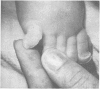
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlain J. L., 3rd, Perry L. W. Infantile periarteritis nodosa with coronary and brachial aneurysms: a case diagnosed during life. J Pediatr. 1971 Jun;78(6):1039–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetterman G. H., Hashida Y. Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS): a disease widespread in Japan which demands our attention. Pediatrics. 1974 Sep;54(3):268–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Koike S., Yamamoto M., Ito Y., Yano E. Coronary aneurysms in infants and young children with acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. J Pediatr. 1975 Jun;86(6):892–898. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Kosaki F., Okawa S., Shigematsu I., Yanagawa H. A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics. 1974 Sep;54(3):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMartin D. E., Stone A. J., Franch R. H. Multiple coronary-artery aneurysms in a child with angina pectoris. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 21;290(12):669–670. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403212901208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS F. B., FETTERMAN G. H. POLYARTERITIS NODOSA IN INFANCY. J Pediatr. 1963 Oct;63:519–529. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kobayashi N., Matsuya S. Myocardial infarction due to coronary thromboarteritis, following acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) in an infant. Pediatrics. 1974 Sep;54(3):277–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]