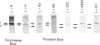Abstract
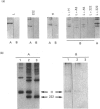
The ability to incorporate iron in vitro was studied in homopolymers of human ferritin L-chain, human ferritin H-chain and its variants and in homopolymer mixtures. The H-chain variants carried amino acid substitutions in the ferroxidase centre and/or in carboxy residues on the cavity surface. Iron incorporation was examined by gel electrophoresis of the reaction products by staining for iron and protein. It was found that inactivation of the ferroxidase centre combined with the substitution of four carboxy groups on the cavity abolished the ability of H-chain ferritin to incorporate iron. Competition experiments with limited amounts of iron showed that, at neutral pH, L-chain ferritin is more efficient in forming iron cores than the H-chain variants altered at the ferroxidase activity or in the cavity. Competition experiments at pH 5.5 demonstrated that L-chain apoferritin is able to incorporate iron only when in the presence of H-chain variants with ferroxidase activity. The results indicate that L-chain apoferritin has a higher capacity than the H-chain apoferritin to induce iron-core nucleation, whereas H-chain ferritin is superior in promoting Fe(II) oxidation. The finding of cooperative roles of the H- and L-chains in ferritin iron uptake provides a clue to understanding the biological function of isoferritins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arosio P., Adelman T. G., Drysdale J. W. On ferritin heterogeneity. Further evidence for heteropolymers. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4451–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker G. R., Boyer R. F. Iron incorporation into apoferritin. The role of apoferritin as a ferroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13182–13185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Harrison P. M., Hechel D., Nowik I., Treffry A. Iron (III) can be transferred between ferritin molecules. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Jun 22;244(1311):211–217. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Harrison P. M., Hechel D., Nowik I., Treffry A. Mössbauer spectroscopic investigation of structure-function relations in ferritins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 11;1118(1):48–58. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90440-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Harrison P. M., Nowik I., Treffry A. Mössbauer spectroscopic study of the initial stages of iron-core formation in horse spleen apoferritin: evidence for both isolated Fe(III) atoms and oxo-bridged Fe(III) dimers as early intermediates. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5486–5493. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Vecoli C., Belcher D. M., Jain S. K., Drysdale J. W. Structural and functional relationships of human ferritin H and L chains deduced from cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11755–11761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Cooper S., Levi S., Arosio P. Mutated recombinant human heavy-chain ferritins and myelosuppression in vitro and in vivo: a link between ferritin ferroxidase activity and biological function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzola M., Dezza L., Bergamaschi G., Barosi G., Bellotti V., Caldera D., Ciriello M. M., Quaglini S., Arosio P., Ascari E. Biologic and clinical significance of red cell ferritin. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):1078–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford G. C., Harrison P. M., Rice D. W., Smith J. M., Treffry A., White J. L., Yariv J. Ferritin: design and formation of an iron-storage molecule. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Feb 13;304(1121):551–565. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. M., Ford G. C., Rice D. W., Smith J. M., Treffry A., White J. L. Structural and functional studies on ferritins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Aug;15(4):744–748. doi: 10.1042/bst0150744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. M., Treffry A., Lilley T. H. Ferritin as an iron-storage protein: mechanisms of iron uptake. J Inorg Biochem. 1986 Aug;27(4):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(86)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. M., Artymiuk P. J., Yewdall S. J., Smith J. M., Livingstone J. C., Treffry A., Luzzago A., Levi S., Arosio P., Cesareni G. Solving the structure of human H ferritin by genetically engineering intermolecular crystal contacts. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):541–544. doi: 10.1038/349541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. M., Treffry A., Artymiuk P. J., Harrison P. M., Yewdall S. J., Luzzago A., Cesareni G., Levi S., Arosio P. Identification of the ferroxidase centre in ferritin. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Luzzago A., Cesareni G., Cozzi A., Franceschinelli F., Albertini A., Arosio P. Mechanism of ferritin iron uptake: activity of the H-chain and deletion mapping of the ferro-oxidase site. A study of iron uptake and ferro-oxidase activity of human liver, recombinant H-chain ferritins, and of two H-chain deletion mutants. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18086–18092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Luzzago A., Franceschinelli F., Santambrogio P., Cesareni G., Arosio P. Mutational analysis of the channel and loop sequences of human ferritin H-chain. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):381–388. doi: 10.1042/bj2640381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Salfeld J., Franceschinelli F., Cozzi A., Dorner M. H., Arosio P. Expression and structural and functional properties of human ferritin L-chain from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5179–5184. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Hoy T. G., Harrison P. M. The formation of ferritin from apoferritin. Kinetics and mechanism of iron uptake. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(1):151–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1260151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S., Bannister J. V., Williams R. J. Structure and composition of ferritin cores isolated from human spleen, limpet (Patella vulgata) hemolymph and bacterial (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) cells. J Mol Biol. 1986 Mar 20;188(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollazzo M., Frank R., Cesareni G. High-level expression of RNAs and proteins: the use of oligonucleotides for the precise fusion of coding-to-regulatory sequences. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffry A., Harrison P. M., Luzzago A., Cesareni G. Recombinant H-chain ferritins: effects of changes in the 3-fold channels. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81350-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade V. J., Levi S., Arosio P., Treffry A., Harrison P. M., Mann S. Influence of site-directed modifications on the formation of iron cores in ferritin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1443–1452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardeska J. G., Viglione B., Chasteen N. D. Metal ion complexes of apoferritin. Evidence for initial binding in the hydrophilic channels. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6677–6683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetz K., Crichton R. R. Chemical modification as a probe of the topography and reactivity of horse-spleen apoferritin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):545–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Meagher A., Huynh B. H., Sayers D. E., Theil E. C. Iron(III) clusters bound to horse spleen apoferritin: an X-ray absorption and Mössbauer spectroscopy study that shows that iron nuclei can form on the protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 27;26(2):497–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00376a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]