Abstract
Background
Prostate cancer, the second most common male malignancy worldwide, treatment-related complications cause both physical dysfunction and psychosocial sequelae, significantly impairing quality of life. Now requires integrated biopsychosocial rehabilitation beyond disease-focused treatment, comprehensive assessment of psychosocial adaptation and illness perception is essential for developing evidence-based, patient-centered rehabilitation strategies to optimize post-therapy recovery.
Objective
This study aims to systematically review and synthesize qualitative evidence on post-treatment psychosocial experiences in prostate cancer patients, thoroughly analyze patients’ lived experiences and coping strategies, and provide an evidence-based foundation for establishing a tiered psychosocial support system and developing clinical intervention protocols.
Methods
This systematic review followed the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) methodology for qualitative meta-aggregation, with reporting structured according to the ENTREQ statement. Evidence was graded using the ConQual approach and critically appraised with the JBI Qualitative Assessment and Review Instrument (JBI-QARI). We systematically searched six major English databases for qualitative or mixed-methods studies investigating psychosocial experiences in post-treatment prostate cancer patients, with the literature search updated to February 28, 2024. Two reviewers independently performed study selection, followed by collaborative thematic synthesis to identify core themes.
Results
A total of 22 studies from 12 countries were included, with 65 findings extracted and categorized into 4 synthesized findings consisting of 8 distinct categories: (1) Psychological and emotional responses (fear and anxiety responses, depression and emotional distress); (2) Healthcare information and systemic barriers (disease-related information needs, barriers in healthcare systems); (3) Social support and interpersonal adaptation (support system needs, social role and relationship adaptation); (4) Internal adaptation and external actions (internal psychological adjustment, external coping behaviors).
Conclusion
Prostate cancer survivors face multifaceted psychosocial challenges during post-treatment recovery, with psychological and social responses impacting rehabilitation outcomes. Inadequate social support systems and gaps in healthcare information emerge as major barriers to recovery. To address these issues, healthcare providers should enhance communication effectiveness, while policymakers need to strengthen social support networks, government and corporate sectors should implement targeted policies, and family members should provide empathetic understanding and active encouragement, collectively fostering comprehensive patient support.
Systematic review registration
https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/recorddashboard, CRD42024537363.
Keywords: prostatic neoplasms, psychosocial factors, post-treatment, qualitative research, systematic review
1. Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most frequently diagnosed malignancy in men worldwide and the sixth leading cause of cancer-related deaths (1, 2). Epidemiological projections indicate a rising global burden, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases and 740,000 deaths annually by 2040 (3). Current treatments, such as surgery, hormone therapy, and radiation, have improved survival rates. However, these treatments often cause long-term side effects, including urinary problems, sexual difficulties, bone pain, and extreme tiredness (4).
Beyond physical morbidity, psychosocial sequelae profoundly impact patient well-being, such as anxiety about their illness, depression, and concerns about masculinity (5). A study revealed that the prevalence rates of PCa post-treatment depression and anxiety were 18.44 and 18.49%, respectively (6), patients with high-risk PCa exhibited elevated risks of both major depressive disorder and suicide mortality compared to lower-risk counterparts (7). Major depressive disorder is associated with increased healthcare expenditures, diminished quality-adjusted life years, and reduced overall survival duration among PCa survivors, these challenges greatly reduce their quality of life and ability to engage in daily activities (8).
Several qualitative meta-syntheses have been conducted on related topics, but they present notable limitations. One such study focused exclusively on the experiences of female partners of PCa survivors, rather than examining the survivors’ own perspectives (9), while another meta-synthesis specifically examined psychosocial experiences among African American PCa survivors (10). However, with recent advancements in qualitative systematic review methodology and the establishment of rigorous quality appraisal standards, new primary qualitative studies have emerged investigating post-treatment psychosocial adaptation in broader PCa populations. This methodological evolution necessitates an updated systematic review incorporating contemporary evidence to provide a more comprehensive understanding of survivors’ experiences.
This study employed the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) methodology (11) for systematic reviews to comprehensively synthesize existing evidence on post-treatment psychosocial experiences in PCa patients. Our approach incorporated a rigorous credibility assessment to evaluate findings and grade the synthesized results, aiming to provide an evidence-based foundation for establishing a tiered psychosocial support system.
2. Methods
This systematic qualitative review utilized the meta-aggregation methodology developed by the JBI. Following established guidelines, the study was conducted in accordance with the Enhancing Transparency in Reporting the Synthesis of Qualitative Research (ENTREQ) checklist (12) (in Supplementary Material 1). The study protocol was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (registration number: CRD42024537363).
2.1. Search strategy
We followed the three-step search method recommended by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI). First, we searched PubMed and CINAHL to find key words in titles, summaries, and subject terms. Next, we conducted a comprehensive computer search of six important databases: PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, Embase, PsycINFO, and Cochrane Library. The search strategy incorporated both Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and free-text terms, including: “Prostatic Neoplasms” “Neoplasms, Prostate” “Prostate Cancer” “Psychological Factors” “Psychological Side Effects” “Qualitative Research” and related terms. We looked for all qualifying studies about PCa patients’ emotional and social experiences after treatment. Finally, we checked the reference lists of included studies to find more relevant papers. Two researchers (LFD and LT) separately reviewed all titles, summaries, and full papers. When they disagreed, they asked a third researcher (JLZ) for help. We searched all records from when each database started until February 28, 2024, the search strategy is given in Supplementary Material 2.
2.2. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.2.1. Inclusion criteria
Participants: Patients diagnosed with PCa who had undergone treatment (age >18 years), including surgical therapy, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, etc.
Phenomenon of Interest: Psychosocial experiences of PCa patients following treatment.
Context: Psychosocial experiences of participants across all settings (home, hospital, and community).
Study Design: Qualitative studies, including phenomenology, ethnography, grounded theory, and action research. Mixed-methods studies were also included if qualitative data were reported separately.
2.2.2. Exclusion criteria
Studies only about family members or healthcare workers; Studies not in English; Reviews, case reports or letters to the editor; Studies without full text or missing important data.
2.3. Literature screening
Two graduate students trained in qualitative research (LFD and LT) independently screened and extracted the literature. When disagreements occurred, a third researcher (JLZ) made the final decision. We used EndNote 20 to remove duplicate records. First, we screened titles and abstracts to exclude studies that did not meet our requirements. Then, we conducted a second screening by reading full texts to select studies for final inclusion.
2.4. Quality appraisal
To ensure the reliability of studies included in this meta-synthesis, we used the standard JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Qualitative Research (JBI-QARI). The JBI-QARI evaluates studies based on the following criteria: congruity between research methodology and stated philosophical perspective, research objectives, data collection methods, representation and analysis of data, interpretation of results, statement locating the researcher culturally or theoretically, influence between the researcher and participants, ethical considerations, adequacy of research findings, and reasonableness of conclusions. Each study was evaluated using the following classification: “Yes”: The study fully satisfies all methodological requirements of the item; “No”: The study unequivocally fails to meet the item’s essential criteria; “Unclear”: Incomplete reporting precludes definitive judgment; “Not applicable”: The criterion is irrelevant to the study’s design. “Yes” = 1 point and “No”/“Unclear” = 0 points; “Not applicable” items were excluded from the total score calculation, the total possible score is 10 points. Two graduate students trained in qualitative research methods (LFD and LT) independently evaluated the methodological quality of included studies. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion or by arbitration from a third reviewer (JLZ). Only studies achieving a total score ≥6 points were included in the final analysis.
2.5. Data extraction and synthesis
Two independent researchers (LFD and LT) extracted data based on the JBI qualitative data extraction table, covering author, country, research method, data collection method, number of interviewees, phenomenon of interest, and theme extraction, and original research results and examples. If the research subjects included other cancer patients, family members, or healthcare workers, only data related to PCa patients were extracted. A second reviewer checked the data extraction, and consensus was reached through discussion. By maintaining consistent extraction criteria, a large amount of evidence relevant to the research purpose was obtained.
A meta-aggregation approach was used to synthesize the findings. Based on an in-depth understanding of the philosophical underpinnings and methodology of each qualitative study, the included literature was repeatedly read, translated, analyzed, and interpreted. The research findings were coded and similar findings were merged into new categories through a manual integration method.
By analyzing the links between the categories, we summarized them into final synthesized findings, and each synthesized finding was graded according to the ConQual approach (13). The ConQual assessment comprises dependability and credibility. The dependability evaluation specifically examines: (1) Congruity between research methodology and research questions/objectives. (2) Consistency between methodology and data collection methods. (3) Alignment between methodology and data representation/analysis. (4) Explicit statement of researcher’s cultural/theoretical positioning. (5) Addressing of mutual researcher-participant influence. Findings with 4–5 “Yes” responses remain unchanged (no adjustment to the original level), those with 2–3 “Yes” responses move down 1 level, and findings with 0–1 “Yes” responses move down 2 levels. Credibility is assessed at three levels: (1) Unequivocal (findings supported by irrefutable evidence). (2) Equivocal (findings with questionable evidence linkage). (3) Unsupported (findings lacking data support).
3. Results
3.1. Search outcomes
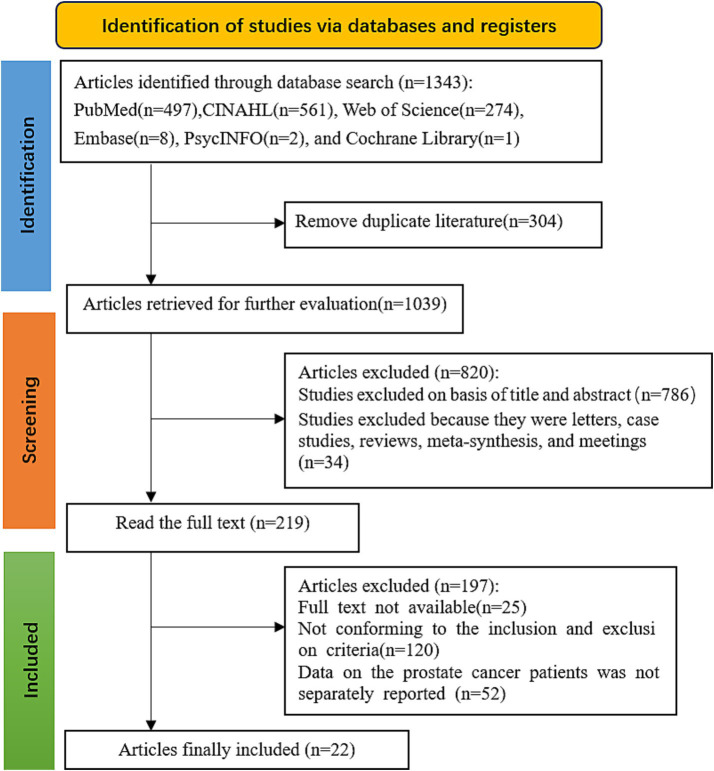
A total of 1,343 studies were retrieved. After removing duplicates with EndNote 20, 1,039 remained. After screening titles and abstracts, 820 were excluded, leaving 219 for full-text screening. After reading the full texts, 197 were excluded. Finally, 22 studies were included, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of the literature search and selection procedure for inclusion of qualitative studies.
3.2. Characteristics of included studies
The review included 22 studies (14–35) comprising 437 PCa patients across 12 countries: United Kingdom (n = 5), Japan (n = 4), Australia (n = 3), USA (n = 3), China (n = 3), Sweden (n = 2), Iran (n = 1), France (n = 1), Germany (n = 1), Canada (n = 1), Netherlands (n = 1), and Norway (n = 1). These comprised 1 grounded theory study and 21 phenomenological studies. Data collection methods were semi-structured interviews (n = 20) and focus group interviews (n = 2). The baseline characteristics of included studies are presented in Table 1. Study findings and their illustrations are detailed in Supplementary Material 3.
Table 1.
Detailed characterization of the studies included in this systematic review.
| Author | Year | Country | Category | Population | Phenomenon of interest | Themes extraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexis et al. (23) | 2023 | United Kingdom | Phenomenological research | 20 | Supportive experiences of PCa patients after treatment | A1. Spiritual belief. A2. Questioning of male self-worth. A3. Desire for support from family and organizations |
| Adam et al. (25) | 2023 | United Kingdom | Phenomenological research | 22 | Treatment burden experience of PCa survivors | B1. Change in perception of treatment burden. B2. Fear of biopsy. B3. Take action to manage disease |
| Vyas et al. (22) | 2022 | United Kingdom | Phenomenological research | 19 | Experiences after radical treatment for PCa | C1. Reflecting on the illness. C2. Impacts interpersonal relationships. C3. Feeling distressed about sexual life |
| Matheson et al. (21) | 2020 | United Kingdom | Phenomenological research | 28 | Experience of psychological distress among PCa survivors | D1. Impacts masculinity, functioning, and connectedness. D2. Inability to control emotions |
| Bamidele et al. (24) | 2019 | United Kingdom | Constructivist grounded theory | 25 | Psychosocial experiences of PCa patients | E1. Gaining a sense of control over the disease. E2. Stigmatization. E3. Communication barriers between spouses. E4. Need to support family |
| Hayashi et al. (26) | 2022 | Japan | Phenomenological research | 38 | Experiences of sexual dysfunction following PCa treatment | F1. Decision conflict. F2. Loss of personal values. F3. Acceptance and Management of illness |
| Iguchi et al. (32) | 2022 | Japan | Phenomenological research | 8 | Fatigue and burden of PCa patients | G1. Avoiding social interaction. G2. Lack of doctor-patient communication |
| Akakura et al. (20) | 2021 | Japan | Phenomenological research | 23 | Experience of the impact of disease progression on daily physical activities | H1. Increased family burden. H2. Inadequate awareness of bone metastasis. H3. Dissatisfaction with treatment outcomes |
| Liu et al. (35) | 2023 | Australia | Phenomenological research | 16 | Work-related Experiences of PCa Survivors | I1. Efforts to resume normal work I2. Insufficient doctor-patient communication I3. Corporate support I4. Support from coworkers |
| Akakura et al. (19) | 2020 | Australia, Japan, China | Phenomenological research | 12 | Cognitive aspects of PCa patients in the Asia-Pacific region | J1. Concerns about expected lifespan J2. Insufficient understanding of the disease |
| Chambers et al. (31) | 2018 | Australia | Phenomenological research | 28 | The need for support to improve the quality of life for patients with advanced prostatic cancer | K1. Fear of the future, uncertainty. K2. Unwillingness to seek help. K3. Appeals being ignored. K4. Seeking solutions for side effects. K5. Shortage of medical resources in rural areas. K6. Economic burden of disease |
| Burbridge et al. (15) | 2020 | America, France, Germany | Phenomenological research | 25 | Emotional response experiences in patients with mCRPC | L1. Anxiety and fear. L2. Low Mood and depression. L3. Accept life-prolonging treatment |
| Holmstrom et al. (30) | 2019 | America | Phenomenological research | 19 | Symptoms and life impact in patients with mCRPC | M1. Changes in daily activities. M2. Keep a positive attitude. M3. Urinary frequency affects sleep quality |
| Tomaszewski et al. (17) | 2017 | America | Phenomenological research | 19 | Life experiences of PCa patients | N1. Feelings of depression and anxiety |
| Pan et al. (28) | 2022 | China | Phenomenological research | 30 | Experiences of treatment decision-making in PCa patients | O1: Limited decision participation. O2: Need disease knowledge and option autonomy |
| Wang et al. (33) | 2022 | China | Phenomenological research | 13 | Experiences of sexuality and intimacy after PCa treatment | P1. Adaptation of sexual behaviors and intimate relationships. P2. Inadequate sexual health support |
| Rönningå et al. (34) | 2022 | Sweden | Phenomenological research | 11 | Experience of PCa patients in the face of uncertainty regarding their disease status | Q1. Uncertainty about disease progression. Q2. Worrying about my family’s future |
| Doveson et al. (27) | 2020 | Sweden | Phenomenological research | 16 | Perspectives of PCa patients on life-extending treatments | R1. Consider life-prolonging treatment. R2. Reflection on life’s end. R3. Fear of uncontrolled symptoms at the end of life |
| Mardani et al. (14) | 2023 | Iran | Phenomenological research | 12 | Experience of PCa patients with disease recurrence | S1. Fear of not being fully cured. S2. Fear of cancer recurrence. S3. Efforts to adjust lifestyle to cope with the disease. S4. Relying on spiritual faith |
| Langelier et al. (16) | 2022 | Canada | Phenomenological research | 15 | PCa patients’ experiences of coping with masculinity | T1. Redefining masculinity. T2. Building a sense of control. T2. Maintaining social connections |
| van Ee et al. (18) | 2018 | Netherlands | Phenomenological research | 22 | Experience of older adult men diagnosed with PCa | U1. Afraid of chemotherapy. U2. Worried about PSA test results. U3. Reluctant to tell children. U4. Supported by grandchildren. U5.dissatisfied with nursing staff |
| Aunan et al. (29) | 2021 | Norway | Phenomenological research | 16 | PCa survivors’ experiences of the value of informational support | V1: Need for information and support. V2: Seeking peer support |
3.3. Quality appraisal
The JBI-QARI quality assessment reports of the 22 studies showed that the scores for all 10 items ranged from 7 to 10. Most studies performed poorly on 2 items (Q6 and Q7). All 22 studies showed consistency between methodology and philosophical approach; 2 studies culturally or theoretically positioned the researcher. The quality assessment results are shown in Table 2.
Table 2.
JBI QARI assessment results of included qualitative studies.
| Author | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Overall score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexis et al. (23) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Adam et al. (25) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Vyas et al. (22) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Matheson et al. (21) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Bamidele et al. (24) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 10 |
| Hayashi et al. (26) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Iguchi et al. (32) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Akakura et al. (20) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Liu et al. (35) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 10 |
| Akakura et al. (19) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Chambers et al. (31) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Burbridge et al. (15) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | 8 |
| Holmstrom et al. (30) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Tomaszewski et al. (17) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | 8 |
| Pan et al. (28) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Wang et al. (33) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Rönningå et al. (34) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | 7 |
| Doveson et al. (27) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Mardani et al. (14) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | 8 |
| Langelier et al. (16) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | Yes | 7 |
| van Ee et al. (18) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| Aunan et al. (29) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
JBI QARI appraisal instruments: Q1. Is there congruity between the stated philosophical perspective and the research methodology? Q2. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the research question or objectives? Q3. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the methods used to collect data? Q4. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the representation and analysis of data? Q5. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the interpretation of results? Q6. Is there a statement locating the researcher culturally or theoretically? Q7. Is the influence of the researcher on the research, and vice-versa, addressed? Q8. Are participants, and their voices, adequately represented? Q9. Is the research ethical according to current criteria or, for recent studies, and is there evidence of ethical approval by an appropriate body? Q10. Do the conclusions draw in the research report flow from the analysis, or interpretation, of the data?
3.4. Findings of the review
Systematic analysis of the 22 eligible studies (14–35) identified 65 outcomes, as presented in Table 3. Through inductive reasoning and integration of similar outcomes, 4 major integrated results were formed, comprising 8 categories: (1) Psychological and emotional responses (fear and anxiety responses, depression and emotional distress); (2) Healthcare information and systemic barriers (disease-related information needs, barriers in healthcare systems); (3) Social support and interpersonal adaptation (support system needs, social role and relationship adaptation); (4) Internal adaptation and external actions (internal psychological adjustment, external coping behaviors).
Table 3.
Findings extracted from the included studies, categories and synthesized findings.
| Findings | Categories | Synthesized findings |
|---|---|---|
| S1. Fear of not being fully cured S2. Fear of cancer recurrence L1. Anxiety and fear U1. Afraid of chemotherapy U2. Worried about PSA test results B2. Fear of biopsy R3. Fear of uncontrolled symptoms at the end of life K1. Fear of the future, uncertainty Q1. Uncertainty about disease progression Q2. Worrying about my family’s future |
Category 1: Fear and Anxiety Responses Prostate cancer patients commonly experience intense fears of disease recurrence, treatment side effects, and future uncertainty. |
Synthesized finding 1: Psychological and Emotional Responses Prostate cancer patients experience profound psychological distress characterized by fears of disease progression, treatment-related anxieties, and emotional disturbances. |
| L2. Low mood and depression N1. Feelings of depression and anxiety J1. Concerns about expected lifespan H3. Dissatisfaction with treatment outcomes D2. Inability to control emotions C3. Feeling distressed about sexual life |
Category 2: Depression and Emotional Distress Prostate cancer patients develop depressive symptoms and emotional distress related to treatment outcomes, sexual dysfunction, and perceived loss of masculinity. |
|
| J2. Insufficient understanding of the disease H2. Inadequate awareness of bone metastasis F1. Decision conflict O1. Limited decision participation O2. Need disease knowledge and option |
Category 3: Disease-Related Information Needs Prostate cancer patients consistently demonstrate unmet needs regarding disease knowledge, treatment options, and prognostic information. |
Synthesized finding 2: Healthcare Information and Systemic Barriers Inadequate health communication and systemic service barriers collectively create significant obstacles to optimal care acquisition for prostate cancer patients. |
| U5. Dissatisfied with nursing staff E2. Stigmatization K5. Shortage of medical resources in rural areas K6. Economic burden of disease G2. Lack of doctor-patient communication I2. Insufficient doctor-patient communication |
Category 4: Barriers in Healthcare Systems The healthcare system presents structural barriers that compromise prostate cancer treatment efficacy. |
|
| A3. Desire for support from family and organizations K3. Appeals being ignored P2. Inadequate sexual health support I3. Corporate support I4. Support from coworkers |
Category 5: Support System Needs Patients with prostate cancer have multidimensional needs for family, social, and institutional support, yet they often face ignored support requests and insufficient sexual health support. |
Synthesized finding 3: Social Support and Interpersonal Adaptation Prostate cancer patients face social network reconstruction, needing to sustain existing connections and adapt to disease-induced changes in intimacy and communication. |
| T3. Maintaining social connections U3. Reluctant to tell children U4. Supported by grandchildren H1. Increased family burden D1. Impacts masculinity, functioning, and connectedness C2. Impacts interpersonal relationships A2. Questioning of male self-worth E3. Communication barriers between spouses E4. Need to support family F2. Loss of personal values M1. Changes in daily activities M3. Urinary frequency affects sleep quality K2. Unwillingness to seek help G1. Avoiding social interaction P1. Adaptation of sexual behaviors and intimate relationships |
Category 6: Social Role and Relationship Adaptation The disease impacts the gender identity, family roles, and personal value systems of prostate cancer patients. |
|
| S4. Relying on spiritual faith T2. Building a sense of control A1. Spiritual belief C1. Reflecting on the illness E1. Gaining a sense of control over the disease B1. Change in perception of treatment burden R2. Reflection on life’s end M2. Keep a positive attitude |
Category 7: Internal Psychological Adjustment Prostate cancer patients utilize spiritual faith for psychological adaptation, reflecting on their illness to regain a sense of control. |
Synthesized finding 4: Internal Adaptation and External Actions Prostate cancer patients address disease-related challenges through a combination of internal psychological and spiritual adaptation, and external modifications in lifestyle and active engagement in support-seeking behaviors. |
| S3. Efforts to adjust lifestyle to cope with the disease L3. Accept life-prolonging treatment T1. Redefining masculinity B3. Take action to manage disease F3. Acceptance and management of illness R1. Consider life-prolonging treatment V2. Seeking peer support K4. Seeking solutions for side effects I1. Efforts to resume normal work |
Category 8: External Coping Behaviors Prostate cancer patients utilize multifaceted external coping strategies for disease management. |
3.4.1. Synthesized finding 1: psychological and emotional responses
3.4.1.1. Category 1: fear and anxiety responses
As PCa progresses, patients exhibit progressive psychological deterioration characterized by an anxiety-fear complex. This includes fear of treatment outcomes, PSA monitoring-related anticipatory anxiety, and chemotherapy phobia (13). Invasive procedures such as transrectal prostate biopsy often induce significant pain, leading to decreased patient compliance in some cases.
“It was traumatic enough to say that I’m just sick of this idea of giving biopsies, seeing doctors. I even missed giving a PSA on the three monthly after May” (20).
With disease progression, patients face increasing risks of treatment failure and heightened uncertainty regarding survival outcomes, which may trigger profound anxiety about disease prognosis.
“Well, that’s only 3 months away, it’s only 2 months away actually. What’s going to happen between now and then” (26).
3.4.1.2. Category 2: depression and emotional distress
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) induces endocrine alterations in PCa patients, causing feminizing changes, body image distress, and sexual dysfunction that leads to marked sexual dissatisfaction in many patients.
“I’m not happy about that at all because although I’m 76 you know, as I say, the desire is still very much there” (22).
Patients following radical prostatectomy commonly develop postoperative complications including urinary incontinence and sexual dysfunction. These sequelae often induce feelings of social discrimination and internalized stigma, which may progress to adjustment disorders characterized by diminished treatment satisfaction, emotional instability, and depressive symptoms.
“It’s just spontaneous. I just all of a sudden feel sad and want to cry” (21).
3.4.2. Synthesized finding 2: healthcare information and systemic barriers
3.4.2.1. Category 3: disease-related information needs
Patients demonstrated a strong desire for disease-related knowledge, most displayed limited awareness of PCa treatment options and their potential adverse effects, along with deficient understanding of disease symptomatology, clinical staging, and advanced-stage manifestations.
“The urologist said I could call if I had any questions after the consultation. I called, several times, but never got in touch. I was very disappointed…doctor is so busy and unavailable” (29).
Patients expressed clear preferences for shared decision-making with healthcare providers, emphasizing the need for comprehensive disease education and preservation of autonomous treatment choice, rather than physician-dominated decision-making.
“I was worried concerning future recurrence, I gave up on sexual function and chose total resection instead of nerve-sparing prostatectomy” (26).
3.4.2.2. Category 4: barriers in healthcare systems
Deficiencies in healthcare systems adversely impact patient care experiences through multiple pathways, including impaired physician-patient communication and insufficient psychosocial support provision, ultimately diminishing patient satisfaction with both medical and nursing care.
“…and I thought that a nurse practitioner was someone who, well, who sympathized with you a bit, provided care, checked whether quicker treatments were possible. Well, the name says it all, practitioner” (18).
Patients with advanced PCa face major challenges during treatment, especially in rural areas with limited healthcare services. Many must travel long distances to receive care. Frequent hospital visits and treatments take up a lot of time and cause financial problems, creating extra stress for patients and their families (36).
“I’m up in the country and there was really no services in my town, an hour and a half trip to the closest place where could get anything done…They did not even have chemotherapy services here.” (31).
3.4.3. Synthesized finding 3: social support and interpersonal adaptation
3.4.3.1. Category 5: support system needs
Post-treatment PCa patients frequently struggle to resume normal social functioning, Urinary incontinence and muscle weakness exacerbate occupational challenges and interpersonal relationship maintenance. Despite expressing needs for multifaceted support, internalized shame and traditional masculinity norms deter patients from seeking help for sensitive issues like sexual dysfunction. Healthcare providers should proactively inquire about these unmet needs during follow-up consultations.
“… the doctors and nurses do not give the right support to the black community. Because when I started to seek advice and support, I could not find none, I could not find nothing” (23).
While financial pressures drive many PCa patients to urgently seek early return-to-work, occupation-dependent disparities exist: corporate employees benefit from organizational support enabling treatment compliance, whereas self-employed individuals face operational disruption and income loss due to lacking safeguards, highlighting the need for equitable workplace reintegration policies.
“We were able to work around the times when I had my immune system down, I was able to get support from other people within the group to carry out the work that I was going to do” (35).
3.4.3.2. Category 6: social role and relationship adaptation
The multifaceted post-therapeutic symptomatology exerts profound impacts on patients’ psychosocial functioning and interpersonal dynamics. Sexual dysfunction frequently precipitates dyadic intimacy impairment and conjugal communication deficits.
“…the relationship wasn’t that great…the sexual aspect of things went out of the window… I feel that there’s something missing, and sort of when am I going to get that back…” (24).
Concurrently, urinary incontinence and treatment-related physical changes may trigger masculine identity conflict, leading to negative self-perception, reduced healthcare engagement, and social withdrawal behaviors.
“Going out has become troublesome… I have stopped going to those completely. I do not even want to go outside anymore” (32).
Some patients demonstrated improved psychosocial adaptation through family support systems, particularly spousal and intergenerational relationships (18). These support networks facilitated adaptive coping strategies that enhanced intimate partner connections and thereby reduced symptom-related psychosocial distress.
“We do not need to talk about this, as she knows my situation [erectile dysfunction]…. Our relationship is good so that we do not need any communication, she understands this.” (33).
3.4.4. Synthesized finding 4: internal adaptation and external actions
3.4.4.1. Category 7: internal psychological adjustment
Patients adapt to disease challenges through internal psychological mechanisms, including therapeutic cognition reappraisal (25), religious or spiritual comfort-seeking.
“I believe that, I have to do my own part and God will do his own part because God heals it. He’s the one that can heal me” (23).
Through the process of illness reflection, patients reconstruct their understanding of life’s finitude to reconcile with disease prognosis, thereby maintaining a sense of control over their condition.
“…cost what it will cost, I have to take charge of my life, I have to be looked up to again as a man…” (24).
3.4.4.2. Category 8: external coping behaviors
In disease management, PCa patients employ not only internal psychological adjustments but also external behavioral adaptation strategies, including active participation in life-prolonging therapies and deliberate lifestyle modifications (14).
“In no way have I imagined that I will all of a sudden be completely cured. I can … keep going and feel well a little longer than I would otherwise have done” (27).
Peer support allows PCa patients to share lived experiences, work together to manage complications arising from treatment, and psychologically reconceptualize masculine identity.
“…talking to others in the same situation, how others have experienced getting PCa and side effects…I think it’s very reassuring to talk to others who have been through the same” (29).
3.5. Evidence quality evaluation results
This study evaluated the quality of four synthesized findings using the ConQual approach, with all results maintaining a moderate evidence grade (B), as shown in Table 4. For dependability, all met the 4–5 “Yes” criteria and thus required no downgrade. For credibility, all findings except “Internal Adaptation and External Actions” (remained unchanged) were downgraded by one level. Ultimately, all four synthesized findings were rated as moderate (B), indicating they possess moderate levels of credibility and dependability.
Table 4.
ConQual summary of findings.
| Synthesized finding | Type of research | Dependability | Credibility | ConQual score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psychological and Emotional Responses | Qualitative | No change (scored 5/5 for the 5 criteria in 1 study, 4/5 in 8 studies,3/5 in 3 studies) | Downgrade one level* | Moderate (B) |
| Healthcare Information and Systemic Barriers | Qualitative | No change (scored 5/5 for the 5 criteria in 2 studies, 4/5 in 8 studies) | Downgrade one level* | Moderate (B) |
| Social Support and Interpersonal Adaptation | Qualitative | No change (scored 5/5 for the 5 criteria in 2 studies, 4/5 in 10 studies,3/5 in 1 studies) | Downgrade one level* | Moderate (B) |
| Internal Adaptation and External Actions | Qualitative | No change (scored 5/5 for the 5 criteria in 2 studies, 4/5 in 8 studies,3/5 in 3 studies) | Remains unchanged | Moderate (B) |
*The evidence level was downgraded due to methodological heterogeneity or quality variations.
4. Discussion
4.1. Correctly viewing the disease progression, regulating negative emotions
The findings of this study demonstrate that PCa patients commonly experience multiple psychosocial distresses, including disease-related anxieties, PSA test-related anxiety, future uncertainty, depressive symptoms, emotional dysregulation, treatment dissatisfaction, life expectancy concerns, and sexual dysfunction.
Healthcare professionals are critical in helping them maintain a correct mindset toward the progression of the illness and actively manage negative emotions. Anxiety about abnormal PSA levels and fear of cancer recurrence are significant psychological challenges for PCa survivors after treatment (37, 38). Healthcare professionals should educate patients to correctly perceive PSA levels and shift their focus from merely reducing levels to enhancing their overall well-being. The decision-making process should focus on communication to build patient trust in the medical staff and mitigate uncertainty-associated fear.
Incorporating spiritual beliefs can increase patients’ morale and regulate their negative emotions. A study in Iran highlighted that some patients use spiritual beliefs to cope with fears of an incomplete cure and cancer recurrence (14), self-efficacy helps improve depression and anxiety in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy (39). Sharing life experiences with peers, engaging in social activities, and engaging in healthy behaviors are critical (40), whether through face-to-face interactions, phone calls, online chats, or meetings, provides patients with real insights and enables them to maintain optimistic attitudes and overcome stigmatization (41). Psychological care interventions can positively affect patients’ depression and anxiety (42), healthcare providers should integrate spiritual care into their practices to enhance emotional well-being.
Empowering patients is vital for understanding the disease, boosting their psychological health, and reducing uncertainty regarding disease progression. Decision aids can effectively reduce conflict, enhance understanding of the disease and treatment options, and increase risk awareness and satisfaction (43). Canadian researchers conducted a six-month PCa empowerment program (PC-PEP) (44), focusing on providing health education, empowerment, dietary advice, and social support, which notably reduced the psychological impact of treatment-related side effects of PC-PEP. Another PC-PEP initiative adopted a multifaceted approach through online and real-time interactions to empower the patients (45). Empowerment addresses biopsychosocial needs at various treatment stages, and enhances psychological well-being.
4.2. Optimizing symptom management plans to alleviate symptom burden
The findings of this qualitative meta-synthesis indicate that PCa patients develop lifestyle modifications, social disengagement, compromised interpersonal relationships secondary to disease manifestations, and treatment-induced complications. In response, patients adopt comprehensive adaptive approaches encompassing behavioral adjustments, gender role redefinition, illness self-regulation, peer support, and cognitive-emotional adaptation to mitigate these impacts.
Post-treatment PCa patients require prompt restoration of daily functioning, necessitating systematic symptom management interventions (46). Healthcare professionals should implement enhanced symptom management protocols and improve clinician understanding of patient experiences through personalized discharge plans, lifestyle guidance, and self-management education to reduce symptom burden. Structured exercise programs provide multisystem benefits, counteracting androgen deprivation therapy complications (47), improving incontinence recovery post-prostatectomy (48), potentially modulating PSA dynamics (49), and enhancing overall physical, psychological, and social well-being (50–52). These integrated approaches collectively optimize quality of life and functional recovery.
Post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence significantly affects health-related quality of life (HRQOL). Conventional conservative treatments include pelvic floor muscle training, biofeedback, and electrical stimulation (48). Proper guidance and supervision of pelvic floor exercises can shorten the recovery time (53), a systematic review demonstrated that preoperative pelvic floor muscle training can improve urinary incontinence at 3 months following radical prostatectomy (54). Patients with indwelling catheters require education on catheter maintenance for drainage patency and catheter-associated urinary tract infections prevention, alongside nocturnal fluid restriction to reduce nocturia.
Fatigue is another critical issue that can hinder daily and social activities, and some patients report that it pushes them toward depression (32). Patients affected by fatigue should reduce their activity levels, switch to less demanding jobs, or take breaks before returning to work to aid physical recovery (35). Those who need care from spouses or children may feel uncomfortable changing their family role, it is important to accept help from family members and life-prolonging treatments, and plan together to complete previously enjoyable activities.
Patients experiencing sexual dysfunction (SD) feel lonely, and their partners are unwilling to understand their SD issues or unable to tolerate sexless relationships (55). They should correctly understand body changes without feeling guilty about disruptions in their sexual lives. Researchers have explored alternative methods for achieving sexual pleasure without clinical intervention, such as oral stimulation by a partner, which can be satisfactory, even without full erection (24). The healthcare system provides psychosexual support and offers guidance on how to navigate marital communication (24). Such support can improve the quality of communication between spouses, thereby enhancing the overall QoL. Music therapy or prescribed pain medications can be effective in pain management. Music therapy has shown benefits in reducing anxiety, depression, and pain in cancer patients (56, 57), its application during prostate biopsies has been shown to alleviate both pain and procedural stress.
4.3. Improving the social support system to safeguard patient interests
This systematic review reveals PCa patients face multifaceted challenges including disease knowledge deficits, decision-making conflicts with limited autonomy, and communication barriers exacerbated in resource-limited settings. Additional burdens encompass financial toxicity, social stigmatization, and dissatisfaction with care quality. These findings substantiate the imperative for implementing shared decision-making protocols and establishing psychosocial support systems.
Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive explanations of treatment options, including the benefits, limitations, and mechanisms of both surgery and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), as misunderstandings may compromise therapeutic adherence (58). One patient mentioned that post-treatment support from healthcare professionals can significantly boost confidence (35), and improving the perioperative management model for PCa can help enhance patients’ mental states, quality of life, and self-care abilities (59). Nurses who provide emotional support, information, planning and follow-up, and comprehensive assessments of patients’ conditions are essential to PCa care team (60). A clinical study demonstrated that compassion-centered spiritual care significantly reduced depression levels (61), while systematic evidence confirms the need to integrate spiritual care into the management of patients with serious illnesses (62). Healthcare workers should empathize with patients with PCa to understand their emotions and high-quality service attitudes. For patients in rural or remote areas or those who cannot frequently visit medical facilities because of poor health, health care providers can employ online or telephone services to monitor post-discharge health.
Population aging and healthcare workforce shortages necessitate medical robotics innovation, robotic-assisted systems enhance psychological intervention efficacy and service quality. German hospitals use robots to assist early postoperative patient activities (63). In Switzerland, the Lio mobile robot performs autonomous disinfection and assists staff and patients (64). Robots can be used in psychological health interventions for patients with anxiety or depression. A meta-analysis in the UK found that social assistive robots might improve patients’ loneliness, stress, and pain and alleviate pain throughout their life cycle (65). Robots, such as Paro, have been used to improve psychological symptoms, reduce medication usage, and enhance social interactions among the older adult (66). Such robots could benefit patients with PCa by providing psychological counseling and assessing the therapeutic effects.
Governments and businesses must support patients’ employment needs by understanding their physical limitations, providing suitable job positions, and establishing cancer support centers and community groups (35). Regular organizations for early PCa screening and popularization of knowledge on cancer prevention are urgently needed. Governments should support “living with cancer” initiatives, such as establishing agencies such as the Fair Employment Opportunity Commission, tax relief for businesses employing cancer patients (35) and developing policies to encourage healthcare professionals from large hospitals to offer free clinics in remote areas, ensuring that patients in underserved locations receive consistent and high-quality healthcare.
4.4. Limitations
Considering the limitations of this study, these results should be interpreted with caution: (1) Only 22 qualitative studies were included in this analysis; (2) All studies were conducted in just 12 countries and restricted to English-language publications; (3) The majority of the included qualitative studies demonstrated moderate methodological rigor (scoring 7–9 points). These limitations hinder a comprehensive understanding of the psychosocial experiences of PCa patients. We hope future research will incorporate more qualitative studies to explore the psychosocial dimensions of PCa patients’ experiences.
5. Conclusion
This systematic review of qualitative studies examines the psychosocial experiences of PCa survivors across different countries. The findings indicate that treatment complications, healthcare system barriers, and insufficient social support often lead to psychological distress and reduced quality of life. Healthcare professionals should address both physical and psychological needs while providing emotional support and coping strategies. The adoption of innovative care technologies is recommended to enhance efficiency and improve service delivery. Policy support from governments and businesses remains crucial to safeguard patients’ livelihood, security, and employment needs. Family members play an important role by fostering positive emotions through improved communication and facilitating reintegration into daily life.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all members of our research team for their valuable contributions. We are particularly grateful to the faculty members of the urology department staff at Deyang People’s Hospital for their expert guidance in study design and manuscript preparation. Their insightful suggestions significantly improved the quality of this work.
Funding Statement
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Sichuan Medical and Health Care Promotion Institute Scientific Research Project (Grant no. KY2024SJ0102), the Key Research and Development Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant no. 2022YFS0109), and the “Xinglin Scholar” Hospital Special Fund from Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant no. YYZX2022054).
Author contributions
JX: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision. LD: Data curation, Visualization, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Investigation. LTan: Validation, Project administration, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DL: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Supervision, Conceptualization. YC: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Supervision. LTang: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. JZ: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Visualization, Validation, Data curation. XY: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation. XL: Investigation, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Project administration, Formal analysis, Data curation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1625611/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.Tian YQ, Yang JC, Hu JJ, Ding R, Ye DW, Shang JW. Trends and risk factors of global incidence, mortality, and disability of genitourinary cancers from 1990 to 2019: systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1119374. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1119374, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang L, Lu B, He M, Wang Y, Wang Z, Du L. Prostate Cancer incidence and mortality: global status and temporal trends in 89 countries from 2000 to 2019. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:811044. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.811044, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sung H, Ferlay J, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cornford P, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, Van den Broeck T, Brunckhorst O, Darraugh J, et al. Eau-Eanm-Estro-Esur-Isup-Siog guidelines on prostate Cancer-2024 update. Part I: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. (2024) 86:148–63. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.03.027, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sharpley CF, Christie DRH, Bitsika V. Depression and prostate Cancer: implications for urologists and oncologists. Nat Rev Urol. (2020) 17:571–85. doi: 10.1038/s41585-020-0354-4, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Watts S, Leydon G, Birch B, Prescott P, Lai L, Eardley S, et al. Depression and anxiety in prostate Cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of prevalence rates. BMJ Open. (2014) 4:e003901. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003901, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crump C, Stattin P, Brooks JD, Sundquist J, Bill-Axelson A, Edwards AC, et al. Long-term risks of depression and suicide among men with prostate cancer: a national cohort study. Eur Urol. (2023) 84:263–72. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.04.026, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Erim DO, Bensen JT, Mohler JL, Fontham ETH, Song L, Farnan L, et al. Prevalence and predictors of probable depression in prostate Cancer survivors. Cancer. (2019) 125:3418–27. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32338, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Green A, Winter N, DiGiacomo M, Oliffe JL, Ralph N, Dunn J, et al. Experiences of female Partners of Prostate Cancer Survivors: a systematic review and thematic synthesis. Health Soc Care Community. (2022) 30:1213–32. doi: 10.1111/hsc.13644, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Okoro FO, Song L, Auten B, Whitaker-Brown C, Cornelius J. African-American survivors of prostate cancer: a meta-synthesis of qualitative studies. J Cancer Surviv. (2021) 15:40–53. doi: 10.1007/s11764-020-00909-4, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lockwood C, Munn Z, Porritt K. Qualitative research synthesis: methodological guidance for systematic reviewers utilizing meta-aggregation. Int J Evid Based Healthc. (2015) 13:179–87. doi: 10.1097/xeb.0000000000000062, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: Entreq. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2012) 12:181. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-181, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Munn Z, Porritt K, Lockwood C, Aromataris E, Pearson A. Establishing confidence in the output of qualitative research synthesis: the Conqual approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:108. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-108, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mardani A, Farahani MA, Khachian A, Vaismoradi M. Fear of Cancer recurrence and coping strategies among prostate Cancer survivors: a qualitative study. Curr Oncol. (2023) 30:6720–33. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30070493, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Burbridge C, Randall JA, Lawson J, Symonds T, Dearden L, Lopez-Gitlitz A, et al. Understanding symptomatic experience, impact, and emotional response in recently diagnosed metastatic castration-resistant prostate Cancer: a qualitative study. Support Care Cancer. (2020) 28:3093–101. doi: 10.1007/s00520-019-05079-3, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Langelier DM, Jackson C, Bridel W, Grant C, Culos-Reed SN. Coping strategies in active and inactive men with prostate Cancer: a qualitative study. J Cancer Surviv. (2022) 16:421–31. doi: 10.1007/s11764-021-01037-3, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tomaszewski EL, Moise P, Krupnick RN, Downing J, Meyer M, Naidoo S, et al. Symptoms and impacts in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate Cancer: qualitative study findings. Patient. (2017) 10:567–78. doi: 10.1007/s40271-017-0227-y, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.van Ee IB, Hagedoorn M, Smits CHM, Kamper AM, Honkoop HA, Slaets JPJ. This is an older men's world: a qualitative study of men's experiences with prostate Cancer. Eur J Oncol Nurs. (2018) 37:56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2018.11.002, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Akakura K, Bolton D, Grillo V, Mermod N. Not all prostate cancer is the same-patient perceptions: an Asia-Pacific region study. BJU Int. (2020) 126:38–45. doi: 10.1111/bju.15129, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Akakura K, Uemura H, Miyazaki K, Stroupe A, Seo C, Uzumcu A, et al. A qualitative research study in Japan investigating patients' experience with metastatic castration-resistant prostate Cancer: from diagnosis to decision for Ra-223 treatment. Future Oncol. (2021) 17:5103–18. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0773, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matheson L, Nayoan J, Rivas C, Brett J, Wright P, Butcher H, et al. A qualitative exploration of prostate Cancer survivors experiencing psychological distress: loss of self, function, connection, and control. Oncol Nurs Forum. (2020) 47:318–30. doi: 10.1188/20.Onf.318-330, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vyas N, Brunckhorst O, Fox L, Van Hemelrijck M, Muir G, Stewart R, et al. Undergoing radical treatment for prostate Cancer and its impact on wellbeing: a qualitative study exploring men's experiences. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0279250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279250, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Alexis O, Worsley AJ. Black men's experiences of support following treatment for prostate Cancer in England: a qualitative study. Eur J Oncol Nurs. (2023) 62:102232. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2022.102232, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bamidele O, McGarvey H, Lagan BM, Parahoo K, Chinegwundoh Mbe F, McCaughan E. "man in the driving seat": a grounded theory study of the psychosocial experiences of black African and black Caribbean men treated for prostate Cancer and their partners. Psychooncology. (2019) 28:1712–20. doi: 10.1002/pon.5150, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Adam R, Duncan L, Maclennan SJ, Locock L. Treatment burden in survivors of prostate and colorectal cancers: a qualitative interview study. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e068997. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068997, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hayashi S, Oishi F, Sato K, Fukuda H, Ando S. Sexual dysfunction associated with prostate Cancer treatment in Japanese men: a qualitative research. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 30:3201–13. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06728-2, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Doveson S, Holm M, Axelsson L, Fransson P, Wennman-Larsen A. Facing life-prolonging treatment: the perspectives of men with advanced metastatic prostate Cancer – an interview study. Eur J Oncol Nurs. (2020) 49:101859. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2020.101859, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pan S, Mao J, Wang L, Dai Y, Wang W. Patient participation in treatment decision-making of prostate Cancer: a qualitative study. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 30:4189–200. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06753-1, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Aunan ST, Wallgren GC, Hansen BS. The value of information and support; experiences among patients with prostate cancer. J Clin Nurs. (2021) 30:1653–64. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15719, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Holmstrom S, Naidoo S, Turnbull J, Hawryluk E, Paty J, Morlock R. Symptoms and impacts in metastatic castration-resistant prostate Cancer: qualitative findings from patient and physician interviews. Patient. (2019) 12:57–67. doi: 10.1007/s40271-018-0349-x, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chambers SK, Hyde MK, Laurie K, Legg M, Frydenberg M, Davis ID, et al. Experiences of Australian men diagnosed with advanced prostate Cancer: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. (2018) 8:e019917. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019917, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Iguchi T, Nakamura Y, Akiyama T, Chand K, Yu E. Descriptive study on burden and communication of fatigue among castration-resistant prostate Cancer patients in Japan. Curr Med Res Opin. (2022) 38:417–26. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2021.2006534, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang T, Cheng HL, Wong PKK, Dong W. Men's experiences of sex and intimacy after prostate Cancer treatment in China: a qualitative study. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 30:3085–92. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06720-w, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rönningås U, Holm M, Doveson S, Fransson P, Beckman L, Wennman-Larsen A. Signs and symptoms in relation to progression, experiences of an uncertain illness situation in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate Cancer-a qualitative study. Eur J Cancer Care. (2022) 31:e13592. doi: 10.1111/ecc.13592, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu WH, Fox J, Yates P. Work-related experiences of prostate Cancer survivors in Australia: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:1806. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16706-4, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Adam R, Nair R, Duncan LF, Yeoh E, Chan J, Vilenskaya V, et al. Treatment burden in individuals living with and beyond Cancer: a systematic review of qualitative literature. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0286308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286308, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.James C, Brunckhorst O, Eymech O, Stewart R, Dasgupta P, Ahmed K. Fear of Cancer recurrence and Psa anxiety in patients with prostate Cancer: a systematic review. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 30:5577–89. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-06876-z, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wang Y, Xiao M, Zhang Y, Hong Z, Zhang R, Xu Q, et al. Investigation of awareness rate of prostate-specific antigen (Psa) among the general public in China and analysis of influencing factors. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1080800. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1080800, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang L, Luo J, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang W. Social support, anxiety, and depression in patients with prostate Cancer: complete mediation of self-efficacy. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 30:6851–6. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-07065-8, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Loughney L, McGowan R, O'Malley K, McCaffrey N, Furlong B, Walsh D. Perceptions of wellbeing and quality of life following participation in a community-based pre-operative exercise programme in men with newly diagnosed prostate cancer: a qualitative pilot study. PLoS One. (2021) 16:1–15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Baudot A, Barth N, Colas C, Garros M, Garcin A, Oriol M, et al. The Acti-pair program helps men with prostate Cancer increase physical activity with peer support: a mixed method pilot study. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1321230. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1321230, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yang L, Ling D, Ye L, Zeng M. Psychological nursing intervention on anxiety and depression in patients with urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a randomized controlled study protocol. Medicine. (2020) 99:e23127. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000023127, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Coronado-Vázquez V, Canet-Fajas C, Delgado-Marroquín MT, Magallón-Botaya R, Romero-Martín M, Gómez-Salgado J. Interventions to facilitate shared decision-making using decision aids with patients in primary health care: a systematic review. Medicine. (2020) 99:e21389. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000021389, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ilie G, Rendon R, Mason R, MacDonald C, Kucharczyk MJ, Patil N, et al. A comprehensive 6-Mo prostate Cancer patient empowerment program decreases psychological distress among men undergoing curative prostate Cancer treatment: a randomized clinical trial. Eur Urol. (2023) 83:561–70. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.02.009, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lawen T, Ilie G, Mason R, Rendon R, Spooner J, Champion E, et al. Six-month prostate Cancer empowerment program (pc-pep) improves urinary function: a randomized trial. Cancers. (2024) 16:958. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050958, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wollersheim BM, van der Poel HG, van Asselt KM, Pos FJ, Tillier CN, Akdemir E, et al. Quality of early prostate Cancer follow-up care from the patients' perspective. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 30:10077–87. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-07396-6, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Edmunds K, Tuffaha H, Scuffham P, Galvão DA, Newton RU. The role of exercise in the Management of Adverse Effects of androgen deprivation therapy for prostate Cancer: a rapid review. Support Care Cancer. (2020) 28:5661–71. doi: 10.1007/s00520-020-05637-0, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Heydenreich M, Puta C, Gabriel HH, Dietze A, Wright P, Zermann DH. Does trunk muscle training with an oscillating rod improve urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy? A prospective randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. (2020) 34:320–33. doi: 10.1177/0269215519893096, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lee DJ, Byeon JY, Park DH, Oh CG, Lee J, Choi YD, et al. Effects of exercise during active surveillance for prostate Cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Support Care Cancer. (2024) 32:406. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08606-z, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Burke S, Wurz A, Bradshaw A, Saunders S, West MA, Brunet J. Physical activity and quality of life in Cancer survivors: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research. Cancers. (2017) 9:53. doi: 10.3390/cancers9050053, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rendeiro JA, Rodrigues C, de Barros Rocha L, Rocha RSB, da Silva ML, da Costa Cunha K. Physical exercise and quality of life in patients with prostate cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Support Care Cancer. (2021) 29:4911–9. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06095-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tzenios N, Tazanios ME, Chahine M. The impact of body mass index on prostate Cancer: An updated systematic review and Meta-analysis. Medicine. (2022) 101:e30191. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000030191, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Filocamo MT, Li Marzi V, Del Popolo G, Cecconi F, Marzocco M, Tosto A, et al. Effectiveness of early pelvic floor rehabilitation treatment for post-prostatectomy incontinence. Eur Urol. (2005) 48:734–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.06.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhou L, Chen Y, Yuan X, Zeng L, Zhu J, Zheng J. Preoperative pelvic floor muscle exercise for continence after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1186067. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1186067, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hayashi S, Sato K, Oishi F, Fukuda H, Hayama Y, Ando S. Care needs of Japanese men for sexual dysfunction associated with prostate Cancer treatment. Support Care Cancer. (2023) 31:378. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-07837-w, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.He H, Li Z, Zhao X, Chen X. The effect of music therapy on anxiety and pain in patients undergoing prostate biopsy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Complement Ther Med. (2023) 72:102913. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2022.102913, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bradt J, Dileo C, Myers-Coffman K, Biondo J. Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in people with Cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2021) 10:CD006911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006911.pub4, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Desai K, McManus JM, Sharifi N. Hormonal therapy for prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. (2021) 42:354–73. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab002, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhang M, Hu X, Jia J, Wu D. The effect of a modified perioperative management model on the mental state, quality of life, and self-care ability score of patients after radical prostatectomy: a retrospective study. Medicine. (2023) 102:e33556. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000033556, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lamb AD, Thompson S, Kinsella N, Gerbitz I, Chapman E, Putt L, et al. Corrigendum to “aiming for a holistic integrated Service for men Diagnosed with prostate Cancer-definitions of standards and skill sets for nurses and allied healthcare professionals”. Eur J Oncol Nurs. (2017) 29:31–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2017.07.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mascaro JS, Palmer PK, Ash MJ, Florian MP, Kaplan DM, Palitsky R, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a compassion-centered spiritual health intervention to improve hospital inpatient outcomes. PLoS One. (2025) 20:e0313602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313602, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Balboni TA, VanderWeele TJ, Doan-Soares SD, Long KNG, Ferrell BR, Fitchett G, et al. Spirituality in serious illness and health. JAMA. (2022) 328:184–97. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.11086, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Warmbein A, Hübner L, Rathgeber I, Mehler-Klamt AC, Huber J, Schroeder I, et al. Robot-assisted early mobilization for intensive care unit patients: feasibility and first-time clinical use. Int J Nurs Stud. (2024) 152:104702. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2024.104702, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Miseikis J, Caroni P, Duchamp P, Gasser A, Marko R, Miseikiene N, et al. Lio-a personal robot assistant for human-robot interaction and care applications. IEEE Robot Autom Lett. (2020) 5:5339–46. doi: 10.1109/lra.2020.3007462, PMID: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Nichol B, McCready J, Erfani G, Comparcini D, Simonetti V, Cicolini G, et al. Exploring the impact of socially assistive robots on health and wellbeing across the lifespan: An umbrella review and Meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. (2024) 153:104730. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2024.104730, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Rashid NLA, Leow Y, Klainin-Yobas P, Itoh S, Wu VX. The effectiveness of a therapeutic robot, 'Paro', on Behavioural and psychological symptoms, medication use, Total sleep time and sociability in older adults with dementia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. (2023) 145:104530. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2023.104530, PMID: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.