Abstract
Background
Numerous studies have confirmed that inflammation promotes the occurrence, development and prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC).
Objective
This study focuses on the potentially prognostic value of the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in CRC patients.
Data Sources
This study was registered at PROSPERO (ID: CRD42020219215). Relative studies were searched on PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, and clinical trial databases by two back-to-back reviewers. Study Selection and Intervention: Studies were screened according to the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria, comparing prognosis differences between low PLR levels and high PLR levels for CRC patients. Main Outcome Measures: Studies were integrated and compared to analyze the value of PLR in predicting overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), disease-free survival (DFS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) of CRC. Results: Outcomes were compared using Review Manager (version 5.4) software from Cochrane Collaboration. A total of 27 literary works, including 13,330 patients, were incorporated into our study. The final results showed that higher PLR levels had worse OS (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.40, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.21–1.62, P < 0.00001), DFS (HR = 1.44, 95% CI = 1.09–1.90, P = 0.01) and RFS (HR = 1.48, 95% CI = 1.13–1.94, P = 0.005) than lower PLR levels, respectively. However, there was no evidence of significance for PFS (HR = 1.14, 95% CI = 0.84–1.54, P = 0.40) and CSS (HR = 1.16, 95% CI = 0.88–1.53, P = 0.28) in the final meta-analysis.
Limitations
Our study has the following limitations. First of all, we only included literature published in English, which means that some publication bias may be inevitable. In addition, our study used aggregate data, not individual data; furthermore, we did not define the exact cut-off value representing the PLR level.
Conclusion
An elevated PLR seems to be an adverse prognostic factor affecting survival outcomes in patients with CRC. Meanwhile, more prospective studies are required to confirm our conclusion.
PROSPERO ID: CRD42020219215.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, overall survival, progression-free survival, cancer-specific survival, disease-free survival, meta-analysis
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer in the world and the second-leading cause of cancer-related death (1), the incidence of which shows a younger trend (2). At present, the diagnosis and treatment of CRC have been significantly improved. However, due to local tumor recurrence and metastasis, patients' long-term survival is poor, and OS and FPS are not ideal. It is predicted that the greatest impact and the fastest increase in the burden of cancer in the coming decades will continue to be in low- and middle-income countries, many of which are already facing overwhelming difficulties (3). Adding to the tension, current tumor markers, such as CEA and pik3, lack accuracy or are expensive. Therefore, it is particularly important to find an economical, convenient and effective biomarker to predict CRC prognosis.
Blood routine examination, including a series of indicators reflecting the level of inflammation, is simple and cheap but has not been paid attention to. As early as 1863, a German pathologist named Rudolf Virchow noticed “lymphoreticular infiltrate” in tumor tissue and linked inflammation to cancer (4). Additionally, immune cells are the main cellular components of tumor lesions and play an important role in the anti-tumor process (5), including CRC. The tumor microenvironment is the internal environment for tumor cell survival, which is composed of tumor cells, immune cells, cytokines, and cell metabolites. It has been reported that host cell interaction in the tumor microenvironment, such as immune cell infiltration, plays a crucial role in tumor progression and is closely related to patient prognosis (6). The platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), as one of the evaluation indexes of systemic inflammatory response, not only can reflect the body's inflammatory response and is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis of various tumors, such as lung cancer, ovarian cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and so on (7–11) but also is available, inexpensive and repeatable in clinical laboratory examination. However, the relationship between the PLR and CRC remains controversial. Some studies reported that an elevated PLR was an independent adverse prognostic factor in patients with CRC (12–23), yet others showed that the PLR could not be a related prognostic biomarker of CRC (11, 24–35).
In this study, a meta-analysis was conducted on published survival data on the PLR and prognosis of CRC, and the relationship between different PLR levels and survival outcomes in patients with CRC was finally determined.
Materials and methods
Search strategy
This study was registered at PROSPERO (ID: CRD42020219215). Two authors independently searched relevant literature from PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, and clinical trial databases with the following search terms: (colorectal neoplasms or “CRC” or ((cancer* or carcinoma* or neoplasm* or adenoma* or adenocarcinom* or tumour* or tumor* or polyp* or malignan*) and (colorectal* or colon* or rect* or anal or anus or “large bowel”))) and (platelet to lymphocyte ratio or platelet lymphocyte ratio or “PLR”). We limited the research method to cohort studies, and the retrieval time was limited from the database construction to December 28, 2021. Subject words and random words were used during retrieval.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies meeting the following criteria were included: (1) original articles published in English; (2) studies that compared prognosis in patients with CRC between different PLR levels; (3) patients were diagnosed with CRC by histopathological examination; (4) study methods were cohort studies; (5) studies that carried out multivariate analysis; (6) studies that succeeded in reporting the cut-off value of PLR and HR and a 95% CI. Studies were excluded when: (1) they were non-English studies; (2) they were non-cohort studies; (3) data could not be extracted from original articles; (4) studies failed to report the cut-off value of PLR or HR or a 95% CI; (5) original articles were letters, editorials, comments, supplements, conference abstracts, review articles, or duplicated and unrelated studies.
Data extraction
Two researchers independently screened the literature, extracted the data, and cross-checked it. If there are differences, they will be discussed and resolved or handed over to a third researcher for judgment. For literature lacking information, we will try our best to contact the original author to supplement it. The extracted information is as follows: (1) basic information included in the study: first author’s name, year and country of publication, name of the journal, contact information; (2) basic characteristics of the study: sample size and age, no. of different PLR levels, follow-up time, TNM stage; (3) key elements of quality assessment; (4) main data of outcome indicators.
Statistical analysis
We used Review Manager (version 5.4) software from Cochrane Collaboration for our meta-analysis, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. HR and 95% CI were recorded to assess the strong connection between different PLR levels and CRC prognosis. The heterogeneity of included studies was analyzed and evaluated by combining the Cochrane Q test and I2 test (36). A P-value <0.1 for Q statistic test or I2 > 50% was considered to be significantly heterogeneous. Then a random-effect model (DerSimonian–Laird method) was performed to calculate HR and 95% CI. Otherwise, a P-value >0.1 for Q statistic test or I2 < 50% was considered to use the fixed-effect model (Mantel–Haenszel method). However, it should be noted that when the number of studies is small, there is moderate or substantial heterogeneity and the distribution does not necessarily follow the normal or t-distribution. In this case, the random-effect models are preferred irrespective of the I2 statistic (37–40). When the number of included studies exceeded 10, funnel plots (41) were used to evaluate publication bias. Eventually, the stability and reliability of meta-analysis results were clarified through sensitivity analysis.
Results
Eligible articles
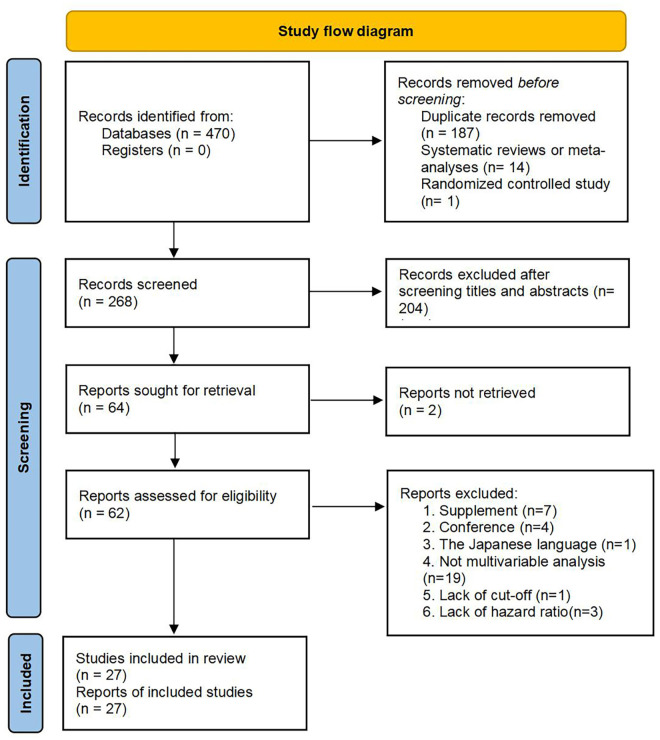
According to the aforementioned retrieval strategies, 470 literary works were identified, including 160 studies from PubMed, nine from Cochrane Library, 181 from Embase, 118 from Web of Science, and two from clinical trials. Because we obtained zero related literary works through other resources, 470 studies were finally screened. According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, there were 187 duplicated records, 15 literary works with inconsistent research types (14 systematic reviews or meta-analyses, one randomized controlled study), two articles retrieved from clinical trials were unpublished, and 204 articles were removed after screening titles and abstracts. After that, after reviewing the full text of the remaining 62 articles, 35 records were excluded due to the following criteria: (1) supplement: n = 7; (2) conference: n = 4; (3) Japanese language: n = 1; (4) not multivariable analysis: n = 19; (5) a lack of cut-off: n = 1; (6) a lack of hazard ratio: n = 3. Consequently, there were 27 studies, including 13,330 CRC patients, included in our meta-analysis (Figure 1). In the included studies, there were 25 records for OS, 11 for PFS, five for CSS, three for DFS and three for RFS. Clinical characters and relevant information extraction of the eligible studies are shown in Table 1 (42–44).
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for study selection. From: Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71.
Table 1.
Main characteristics of included studies.
| Study | Year | Country | Age (median and range) | Sample (male/female) | Survival analysis | HR (95% CI) | Treatment | Cut-off | No. of different level PLR | Stage | Summary results | NOS score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jian-Hui Chen et al. (11) | 2017 | China | – | 808/575 | OS | R(M) | Resection | 210 | PLR ≤ 210 (low) and PLR > 210 (high) | I–IV | Positive(OS) | 8 |
| Ross D Dolan et al. (23) | 2018 | Britian | 65/65–74/75:248/270/283 | 430/371 | CSS;OS | R(M) | Resection | 150 | PLR ≤ 150 and PLR >150 | I–IV | Negative(CSS); Negative(OS) |
8 |
| Zhigui Li et al. (45) | 2019 | China | 62 (19–94) | 176/136 | OS;PFS | R(M) | Resection | 260 | PLR ≤ 260 and PLR >260 | I–III | Positive(OS); Negative(PFS) |
8 |
| Mao-Song Lin et al. (12) | 2017 | China | 61.38 ± 11.35 years (range, 33 to 82 years) | 78/60 | OS | R(M) | colonoectomy | 248 | PLR ≤ 248 and PLR >248 | I–IV | Positive(OS) | 9 |
| Chong Lu et al. (13) | 2017 | China | <60/≥60:817/1028 | 1044/801 | OS;CSS | R(M) | surgery | 130 | PLR ≤ 130 and PLR >130 | I–IV | Positive(OS); Positive(CSS) |
9 |
| Yongxi Song et al. (24) | 2017 | China | 62 (range 13–86) | 982/762 | OS;CSS | M | Resection | 134.6 | PLR < 134.6 and PLR ≥134.6 | I–IV | Negative(OS); Negative(CSS) |
9 |
| Lin Wang et al. (14) | 2020 | China | 20 to 67 | 235/164 | OS | M | Resection | – | – | III | Positive(OS) | 7 |
| Hou-Qun Ying et al. (10) | 2014 | China | <60/≥60:70/135 | 144/61 | RFS/OS/CSS | M | Resection | 176 | PLR < 176 and PLR ≥176 | I–III | Negative(RFS);Negative(OS);Negative(CSS) | 8 |
| Joanna Szkandera et al. (25) | 2014 | Austria | 64 (27–95) | 217/155 | OS | M | Resection | 225 | PLR ≤ 225) / PLR225/Unknown:192/164/16 | II–III | Negative(OS) | 9 |
| Yuka Ahiko et al. (26) | 2021 | Japan | 65 years (25%–75% interquartile range, 57–72 y) | 1111/769 | OS | M | Resection | 136 | PLR < 136)/PL ≥ 136:759/1121 | II–III | Negative(OS) | 9 |
| Ozawa et al. (15) | 2015 | Japan | <65/≥65:78/156 | 142/92 | DFS/CSS | M | Resection | 25.4 | PLR <25.4 (181) and PLR ≥ 25.4 (53) | II | Positive(DFS); Positive(CSS) |
8 |
| Özlem Mermut et al. (27) | 2020 | Turkey | 61 (range: 22–83) | 85/71 | OS | M | Resection | 192 | PLR < 192 (84) and PLR ≥ 192 (72) | II–III | Negative(OS) | 7 |
| Dongyan Cai et al. (16) | 2019 | China | 62.0 ± 10.6 years | 86/78 | OS | M | – | 136 | I–IV | Positive(OS) | 7 | |
| Ender Dogan et al. (28) | 2019 | Turkey | 61 (26–82) | 66/64 | PFS/OS | M | Not clear | 160.66 | PLR <160.66 (low) and PLR ≥ 160. 66 (high) | IV | Negative(PFS)/Negative(OS) | 6 |
| Akihisa Matsuda et al. (29) | 2019 | Japan | 69 (48–90) | 20/13 | PFS/OS | M | Not clear | 173.2 | – | IV | Negative(PFS)/Negative(OS) | 9 |
| Yuchen Wu et al. (46) | 2016 | China | 59 | 35/20 | OS/PFS | M | Not clear | 150 | PLR < 150 (31) / PLR ≥ 150 (24) | IV | Negative(OS)/Positive(PFS) | 8 |
| Jing Yang et al. (30) | 2017 | China | 56 years (range 27–86) | 58/37 | PFS/OS | M | treated with cetuximab | 142 | PLR < 142 / PLR ≥ 142 | IV | Negative(PFS)/Negative(OS) | 8 |
| Akihisa Matsuda et al. (17) | 2020 | Japan | – | 15/6 | PFS | M | Treated With Aflibercept plus FOLFIRI | 193.2 | cutoff: 193.2. high/low:11/10 | IV | Positive(PFS) | 9 |
| Alessandro Passardi et al. (31) | 2016 | Italy | Low 66 (33–83) High 65 (34–81) |
174/115 | PFS/OS | M | – | 169 | PLR, low (<169) / high (≥169):144:145 | I–IV | Negative(PFS)/Negative(OS) | 7 |
| Heming Li et al. (32) | 2021 | China | 63 (36–89) | 30/16 | PFS | M | first-line therapy | 117.81 | PLR, low (<117.81) / high (≥117.81) | IV | Negative(PFS) | 7 |
| Jae Hyun Kim et al. (18) | 2017 | Korea | 65 | 1027/796 | OS/DFS | M | – | 160 | PLR, low (<160) / high (≥160):973/894 | III/IV | Positive(OS)/Positive(DFS) | 9 |
| Derek J. Erstad et al. (19) | 2020 | USA | 58 | 84/67 | OS | M | hepatic resection | 220 | PLR, low (<220) / high (≥220) | IV | Positive(OS) | 7 |
| Marlid Cruz-Ramos et al. (20) | 2019 | Spain | 72.2 | 63/47 | OS/PFS | M | – | 172.4 | PLR, low (<172.4) / high (≥172.4) | IV | Positive(OS)/Positive(PFS) | 7 |
| Gulcan Bulut et al. (33) | 2022 | Turkey | 64 years (32–84 years) | 56/38 | OS/PFS | M | – | 180.36 | PLR, ≥ 180.36/<180.36:47/47 | IV | Negative(OS)/Negative(PFS) | 6 |
| Yan-Yan Wang et al. (34) | 2019 | China | 57 years (IQR 50–64) | 289/163 | OS/DFS | M | – | 186 | PLR, low (<186) / high (≥186) | IV | Negative(OS)/Negative(DFS) | 8 |
| Joey Mercier et al. (21) | 2019 | Canada | – | 95/57 | PFS/OS | M | – | 330 | PLR <330 (112) and PLR ≥ 330 (40) | IV | Positive(PFS)/Positive(OS) | 7 |
| Martin Bailon-Cuadrado et al. (22) | 2018 | Spain | 69.09 ± 11.18 years | 114/87 | OS/RFS | M | Resection | 153 | High PLR (n = 96)/Low PLR (n = 105) | IV | Positive(OS)/Positive(RFS) | 7 |
Quality assessment
After extracting data from the original articles, the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to assess the methodological quality of included studies (22, 45). The NOS is a simple and convenient quality assessment tool widely used to evaluate case control and cohort studies. The NOS consists of three parts: cohort selection, comparability, and results. Each part has evaluation items, each item is represented by ⋆, and the full score is 9. Our quality evaluation table is revealed in Table 2.
Table 2.
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for assessing the quality of the included studies
| Study | Year | Representativeness of the exposed cohort | Selection of the nonexposed cohort | Ascertainment of exposure | Demonstration that outcome of interest was not present at start of study | Comparability of cohorts on the basis of the design or analysis | Assessment of outcome | Was follow-up long enough for outcomes to occur | Adequacy of follow up of cohorts | Totall scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jian-Hui Chen et al. | 2017 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Ross D Dolan et al. | 2018 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Zhigui Li et al. | 2019 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Mao-Song Lin et al. | 2017 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Chong Lu et al. | 2017 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Yongxi Song et al. | 2017 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Lin Wang et al. | 2020 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Hou-Qun Ying et al. | 2014 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Joanna Szkandera et al. | 2014 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Yuka Ahiko et al. | 2021 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Tsuyoshi Ozawa et al. | 2015 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Özlem Mermut et al. | 2020 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Dongyan Cai et al. | 2019 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Ender Dogan et al. | 2019 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | 6 | |||
| Akihisa Matsuda et al. | 2019 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Yuchen Wu et al. | 2016 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Jing Yang et al. | 2017 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Akihisa Matsuda et al. | 2020 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Alessandro Passardi et al. | 2016 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Heming Li et al. | 2021 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Jae Hyun Kim et al. | 2017 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 9 |
| Derek J. Erstad et al. | 2020 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Marlid Cruz-Ramos et al. | 2019 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Gulcan Bulut et al. | 2021 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | 6 | |||
| Yan-Yan Wang et al. | 2019 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | 8 | |
| Joey Mercier et al. | 2019 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 | ||
| Martin Bailon-Cuadrado et al. | 2018 | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆ | ⋆⋆ | ⋆ | 7 |
OS, DFS, RFS and PLR
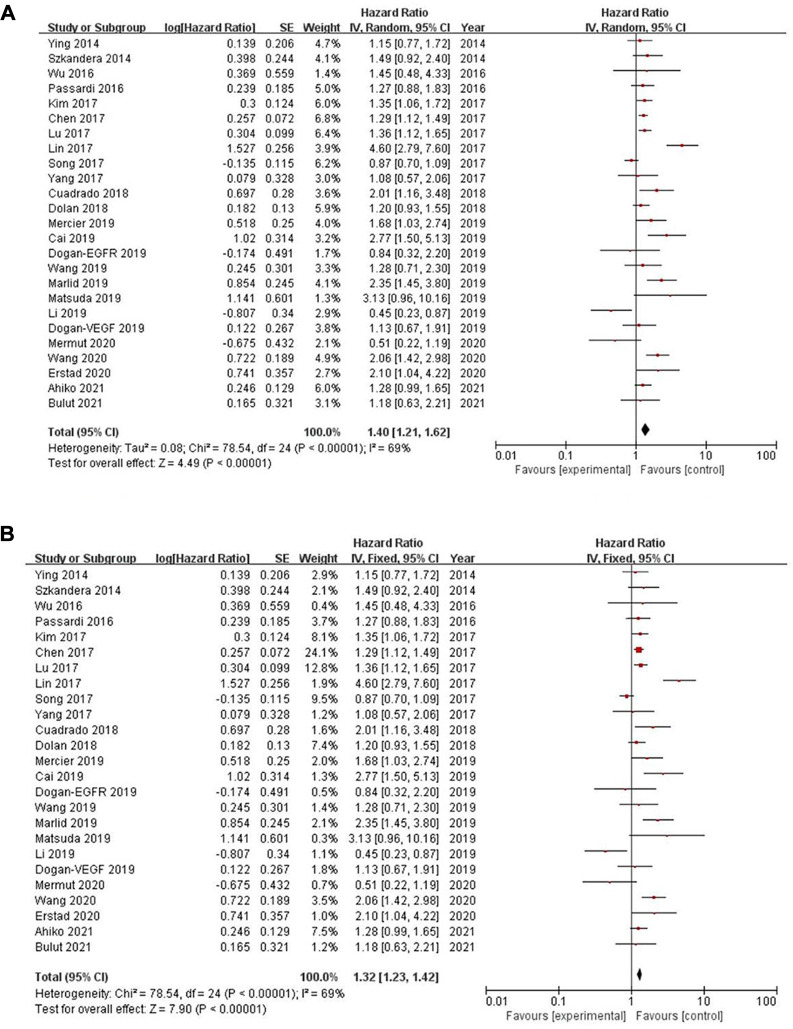
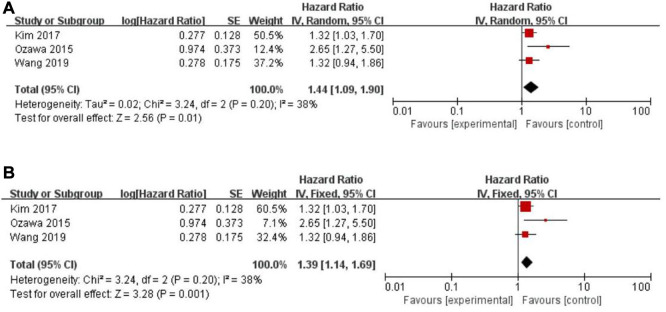
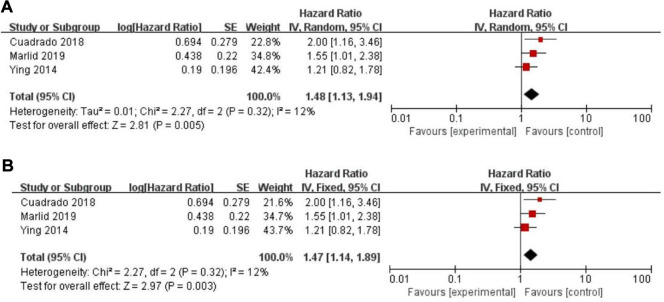
Twenty-five of the included records reported that overall survival (OS) of CRC patients with high PLR levels was significantly shorter than for those with low PLR levels (11–15, 17, 19–27, 29–31, 34, 35, 46–50). Pooled analysis of OS revealed significant differences and moderate heterogeneity between the high and low PLR groups in the random-effect model (HR = 1.40, 95% CI = 1.21–1.62, P < 0.00001, Figure 2A). Meanwhile, there were three studies evaluating hazard ratios for disease-free survival (DFS) (16, 19, 35) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) (11, 21, 23), respectively. As for DFS and RFS only few studies were available, considering that between-trial heterogenicity was still significant, random effect-models were preferred, and an elevated PLR was related to poor prognosis of patients with CRC for DFS and RFS (HR = 1.44, 95% CI = 1.09–1.90, P = 0.01 and HR = 1.48, 95% CI = 1.13–1.94, P = 0.005, respectively, Figures 3A, 4A).
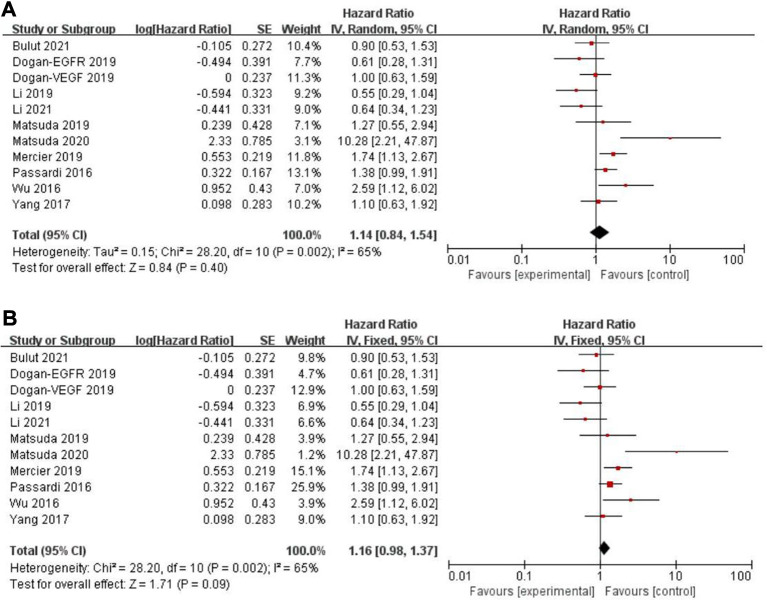
Figure 2.
Forest graph on association of overall survival with different levels of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio groups. (A) random effect model. (B) fixed effect model.
Figure 3.
Forest graph on association of disease-free survival with different levels of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio groups. (A) random effect model. (B) fixed effect model.
Figure 4.
Forest graph on association of recurrence-free survival with different levels of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio groups. (A) random effect model. (B) fixed effect model.
PFS, CSS and PLR
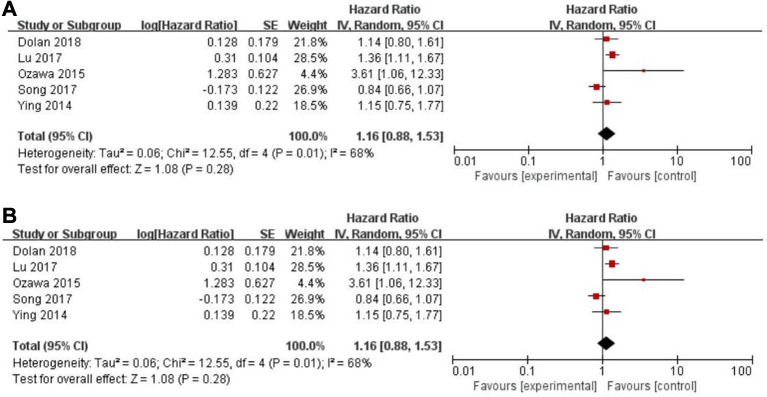
Eleven records assessed progression-free survival (PFS) (18, 29–31, 33, 34, 46, 48, 49, 50), whereas a non-significant association between PFS and the PLR (HR = 1.14, 95% CI = 0.84–1.54, P = 0.40; I2 = 65%, PH = 0.002, Figure 5A) was observed. Another five articles evaluated cancer-specific survival (CSS) (11, 14, 16, 25, 49). However, there was also no evidence of significance for CSS and PLR (HR = 1.16, 95% CI = 0.88–1.53, P = 0.28; I2 = 68%, PH = 0.01, Figure 6A).
Figure 5.
Forest graph on association of progression-free survival with different levels of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio groups. (A) random effect model. (B) fixed effect model.
Figure 6.
Forest graph on association of cancer-specific survival with different levels of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio groups. (A) random effect model. (B) fixed effect model.
Sensitivity analysis
The purpose of sensitivity analysis is to determine the stability and reliability of meta-analysis results. in OS, PFS and CSS tests, random-effect models were adopted according to Q test, so the fixed-effect models were used for sensitivity analysis (51). The results of OS, PFS and CSS (HR = 1.32, 95% CI = 1.23–1.42, P < 0.00001, HR = 1.16, 95% CI = 0.98–1.37, P = 0.09 and HR = 1.16, 95% CI = 0.88–1.53, P = 0.28, respectively, Figures 2B, 5B, 6B) were stable and reliable. In DFS and RFS, the results (HR = 1.39, 95% CI = 1.14–1.69, P = 0.001 and HR = 1.47, 95% CI = 1.14–1.89, P = 0.003, respectively, Figures 3B, 4B) were consistent with those of the original random-effect model, indicating that the meta-analysis results of DFS and RFS were also stable and reliable.
Publication bias assessment
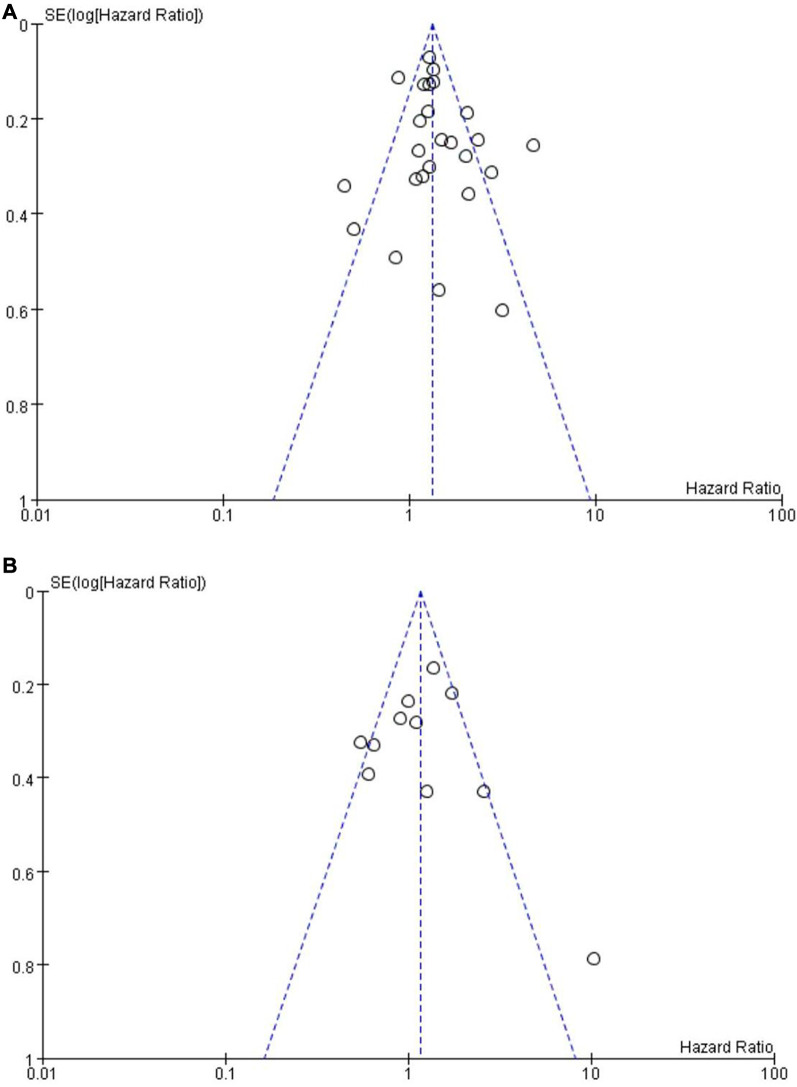
OS and PFS
Since more than ten studies were included in the OS group and the PFS group, a funnel plot was used to evaluate publication bias (Figures 7A,B). The funnel plots for publication bias show no obvious asymmetry, indicating that the pooled results were not influenced by publication bias.
Figure 7.
Funnel plot on the association of overall survival (A) and progression-free survival (B) with different levels of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio groups.
DFS, RFS and CSS
Because of the small number of included studies, funnel plots have not been carried out.
Discussion
Colorectal cancer is the third most common malignant tumor in the world and the second largest cause of cancer-related deaths. In 2018, there were about 1.8 million new cases and 881,000 deaths worldwide (52). The early clinical manifestations of CRC are not typical, and some patients have local progression or metastasis when found, leading to poor survival prognosis. Deeply studying the factors related to the prognosis of CRC and actively looking for tumor markers related to the prognosis of CRC are helpful to guide clinicians to evaluate the prognosis of CRC patients (53). However, two commonly used blood biomarkers, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), are not highly sensitive and specific (54). Some new tumor biomarkers such as circulating tumor cells (CTC) and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) (55) are also faced with high detection costs. Therefore, finding and screening some new, simpler and effective molecular indicators related to the prognosis of CRC is still a hot topic that needs further study.
Nowadays, an increasing number of researchers have confirmed that the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), the neutrophils-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), as the common inflammatory indicators, are of great significance in the diagnosis and prognosis of tumors, including CRC (56, 57). The relationship between PLR and the prognosis of CRC has attracted our attention. Then, we explored the prognostic effect of PLR in 27 studies, including 13,330 patients with CRC. In our study, we searched the literature as comprehensively as possible, consisting of PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, and clinical trial databases. Our primary outcomes were OS and PFS, and secondary outcomes included CSS, DFS and RFR. We used Review Manager (version 5.4) software from Cochrane Collaboration for our meta-analysis, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The heterogeneity of included studies was mainly analyzed and evaluated by combining the Cochrane Q test and I2 test. Thus, in OS, PFS and CSS tests, random-effect models were adopted. As for DFS and RFS only three studies were available respectively, considering that between-trial heterogenicity was still significant, we similarly used random effect-models in the analysis of them. What's more, taking the uncertainty in the estimation of the between-trial heterogeneity, the fixed-effect models were used to verify the results. Eventually, our pooled results demonstrated that an elevated PLR was correlated with poor OS, DFS and RFS, which were consistent with those of previous meta-analysis (58–60). Furthermore, among them, we included more relevant articles, obtained more data and used more stringent methods.
Investigating the reason, PLR is one of the indicators reflecting the body’s inflammatory response, and studies have indicated that inflammation is related to the occurrence and development of tumors to some extent (61). Inflammatory cells can release a variety of bioactive substances in the tumor microenvironment, and the tumor microenvironment is the internal environment for tumor cell survival, which is composed of tumor cells, immune cells, cytokines, and cell metabolites. Simultaneously, various cells interact with inflammatory factors, which further promote the formation of tumors due to the extreme immunosuppressive microenvironment (62). Meanwhile, several studies have pointed out that platelets can secrete P-selectin adhesion factor, which can make inflammatory cells adhere to endothelial cells and have a great adverse impact on tumor production, metastasis and prognosis (63–65). In addition, the angiogenic factors released by platelets can promote endothelial cell growth, induce the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, increase vascular permeability of tissue, and facilitate the invasion and metastasis of tumor cells through blood vessels in the body (66). Moreover, platelets can release tumor growth-promoting factors, resulting in continuous crazy growth of tumor tissue, which affects patient prognosis (67–69). Therefore, in CRC progression, PLR levels will gradually increase, and the higher the PLR, the worse the prognosis.
At the same time, it is interesting to note that under the assistant of R language, several new statistical research methods such as Paule-Mandel (70), Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman (19) etc are developing with each passing day. Ralf Bender et al. (71) simultaneously pointed out that DerSimonian and Laird approach had some limitations, especially in the case of very few studies, and they recommend using Knapp-Hartung method for meta-analyses. It can be seen that everyone is working hard to eliminate the between-trial heterogeneity. And we known this and made our own efforts. Henmi et al. (72) use of fixed effects estimates with a random effects approach to deal with heterogeneity. Böhning D et al. (73) mentioned that if there is strong heterogeneity, the results of the random effect model and the fixed effect model will differ greatly; If there is small heterogeneity, the both approaches will provide similar results. Based on this, in our study, when the random effect models were used for data analysis, the fixed effect models were used to verify the results. The same results are obtained in the statistical results, which mean that the conclusion is stable and reliable. Considering that the heterogeneity between independent studies has not had a huge impact on the production of results and conclusions, nor has it produced new controversial results and conclusions, we have not introduced more complex statistical methods or analysis programs. Of course, we agree that these new statistical methods are very interesting and useful, and we will try to use them in the future.
Our results can better reflect the authenticity of the relationship between PLR and CRC prognosis. However, our study has the following limitations. First of all, we only included literature published in English, which means that some publication bias may be inevitable. In addition, our study used aggregate data, not individual data; furthermore, we did not define the exact cut-off value representing the PLR level. It is really a pity that there is no way to obtain the original data for statistics and determine the exact cut-off value. Because many articles give different cut-off values, we can only try to use “high level” and “low level” to evaluate. At the same time, as an analogy, similar problems have been encountered in similar studies conducted by predecessors. Hamid et al. (74) showed that a low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio, but not a high platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, was inversely correlated with complete pathologic response rate. In his another research about prognostic value of neurophil-to-lysophocyte ratio (NLR) after curative rectal cancer recovery, result indicated that high NLR was associated with worse OS (75). It can be seen that the determination of the clear cut-off value of similar research did puzzling everyone. In addition, in order to avoid the impact of such differences as much as possible, we used both “random effect model” and “fixed effect model” in statistics, and the results are consistent. we know that our research is not perfect, but it provides a relatively useful result for clinical application. we also look forward to high-quality, multi-center RCT research to eliminate these deviations and determine the exact cut-off value.
Despite these limitations, our meta-analysis assessed the impact of an elevated PLR upon OS, PFS, CSS, DFS, and RFS outcomes in CRC patients. Based on existing data, our study suggests that PLR has a certain correlation with CRC patient prognosis, and an elevated PLR is correlated with poorer OS, DFS and RFS. However, no evidence exists that an elevated PLR is significantly associated with worse PFS and CSS. Clinical workers strengthening the detection of this available, inexpensive and repeatable index will have a good reference value for CRC patients. Moreover, with the emergence of more and more convincing studies, the impact of an elevated PLR upon CRC patient prognosis can be further explored and confirmed.
Conclusions
An elevated PLR seems to be an adverse prognostic factor affecting survival outcomes in CRC patients. Meanwhile, more prospective studies are required to confirm our conclusion.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GG and XH conceived this article; XH, HZ, and BL contributed with data acquisition; GG, TG, BY, and GW analyzed the data; and GG and XH wrote the paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1.Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71(3):209–49. 10.3322/caac.21660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Siegel RL, Torre LA, Soerjomataram I, Hayes RB, Bray F, Weber TK, et al. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence in young adults. Gut. (2019) 68(12):2179–85. 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. (2016) 388(10053):1659–724. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Virchow R. Die krankhaften Geschwülste: Die krankhaften Geschwülste. (1978).
- 5.Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V, Fearon DF, Merad M, et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med. (2018) 24(5):541–50. 10.1038/s41591-018-0014-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Galon J, Mlecnik B, Bindea G, Angell HK, Berger A, Lagorce C, et al. Towards the introduction of the “immunoscore” in the classification of malignant tumours. J Pathol. (2014) 232(2):199–209. 10.1002/path.4287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kokcu A, Kurtoglu E, Celik H, Tosun M, Malatyalıoglu E, Ozdemir AZ. May the platelet to lymphocyte ratio be a prognostic factor for epithelial ovarian cancer? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2014) 15(22):9781–4. 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.22.9781 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Que Y, Qiu H, Li Y, Chen Y, Xiao W, Zhou Z, et al. Preoperative platelet-lymphocyte ratio is superior to neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor for soft-tissue sarcoma. BMC Cancer. (2015) 15:648. 10.1186/s12885-015-1654-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li X, Han Z, Cheng Z, Yu J, Yu X, Liang P. Clinical significance of preoperative platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after thermal ablation: a retrospective analysis. Int J Hyperthermia. (2015) 31(7):758–63. 10.3109/02656736.2015.1068958 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pang Q, Zhang LQ, Wang RT, Bi JB, Zhang JY, Qu K, et al. Platelet to lymphocyte ratio as a novel prognostic tool for gallbladder carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21(21):6675–83. 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ying HQ, Deng QW, He BS, Pan YQ, Wang F, Sun HL, et al. The prognostic value of preoperative NLR, d-NLR, PLR and LMR for predicting clinical outcome in surgical colorectal cancer patients. Med Oncol. (2014) 31(12):305. 10.1007/s12032-014-0305-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen JH, Zhai ET, Yuan YJ, Wu KM, Xu JB, Peng JJ, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index for predicting prognosis of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23(34):6261–72. 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6261 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lin MS, Gao MJ, Zhang DL, Li XY, Yu H. Prognostic significance of preoperative platelet-lymphocyte ratio in a Chinese cohort patient with colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2017) 10(8):8686–94. 10.1007/s00384-015-2276-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lu C, Gao P, Yang Y, Chen X, Wang L, Yu D, et al. Prognostic evaluation of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. (2017) 8(49):86287–95. 10.18632/oncotarget.21141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang L, Xiao J, Li MZ, Teng WH, Chen Y. Performance of a nomogram based on the integration of inflammation markers with tumor staging in prognosis prediction of stage III colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. (2020) 12:7077–85. 10.2147/CMAR.S263577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ozawa T, Ishihara S, Nishikawa T, Tanaka T, Tanaka J, Kiyomatsu T, et al. The preoperative platelet to lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic marker in patients with stage II colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. (2015) 30(9):1165–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dongyan C, Xiaofeng D, Xiaosong G, Yong M, Xiaohong W, Dong H. Platelets and podoplanin is prognostic of patient survival after surgery in colorectal cancers. Int J Clin Exp Med. (2019) 12(2):1850–6. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Matsuda A, Yamada T, Matsumoto S, Shinji S, Yoshida H. Prognostic role of the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with aflibercept. In Vivo. (2020) 34(5):2667–73. 10.21873/invivo.12086 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim JH, Lee JY, Kim HK, Lee JW, Jung SG, Jung K, et al. Prognostic significance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with stage III and IV colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23(3):505–15. 10.3748/wjg.v23.i3.505 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Erstad DJ, Taylor MS, Qadan M, Axtell AL, Fuchs BC, Berger DL, et al. Platelet and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratios predict survival in patients with resectable colorectal liver metastases. Am J Surg. (2020) 220(6):1579–85. 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cruz-Ramos M, Del Puerto-Nevado L, Zheng B, López-Bajo R, Cebrian A, Rodríguez-Remirez M, et al. Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to lymphocyte ratio in older patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. (2019) 10(5):742–8. 10.1016/j.jgo.2018.10.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mercier J, Voutsadakis IA. Comparison of hematologic and other prognostic markers in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer. (2019) 50(3):493–506. 10.1007/s12029-018-0108-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bailon-Cuadrado M, Choolani-Bhojwani E, Tejero-Pintor FJ, Sanchez-Gonzalez J, Rodriguez-Lopez M, Perez-Saborido B, et al. Preoperative platelet–lymphocyte ratio is an independent factor of poor prognosis after curative surgery for colon cancer. Updates Surg. (2018;Mar) 70(1):33–9. 10.1007/s13304-017-0503-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dolan RD, McSorley ST, Park JH, Watt DG, Roxburgh CS, Horgan PG, et al. The prognostic value of systemic inflammation in patients undergoing surgery for colon cancer: comparison of composite ratios and cumulative scores. Br J Cancer. (2018) 119(1):40–51. 10.1038/s41416-018-0095-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Song Y, Yang Y, Gao P, Chen X, Yu D, Xu Y, et al. The preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is a superior indicator of prognosis compared with other inflammatory biomarkers in resectable colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17(1):744. 10.1186/s12885-017-3752-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Szkandera J, Pichler M, Absenger G, Stotz M, Arminger F, Weissmueller M, et al. The elevated preoperative platelet to lymphocyte ratio predicts decreased time to recurrence in colon cancer patients. Am J Surg. (2014) 208(2):210–4. 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.10.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ahiko Y, Shida D, Nakamura Y, Imaizumi J, Takamizawa Y, Moritani K, et al. Preoperative nutritional scores as host-related prognostic factors for both overall survival and postoperative complications in patients with stage II to III colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. (2021) 64(10):1222–31. 10.1097/DCR.0000000000002033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mermut Ö, İnanç B, Dursun N, Trabulus DC, Yardımcı AH, Arslan E. Prognostic value of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte/ platelet-lymphocyte ratio in patients with stage II-III rectal cancer who underwent curative resection. Istanbul Med J. (2020) 21(5):384–90. 10.4274/imj.galenos.2020.84553 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dogan E, Bozkurt O, Sakalar T, Derin S, Inanc M, Ozkan M. Impact of neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratio on antiEGFR and bevacizumab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer. J BUON. (2019) 24(5):1861–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Matsuda A, Yamada T, Matsumoto S, Sakurazawa N, Kawano Y, Shinozuka E, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival after TAS-102 treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. (2019) 39(8):4343–50. 10.21873/anticanres.13602 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yang J, Guo X, Wang M, Ma X, Ye X, Lin P. Pre-treatment inflammatory indexes as predictors of survival and cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients with wild-type RAS. Sci Rep. (2017) 7(1):17166. 10.1038/s41598-017-17130-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Alessandro P, Emanuela S, Luigi C, Monia D, Davide T, Silvana L, et al. Inflammatory indexes as predictors of prognosis and bevacizumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7(22):33210–9. 10.18632/oncotarget.8901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Li H, Liu Q, Liang S, Yao P, Lv J, Wang G, et al. Circulating tumor cells and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio are predictive markers for metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Transl Cancer Res. (2021) 10(1):288–97. 10.21037/tcr-20-2032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bulut G, Ozdemir ZN. Prognostic significance of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer. (2022) 53(1):1–6. 10.1007/s12029-021-00616-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang YY, Liu ZZ, Xu D, Liu M, Wang K, Xing BC. Fibrinogen-albumin ratio index (FARI): a more promising inflammation-based prognostic marker for patients undergoing hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. (2019) 26(11):3682–92. 10.1245/s10434-019-07586-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Laliman V, Roïz J. Frequentist approach for detecting heterogeneity in meta-analysis pair-wise comparisons: enhanced Q-test use by using I2 and H2 statistics. Value Health. (2014) 17(7):A576. 10.1016/j.jval.2014.08.1942 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Makambi KH. The effect of the heterogeneity variance estimator on some tests of treatment efficacy. J Biopharm Stat. (2004) 14(2):439–49. 10.1081/BIP-120037191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hartung J, Knapp G. On tests of the overall treatment effect in meta-analysis with normally distributed responses. Stat Med. (2010) 20(12):1771–82. 10.1002/sim.791 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hartung J, Makambi KH. Reducing the number of unjustified significant results in meta-analysis. Commun Stat Simul Comput. (2003) 32(4):1179–90. 10.1081/SAC-120023884 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dean A, Follmann M, Proschan A. Valid inference in random effects meta-analysis. Biometrics. (1999) 55(3):732–7. 10.1111/j.0006-341x.1999.00732.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. (2000) 56(2):455–63. 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tugwell P, David Tovey D. PRISMA 2020. J Clin Epidemiol. (2021) 134:A5–6. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.04.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. (2021) 134:178–89. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. Br Med J. (2021) 372:n160. 10.1136/bmj.n160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lo CK, Mertz D, Loeb M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:45. 10.1186/1471-2288-14-45 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25(9):603–5. 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mermut Z, Nan B, Dursun N, Trabulus F, Arslan E. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Neutrophil-lymphocyte/ Platelet-lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Stage II-III Rectal Cancer Who Underwent Curative Resection. (2020).
- 48.Li Z, Xu Z, Huang Y, Zhao R, Wu X. Prognostic values of preoperative platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, albumin and hemoglobin in patients with non-metastatic colon cancer. Cancer Manag Res. (2019) 11:3265–74. 10.2147/CMAR.S191432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wu Y, Li C, Zhao J, Yang L, Liu F, Zheng H, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios predict chemotherapy outcomes and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer and synchronous liver metastasis. World J Surg Oncol. (2016) 14(1):289. 10.1186/s12957-016-1044-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Passardi A, Scarpi E, Cavanna L, Dall’Agata M, Giorgi UD. Inflammatory indexes as predictors of prognosis and bevacizumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7(22):33210–9. 10.18632/oncotarget.8901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kanters S. Fixed- and random-effects models. Methods Mol Biol. (2022) 2345:41–65. 10.1007/978-1-0716-1566-9_3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Baidoun F, Elshiwy KM, Elkeraie Y, Merjaneh Z, Lak HM. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: recent trends and impact on outcomes. Curr Drug Targets. (2021) 22(9):998–1009. 10.2174/1389450121999201117115717 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhong LP, Li D, Zhu LZ, Fang XF, Yuan Y. A prognostic nomogram for metastasized colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. (2020) 23(7):701–8. 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20190621-00250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Rapado-González Ó, Álvarez-Castro A, López-López R, Iglesias-Canle J, Muinelo-Romay L. Circulating microRNAs as promising biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2019) 11(7):898. 10.3390/cancers11070898 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Haber DA, Velculescu VE. Blood-based analyses of cancer: circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Cancer Discov. (2014) 4(6):650–61. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-1014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kang Y, Zhu X, Lin Z, Zeng M, Shi P, Cao Y, et al. Compare the diagnostic and prognostic value of MLR, NLR and PLR in CRC patients. Clin Lab. (2021) 67(9). 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2021.201130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yamamoto T, Kawada K, Obama K. Inflammation-related biomarkers for the prediction of prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(15):8002. 10.3390/ijms22158002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hong-Xin P, Kang L, Bang-Shun H, Yu-Qin P, Hou-Qun Y, Xiu-Xiu H, et al. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio could be a promising prognostic biomarker for survival of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Febs Open Bio. (2016) 6(7):742–50. 10.1002/2211-5463.12083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhou X, Du Y, Huang Z, Xu J, Qiu T, Wang J, et al. Prognostic value of PLR in various cancers: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9(6):e101119. 10.1371/journal.pone.0101119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Templeton AJ, Ace O, Mcnamara MG, Al-Mubarak M, Vera-Badillo FE, Hermanns T, et al. Prognostic role of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. (2014) 23(7):1204–12. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Trinchieri G. Cancer and inflammation: an old intuition with rapidly evolving new concepts. Annu Rev Immunol. (2012) 30:677–706. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kummar S, Kinders R, Rubinstein L, Parchment RE, Murgo AJ, Collins J, et al. Compressing drug development timelines in oncology using phase “0” trials. Nat Rev Cancer. (2007) 7(2):131–9. 10.1038/nrc2066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Qi C, Wei B, Zhou W, Yang Y, Li B, Guo S, et al. P-selectin-mediated platelet adhesion promotes tumor growth. Oncotarget. (2015) 6(9):6584–96. 10.18632/oncotarget.3164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Tao DL, Tassi Yunga S, Williams CD, McCarty OJT. Aspirin and antiplatelet treatments in cancer. Blood. (2021) 137(23):3201–11. 10.1182/blood.2019003977 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Qi C, Li B, Guo S, Wei B, Shao C, Li J, et al. P-selectin-mediated adhesion between platelets and tumor cells promotes intestinal tumorigenesis in apc(min/+) mice. Int J Biol Sci. (2015) 11(6):679–87. 10.7150/ijbs.11589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Verheul HM, Hoekman K, Lupu F, Broxterman HJ, van der Valk P, Kakkar AK, et al. Platelet and coagulation activation with vascular endothelial growth factor generation in soft tissue sarcomas. Clin Cancer Res. (2000) 6(1):166–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hara Y, Steiner M, Baldini MG. Platelets as a source of growth-promoting factor(s) for tumor cells. Cancer Res. (1980) 40(4):1212–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cedervall J, Hamidi A, Olsson AK. Platelets, NETs and cancer. Thromb Res. (2018) 164(Suppl 1):S148–52. 10.1016/j.thromres.2018.01.049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Goubran HA, Stakiw J, Radosevic M, Burnouf T. Platelet-cancer interactions. Semin Thromb Hemost. (2014) 40(3):296–305. 10.1055/s-0034-1370767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Veroniki AA, Jackson D, Viechtbauer W, Bender R, Bowden J, Knapp G, et al. Methods to estimate the between-study variance and its uncertainty in meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. (2016) 7(1):55–79. 10.1002/jrsm.1164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bender R, Friede T, Koch A, Kuss O, Schlattmann P, Schwarzer G, et al. Methods for evidence synthesis in the case of very few studies. Res Synth Methods. (2018) 9(3):382–92. 10.1002/jrsm.1297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Henmi M, Copas JB. Confidence intervals for random effects meta-analysis and robustness to publication bias. Stat Med. (2010) 29(29):2969–83. 10.1002/sim.4029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Dankmar B, Uwe M, Ekkehart D, Peter S, Chukiat V, Annibale B. Some general points in estimating heterogeneity variance with the DerSimonian-Laird estimator. Biostatistics. (2002) 4:445–57. 10.1093/biostatistics/3.4.445 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hamid HKS, Emile SH, Davis GN. Prognostic significance of lymphocyte-to-monocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in rectal cancer: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Dis Colon Rectum. (2022) 65(2):178–87. 10.1097/DCR.0000000000002291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hamid H, Davis GN, Trejo-Avila M, Igwe PO, Garcia-Marín A. Prognostic and predictive value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio after curative rectal cancer resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Oncol. (2021) 37(Suppl 4):101556. 10.1016/j.suronc.2021.101556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.