Abstract
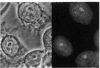
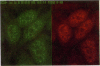
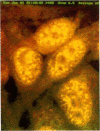
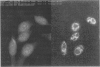
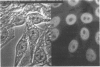
Binding of the human pentraxin plasma proteins, C-reactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid P component (SAP), to the nuclei of human cells was studied using whole acute phase serum as the source of the proteins and confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. CRP and SAP clearly bound to distinct, different structures. Double staining with MoAbs to the Sm D and Sm B/B' components of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins confirmed that CRP bound exclusively to these particles. As expected, SAP bound to chromatin and, in addition, binding to the nucleolus was observed for the first time. These interactions demonstrated under relatively physiological conditions, with native pentraxins unseparated from serum and with nuclear constituents in situ, are likely to be of functional importance in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Feinstein A., Munn E. A., Milstein C. P., Fletcher T. C., March J. F., Taylor J., Bruton C., Clamp J. R. Phylogenetic aspects of C-reactive protein and related proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:49–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Kofler H., Sepp N., Ashworth J., Woodrow D., Pepys M. B., Hintner H. Serum amyloid P component binds to cell nuclei in vitro and to in vivo deposits of extracellular chromatin in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1433–1438. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Melrose S. M., Bhogal B., de Beer F. C., Dyck R. F., Tennent G., Black M. M., Pepys M. B. Amyloid P component is located on elastic fibre microfibrils in normal human tissue. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):652–654. doi: 10.1038/293652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Tennent G. A., Pepys M. B. Pentraxin-chromatin interactions: serum amyloid P component specifically displaces H1-type histones and solubilizes native long chromatin. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):13–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Tollervey D., Pepperkok R., Barabino S. M., Merdes A., Brunner C., Zamore P. D., Green M. R., Hurt E., Lamond A. I. Mammalian nuclei contain foci which are highly enriched in components of the pre-mRNA splicing machinery. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):195–206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Isolation of human C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W. C-reactive protein reacts with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2553–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Marnell L., Zlock L. R., Burlingame R. W. Analysis of the binding of C-reactive protein to chromatin subunits. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1220–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Mold C., Paterson P. Y., Alroy J., Gewurz H. Localization of C-reactive protein in inflammatory lesions of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):565–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Mold C., Stump R. F. Identification of a polypeptide sequence that mediates nuclear localization of the acute phase protein C-reactive protein. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3869–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Zlock L. T., Marnell L. Definition of a C-reactive protein binding determinant on histones. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2167–2171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Zlock L. T., Rubin R. L. Analysis of the binding of C-reactive protein to histones and chromatin. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4266–4270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck R. F., Lockwood C. M., Kershaw M., McHugh N., Duance V. C., Baltz M. L., Pepys M. B. Amyloid P-component is a constituent of normal human glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1162–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin J. D., Gitlin J. I., Gitlin D. Localizing of C-reactive protein in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Nov-Dec;20(8):1491–1499. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Lavender J. P., Pepys M. B. Evaluation of systemic amyloidosis by scintigraphy with 123I-labeled serum amyloid P component. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 23;323(8):508–513. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008233230803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Myers M. J., Lavender J. P., Pepys M. B. Diagnostic radionuclide imaging of amyloid: biological targeting by circulating human serum amyloid P component. Lancet. 1988 Jun 25;1(8600):1413–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Tennent G. A., Woo P., Pepys M. B. Studies in vivo and in vitro of serum amyloid P component in normals and in a patient with AA amyloidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 May;84(2):308–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Wootton R., Pepys M. B. Metabolic studies of radioiodinated serum amyloid P component in normal subjects and patients with systemic amyloidosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1862–1869. doi: 10.1172/JCI114917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks P. S., Saunero-Nava L., Du Clos T. W., Mold C. Serum amyloid P component binds to histones and activates the classical complement pathway. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3689–3694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintner H., Booker J., Ashworth J., Auböck J., Pepys M. B., Breathnach S. M. Amyloid P component binds to keratin bodies in human skin and to isolated keratin filament aggregates in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jul;91(1):22–28. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12463283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H., Robey F. A., Gewurz H. Localization of sites through which C-reactive protein binds and activates complement to residues 14-26 and 76-92 of the human C1q A chain. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1373–1379. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute phase protein. I. An immunohistochemical method for the localization of Cx-reactive protein in rabbits. Association with necrosis in local inflammatory lesions. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:961–974. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., RAKITA L., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute-phase protein. II. Localization of Cx-reactive protein in heart in induced myocardial infarction in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:286–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI104715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley S., Pepys M. B. Immunochemical cross-reactions between pentraxins of different species. Immunology. 1987 Sep;62(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minota S., Morino N., Sakurai H., Yamada A., Yazaki Y. Interrelationship between autoepitope, DNA-binding domain, and CRP-binding domain on a histone H1 molecule. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Mar;66(3):269–271. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama S., Du Clos T. W., Gewurz H., Mold C. Inhibition of antibody responses to phosphocholine by C-reactive protein. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1336–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish W. E. Studies on vasculitis. VII. C-reactive protein as a substance perpetuating chronic vasculitis. Occurrence in lesions and concentrations in sera. Clin Allergy. 1976 Nov;6(6):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Butler P. J. Serum amyloid P component is the major calcium-dependent specific DNA binding protein of the serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Fletcher T. C., Richardson N., Munn E. A., Feinstein A. Analogues in other mammals and in fish of human plasma proteins, C-reactive protein and amyloid P component. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):168–170. doi: 10.1038/273168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Fletcher T. C., Richardson N., Munn E. A., Feinstein A. Analogues in other mammals and in fish of human plasma proteins, C-reactive protein and amyloid P component. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):168–170. doi: 10.1038/273168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Martin A., Taylor-Albert E., Tsuzaka K., Zhang W., Reichlin M. W., Koren E., Ebling F. M., Tsao B., Hahn B. H. Lupus autoantibodies to native DNA cross-react with the A and D SnRNP polypeptides. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):443–449. doi: 10.1172/JCI116980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Jones K. D., Tanaka T., Liu T. Y. Binding of C-reactive protein to chromatin and nucleosome core particles. A possible physiological role of C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7311–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues M. M., Robey P. G. C-reactive protein in human lattice corneal dystrophy. Curr Eye Res. 1982;2(10):721–724. doi: 10.3109/02713688209020002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rordorf C., Schnebli H. P., Baltz M. L., Tennent G. A., Pepys M. B. The acute-phase response in (NZB X NZW)F1 and MRL/l MICE. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1268–1273. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe I. F., Walker L. N., Bowyer D. E., Soutar A. K., Smith L. C., Pepys M. B. Immunohistochemical studies of C-reactive protein and apolipoprotein B in inflammatory and arterial lesions. J Pathol. 1985 Mar;145(3):241–249. doi: 10.1002/path.1711450305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard E. G., Smith P. J., Coetzee S., Strachan A. F., de Beer F. C. Pentraxin binding to isolated rat liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):257–262. doi: 10.1042/bj2790257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson S. J., Christner R. B., Mortensen R. F. Human serum amyloid P-component (SAP) selectively binds to immobilized or bound forms of C-reactive protein (CRP). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 28;1160(3):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90093-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigushin D. M., Pepys M. B., Hawkins P. N. Metabolic and scintigraphic studies of radioiodinated human C-reactive protein in health and disease. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1351–1357. doi: 10.1172/JCI116336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Amos W. B., Fordham M. An evaluation of confocal versus conventional imaging of biological structures by fluorescence light microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):41–48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Stocks M. R., Smith P. R., Maini R. N. Murine lupus monoclonal antibodies define five epitopes on two different Sm polypeptides. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):495–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying S. C., Gewurz A. T., Jiang H., Gewurz H. Human serum amyloid P component oligomers bind and activate the classical complement pathway via residues 14-26 and 76-92 of the A chain collagen-like region of C1q. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]