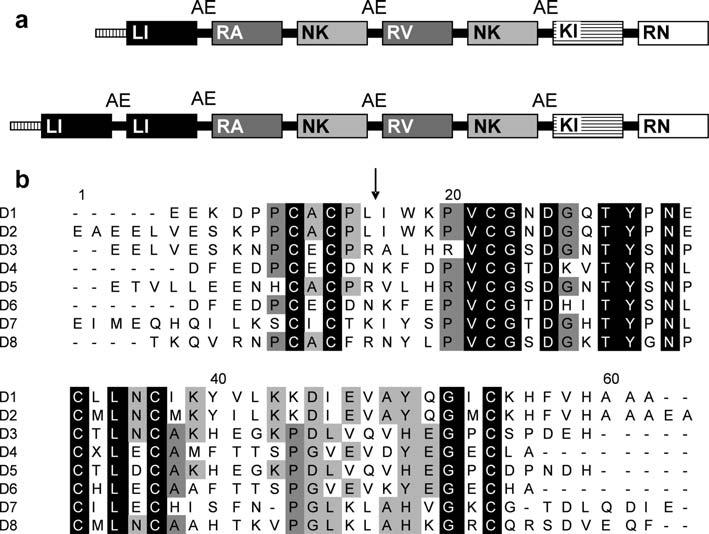
Diagram of the full-length brasiliensin sequence and amino-acid comparison of the eight domains. (a) Representation of the infestin gene (top) in comparison to the Triatoma brasiliensis brasiliensin gene (bottom). Each box represents a domain. Domains with high similarity are the same color. Letters inside the boxes represent the amino acids at the P1 position of the reactive sites (arrow in b). Inter domain loops containing AE residues are indicated. The box with vertical lines at the beginning of each gene represents the signal peptide. (b) Alignment of the translated domains (D1-D8) present in the T. brasiliensis Kazal type serine protease inhibitor gene. Alignment was performed with Clustal W (Thompson et al., 1994). Identical amino acid residues in all domains are black boxed. Dark gray and light gray indicate amino acids present in at least five and four domains, respectively. The arrow indicates the putative reactive site determined by comparison with other Kazal type inhibitors.
