Abstract
Background
Despite achieving remission in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), persistent gastrointestinal symptoms are common in quiescent IBD. While irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is commonly diagnosed in IBD, IBS-like symptoms of recurrent abdominal pain and altered bowel habits can also be attributed to a wide range of overlapping gastrointestinal (GI) etiologies and systemic disorders with GI manifestations that often do not respond to conventional IBS therapies. Delay in diagnosis of these conditions can lead to ongoing patient suffering, reduced quality of life, repetition of invasive testing, increased healthcare utilization, and potentially unnecessary empirical escalation of IBD-related treatments.
Aims
This review provides a practical approach for the evaluation and diagnosis of IBS mimickers in IBD. We summarize the definition, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of the potential etiologies causing unexplained GI symptoms.
Conclusion
Overlapping conditions can co-exist with IBD and explain IBS-like symptoms. The diagnostic work-up in this population should be individualized and tailored to the predominant symptom pattern, associated clinical signs and symptoms and predisposing conditions that can be obtained from a detailed history and physical examination.
Keywords: Irritable bowel syndrome, Inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, Ulcerative colitis
Introduction
Despite effective therapies to induce and maintain remission, many patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) experience new or persistent gastrointestinal symptoms, particularly irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) like symptoms of recurrent abdominal pain and altered bowel habits. In a systematic review and meta-analysis, the pooled prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms in IBD in remission was 32.5% (95% CI 27.4–37.9) [1]. Even when endoscopic or histologic remission was used to define remission, 25.8% (95% CI 20.2–31.7) experienced IBS-like symptoms, highlighting an unmet need in management beyond controlling active inflammation [1]. These symptoms are associated with high morbidity, poor quality of life, and increased healthcare utilization [2]. The clinical approach to persistent GI symptoms in this population can be challenging given the numerous possible underlying organic causes as well as the vast array of diagnostic options. In this review, we discuss conditions outside of active inflammation that can co-exist with IBD and explain persistent GI symptoms. We summarize the definition, pathophysiology, clinical signs and symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of IBS mimickers in IBD. In the review, we assume that active IBD-related inflammation has been ruled out based on the most recent guidelines. This review does not encompass an exhaustive list but covers common conditions that can overlap between motility and IBD specialties (Table 1).
Table 1.
Causes of irritable bowel syndrome-like symptoms in inflammatory bowel disease
| Condition | Clinical signs and symptoms | Key diagnostic tests | Diagnostic criteria | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intestinal microbial overgrowth | ||||
| Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth |
Post-prandial abdominal bloating/distention Abdominal discomfort Diarrhea Flatulence Dyspepsia |
Lactulose or glucose breath tests Small bowel aspiration with quantitative cultures |
Rise from baseline in H2 ≥ 20 ppm within 90 min ≥ 103 CFU/mL on quantitative cultures |
Rifaximin, doxycycline, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, neomycin, norfloxacin, tetracycline or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Elemental diet Recurrent SIBO1 |
| Intestinal methanogen overgrowth |
Constipation Alternating bowel habits Post-prandial abdominal bloating/distention Brain fog |
Lactulose or glucose breath test | CH4 ≥ 10 ppm at any point of the 120-min breath test | Rifaximin + neomycin, Rifaximin + metronidazole Ciprofloxacin + metronidazole |
| Small intestinal fungal overgrowth |
Abdominal bloating/distention Abdominal discomfort Diarrhea Flatulence Belching |
Small bowel aspiration with quantitative cultures | ≥ 103 CFU/mL |
Fluconazole Nystatin |
| Malabsorptive syndromes | ||||
| Carbohydrate malabsorption or maldigestion |
Abdominal discomfort Abdominal cramping Bloating Flatulence Diarrhea |
Hydrogen breath test* Disaccharidase assay Genetic testing *SIBO can lead to false positive hydrogen breath test, rule out SIBO prior to hydrogen breath testing for CHO malabsorption |
H2 ≥ 20 ppm increase from baseline on breath test | Disaccharide dietary restriction and/or enzyme replacement |
| Bile acid malabsorption |
Watery diarrhea Steatorrhea Rectal urgency Abdominal cramping |
Trial of bile acid sequestrants 75SeHCAT* 48-h total fecal bile acids Fasting serum C4 *Not available in the United States |
75SeHCAT radiolabeled BA retention on day 7: ▪ < 5% (severe) ▪ < 10% moderate ▪ < 15% mild Total 48 h fecal BA: > 2337 umol/48 h (abnormal) Fasting serum C4 > 52.5 ng/mL (abnormal) |
Bile acid sequestrants |
| Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency |
Chronic abdominal discomfort Bloating Diarrhea Steatorrhea |
Fecal elastase* Trial of pancreatic enzymes *False positive can occur with diarrhea due to dilution effect |
Fecal elastase: ▪ ≤ 200 μg/g (abnormal) ▪ < 100 μg/g (reflects severe EPI) Nutritional lab markers: • Fat soluble vitamins • Pre-albumin • Iron • Zinc • Magnesium |
Pancreatic enzyme replacement |
| Immune mediated syndromes | ||||
| Mast cell activation syndrome |
GI: ▪ Abdominal bloating ▪ Abdominal cramping ▪ Abdominal pain ▪ Diarrhea ▪ Constipation Skin: ▪ Flushing ▪ Hives ▪ Pruritis Nasal/airway: ▪ Throat scratching ▪ Chest tightness ▪ Rhinitis Physical exam: ▪ Dermatographia Associated conditions: • Atopic diseases • EDS • POTS |
Blood tests: Tryptase* Histamine Chromogranin A Prostaglandin D2 Urine tests (random and/or 24 h): Methylhistamine Leukotriene E4 2,3-dinor 11-ß-prostaglandin F2-alpha *Only positive in 15% of MCAS patients |
Major criteria of characteristic MC activation symptoms in 2 or more systems plus ≥ 1 minor criteria 1. Elevation in blood and/or urine of MC mediators 2. Clinical improvement with MC-directed medical therapy 3. ≥ 20 MCs per HPF in luminal GI tract or bladder biopsies *Obtain labs within 1–6 h of MCAS flare *Hold H1/H2 blockers and other mast cell stabilizers prior to lab work |
H1 histamine receptor blockers H2 histamine receptor blockers Mast cell stabilizers Leukotriene receptor antagonist Consider referral to allergist |
| Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases |
Abdominal pain Abdominal bloating Nausea and vomiting Diarrhea Complications: GI mucosal ulcerations, pyloric stenosis, intestinal strictures, protein losing enteropathy, perforation, anemia, and ascites |
Eosinophilic infiltration on pathology *Rule out secondary causes of increased eosinophils: Parasitic infections with stool ova and parasite, stool giardia antigen and serology for strongyloides |
Suggested protocol: Minimum of 12 biopsies collected per subject during EGD, 4 in each the gastric antrum, gastric body, and duodenum Suggested thresholds: ▪ ≥ 30 eos in ≥ 5 high power field (hpf) for gastric biopsies ▪ ≥ 30 eos in 3 hpf for duodenal biopsies |
Elimination diet Corticosteroids |
| Non-celiac gluten sensitivity |
Abdominal pain Abdominal bloating Irregular bowel movements Fatigue Joint pain Migraines Brain fog |
Clinical history Rule out celiac disease with serologic testing and duodenal biopsies |
Clinical symptoms on a gluten containing diet in the absence of serologic and histologic findings of celiac disease and wheat allergy | Trial of gluten free diet |
| Anorectal disorders | ||||
| Dyssynergic defecation |
Constipation Incomplete evacuation Straining Rectal urgency Abdominal pain Abdominal distention Bloating Diarrhea |
Digital rectal exam Anorectal manometry with balloon expulsion test MR defecography |
Paradoxical contraction or inadequate relaxation of the pelvic floor during attempted defecation *No validated diagnostic criteria for DD in IBD |
Biofeedback therapy |
| Structural anorectal disorders |
Constipation Bloating Obstructed defecation Incomplete evacuation Straining Rectal urgency Fecal or mucus soilage |
MR or XR defecography |
Rectal prolapse Intussusception Descending perineum syndrome Enterocele Rectocele Pelvic organ prolapse Bowel or pouch kinking with bear down Anal or anastomotic stricture |
Biofeedback therapy and/or surgical evaluation |
| Other | ||||
| Endometriosis |
Chronic abdominal pain Altered bowel habits Rectal bleeding Dysmenorrhea Dyspareunia Infertility Intra-abdominal adhesions |
Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound Pelvic MRI w/contrast Laparoscopy |
Identification of endometriosis implant |
Hormonal therapies Surgical removal/fulguration of lesions (implants) Pain management |
| Intra-abdominal adhesions |
Chronic bloating Abdominal cramping Altered bowel habits Chronic abdominal pain Nausea Other clinical features: ▪ Transient, partial or complete bowel obstruction ▪ Development of SIBO ▪ Female infertility ▪ Dyspareunia Clinical clues: ▪ History of abdomino-pelvic surgery ▪ History of radiation therapy ▪ History of endometriosis |
Laparoscopy XR barium study with small bowel follow through Antroduodenal manometry to assess for repeated phase-3 migrating motor complexes in fasting state |
Identification of abdominal adhesions intra-operatively |
Elective lysis of adhesions Abdominal visceral massage Smooth muscle relaxants, i.e., dicyclomine, hyoscyamine, or peppermint based products Minimize fiber supplements and stimulant laxatives Low residue diet |
| Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome |
Abdominal pain Abdominal distention Nausea Constipation Heartburn Vomiting Diarrhea Associated symptoms: Joint hypermobility Autonomic dysfunction Chronic pain syndromes Structural abnormalities, i.e., visceroptosis, pelvic organ prolapse, and redundant colon |
Clinical diagnosis with no available genetic testing Beighton score to assess for generalized joint hypermobility Erect barium testing for visceroptosis |
Beighton score: ▪ Pubertal age to 50 years of age: ≥ 5 points out of 9 ▪ Over age 50: ≥ 4 points out of 9 |
Pelvic physiotherapy Biofeedback therapy Promotility agents |
| Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome |
Nausea Abdominal bloating Diarrhea Constipation Abdominal pain Associated symptoms: Inappropriate tachycardia Palpitations Chest pain Lightheadedness Cognitive difficulties |
Tilt table test | Tilt table test: HR rise ≥ 30 bpm within 10 min of standing or HR ≥ 120 bpm after standing in the absence of orthostatic hypotension |
Multidisciplinary care Avoid precipitating factors Hydration and high salt diet Physical therapy Exercise training Pharmacotherapy (beta blockers, midodrine, pyridostigmine, and/or fludrocortisone) |
| Medications or Supplements |
Abdominal discomfort and/or bloating: • Probiotics/prebiotics • Excessive fiber supplementation • Cholestyramine • Glucagon peptide-1 agonists • Lactulose Constipation: • Iron supplementation • Anti-spasmodic • Opiates • Tricyclic antidepressants • Anti-psychotics • Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors • 5-HT3 receptor antagonists • Calcium channel blockers • Calcium supplementation • Aluminum containing antacids Diarrhea: • 5-aminosalicylates • Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors • Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors • Magnesium containing antacids • Proton pump inhibitors • Metformin |
Detailed medication and supplement history | Improvement of symptoms with discontinuation | Discontinuation of the triggering compound |
Intestinal Microbial Overgrowth
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition where excessive amounts of bacteria typically found in the colon are found in the small intestine and result in various gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms [3]. Patient with IBD, particularly Crohn’s disease, are at increased risk of SIBO [4–6]. In a systematic review and meta-analysis, the proportion of SIBO in patients with IBD was 22.3% (95% CI 19.92–24.68). The odds ratio (OR) for SIBO in patients with IBD was 9.51 (95% CI 3.39–26.68) compared to controls without IBD [7]. The OR was significantly elevated in both CD (OR 10.86; 95% CI 2.76–42.69) and UC (OR 7.96; 95% CI 1.66–38.35). In subgroup analysis, patients with fibrostenosing CD (OR 7.47; 95% CI 2.51–22.20) and prior bowel surgery (OR 2.38; 95% CI 1.65–3.44), had increased odds of SIBO. The underlying pathophysiology behind SIBO in IBD may be due to impaired intestinal mucosal integrity, intestinal stasis caused by strictures, and/or intra-abdominal adhesions and prior intestinal surgeries. Additionally, any structural factor that allows colonic bacteria to enter the small bowel, such as enterocolic fistulas or lack of an ileocecal valve can facilitate SIBO. The symptoms of SIBO are non-specific and non-predictive for SIBO, however commonly patients complain of bloating, abdominal pain, flatulence, nausea, dyspepsia, diarrhea, and constipation. The preferred method to diagnose SIBO is the lactulose or glucose breath test (Table 1) [8]. The test is considered positive if there is a rise in baseline breath hydrogen by ≥ 20 by 90 min. Small bowel aspiration with quantitative cultures during upper endoscopy can be considered, however this method is limited by the risk of contamination by oral flora and the invasive and costly nature of the test [9]. The cornerstone of therapy for SIBO is antibiotics [3]. In a study evaluating patients with IBD and SIBO (n = 117), 57.3% achieved symptomatic improvement after antibiotics. The rate of response was similar between CD and UC (52.1% vs 65.9%, p = 0.18) [10]. An alternative to antibiotics is a 2 to 3 week course of elemental diet, which contains predigested micronutrients that are primarily absorbed in the proximal small bowel and limits nutrients to bacteria in the small intestine [11]. While this has not been directly studied for SIBO in patients with IBD, the elemental diet has been shown to normalize abnormal lactulose breath test and improve symptoms in patients with IBS with a cumulative symptom response rate of 85% (79/93 patients). Unfortunately, this diet is limited by lack of palatability and hence patient adherence. To successfully eradicate SIBO in IBD patients, it is important to address underlying issues that may be predisposing to bacterial overgrowth, such as strictures causing intestinal stasis or post-surgical adhesions. In patients who are prone to SIBO recurrences, the clinician can consider utilizing pro-motility agents such as low dose erythromycin or prucalopride, to augment the phase 3 migrating motor complexes to sweep intestinal debris and extend periods between symptomatic SIBO recurrences [12, 13].
Intestinal Methanogen Overgrowth
Intestinal methanogen overgrowth (IMO) is a condition where methanogenic archaea have overgrown and result in GI symptoms. Since IMO is attributed to anaerobic organisms from the domain archaea, rather than bacteria, it is a separate clinical entity from SIBO [3]. IMO is overall uncommon in IBD and a systematic review and meta-analysis reported a low prevalence of 5.6% (95% CI 2.6–11.8) compared to 25% (95% CI 18.8–32.4) in patients with IBS [14]. The prevalence of IMO was significant lower in CD compared to UC (5.3%; 95% CI 3.0–8.5 vs 20.2%; 95% CI 12.8–29.4). Since intestinal methane gas directly slows intestinal transit, IMO can be associated with constipation and constipation predominant IBS [15]. IMO can only be diagnosed by a lactulose or glucose hydrogen breath test. Per the North American Consensus, a methane level of 10 ppm or more at any point during breath testing is considered diagnostic for IMO [8]. Another efficient method to detect IMO is a single fasting methane breath test. A SMM of ≥ 10 ppm had a sensitivity of 86.4% and specificity of 100% for diagnosing IMO on the glucose and lactulose breath test [16]. In terms of treatment, archaea are more resistant to most antibiotics and respond better to combination therapy (e.g., rifaximin and neomycin rather than neomycin alone).[17, 18] Alternative antibiotics that can be used to treat IMO include rifaximin and metronidazole or ciprofloxacin and metronidazole.
Small Intestinal Fungal Overgrowth
Small intestinal fungal overgrowth is characterized by excessive number of fungal organisms in the small bowel associated with gastrointestinal symptoms [19]. Fungus, mainly Candida species, is a natural inhabitant of the gut in healthy subjects and are usually found at low concentrations in jejunal aspirates [20]. While the prevalence of SIFO in IBD has not been established, patients with intestinal mucosal barrier injury, immunocompromised state, post-colectomy state and steroid or antibiotics use are at increased risk, therefore this condition is relevant for patients with IBD [19, 21]. Candida species, particularly Candida albicans (C. albicans) is significantly more abundant in CD, UC, and general patients with IBD compared to healthy controls [22, 23]. Mice models using a dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) induced model of colitis showed that inflammation is a driver of C. albicans intestinal overgrowth [24]. The exact pathogenesis of SIFO in IBD is not clear, however host deficiency of fungus related factors Dectin-1 or CARD9 results in enhanced susceptibility to pathogenic fungal infections in humans and mice and susceptibility to colitis in mice [25–28]. Interestingly, polymorphic variants in the gene for CARD9 are strongly associated with CD and UC in humans, which suggests a link between fungi and IBD [25, 29, 30]. The most common symptoms of SIFO include abdominal discomfort, gas, bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea [19]. SIFO can be diagnosed by fluid aspiration of the 3rd or 4th portion of the duodenum or jejunum for quantitative cultures. Fungal cultures ≥ 103 colony forming units (CFU)/mL is diagnostic of SIFO [19, 31]. Candida identified in stool is usually considered clinically insignificant as Candida is common in stool cultures of asymptomatic individuals [32]. Treatment options for SIFO include nystatin or fluconazole. In an immunocompetent host, a 2–3 weeks course of oral fluconazole 100 to 200 mg daily is recommended [19]. Oral liquid nystatin is another safe option that can be considered. While data on its efficacy for SIFO is lacking, oral liquid nystatin is not systemically absorbed in the GI tract, therefore toxicity is rare. The dose and ideal treatment duration of nystatin for SIFO therapy is not established. In our clinical practice, we use Nystatin oral liquid 1,000,000 units four times daily for 21 days.
Post-fecal Microbiota Transplantation IBS
Patients with IBD are at increased risk for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) and in cases of recurrent CDI, may undergo fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). While FMT may lead to resolution of recurrent CDI, some patients continue to report ongoing gastrointestinal symptoms. The risk factor for post-FMT IBS-like symptoms are not clear. In a prospective pilot study, there was a trend toward increased post-infectious IBS symptoms (abdominal discomfort, bloating, loose stools, constipation) among FMT recipients who received stool from donors with a positive lactulose breath test (50% vs 14.2%, p = 0.09). Larger studies are needed to assess the incidence of post-FMT IBS-like symptoms in patients with IBD and potential risk factors [33].
Malabsorptive Syndromes
Bile Acid Malabsorption
Patients with ileal CD or ileal resection are at increased risk for bile acid malabsorption (BAM) because the terminal ileum is the major site of bile acid reabsorption [34]. When a short ileal resection < 100 cm in performed, increased hepatic synthesis of bile acids (BA) minimizes the effect on bile acid metabolism and patients may develop watery diarrhea. An ileal resection greater than 100 cm can result in severe bile acid malabsorption and steatorrhea. Excess BAs can cause GI symptoms because they enhance mucosal permeability, induce water and electrolyte secretion and accelerate colonic transit. Common symptoms of bile acid malabsorption include watery diarrhea, steatorrhea, urgency, and abdominal cramping. Importantly, SIBO is a common cause of BAM because deconjugation of bile acids is mediated by bile salt hydrolase enzymes, which are widely expressed by the gut microbiota. Since patients with IBD are at higher risk for SIBO, SIBO should be ruled out in cases where BAM is suspected [35]. While diagnostic testing for BAM exists, symptomatic response to bile acid sequestrants is the preferred method to confirm a diagnosis. The 75Selenium homotaurocholic acid test (SeHCAT) is considered the gold standard for diagnosis of bile acid malabsorption, but it is expensive and is not available in most countries including the United States [36]. The 75SeHCAT test uses noninvasive gamma scintigraphy to measure whole body bile acid retention after ingestion of a capsule containing 75SeHCAT. Subjects with decreased retention of radiolabeled BA have increased loss into the colon. Another diagnostic test is the 48 h total fecal BA excretion test, which is a direct measure of excess BAs that exit the colon. The test requires stool collection on the last 2 days of a 4 day, 100 g fat diet. Excretion of > 2,337 µmol per 48 h (ULN) is considered abnormal. The test is limited by the cumbersome stool collection and lack of widespread availability [34, 36]. A fasting serum C4 is a biomarker that provides a direct measure of hepatic BA synthesis. Relative to 75SeHCAT < 10%, a fasting serum C4 > 48.4 ng/mL had a sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 79% [37]. This test is available in the United States, convenient and a reasonable screening tool, however the test still requires further validation. Additionally, C4 levels have diurnal variation, with gradual rise after 9:00 AM so the test should be performed early in the morning. C4 levels can also be affected by the presence of liver disease and use of statins. Therapeutic trials of BA sequestrants (BAS) are used to confirm diagnosis and for treatment. These agents bind free BAs and prevent colonic effects of increased secretion and motility. Options include colestipol, colesevelam, and cholestyramine. BAS can affect absorption of other medications, therefore other oral medications should be administered at least 1 h before or 4 to 6 h after bile acid sequestrants are consumed. The use of these agents may be limited by side effects of nausea and bloating [34, 36].
Carbohydrate Maldigestion and Malabsorption
Carbohydrate (CHO) malabsorption is a condition where carbohydrates escape digestion and/or absorption and reach the colon causing bacterial fermentation and symptoms of diarrhea, bloating, abdominal cramping, and flatulence. Lactose intolerance is twice as frequent in UC and CD compared to healthy controls and patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders [38]. Fructose malabsorption is also more frequent in CD based on hydrogen test, unrelated to small intestinal transit, intestinal resection or SIBO [38]. Primary carbohydrate malabsorption includes rare congenital defects such as an autosomal recessive lactase deficiency, homozygous recessive sucrase-isomaltase deficiency, and sodium glucose co-transporter 1 (SGLT1) deficiency. Secondary forms arise from any condition where the structural integrity of the small intestine is impaired, i.e., IBD, celiac disease, radiation therapy, SIBO, enteric infections, extensive intestinal resection, or pancreatic dysfunction. Testing options include hydrogen breath testing, disaccharidase assay, and genetic testing. Hydrogen breath testing is a non-invasive and affordable method to diagnose carbohydrate intolerance. ≥ 20 parts per million increase in hydrogen from baseline is considered indicative of impaired absorption of the ingested sugar [8, 39]. The presence of SIBO can result in false positive breath testing for carbohydrate malabsorption and IMO can result in false negative testing because hydrogen is metabolized to form methane gas, therefore it is important to exclude SIBO and IMO prior to diagnosing patients with carbohydrate malabsorption. Disaccharidase testing is limited by the invasive nature of the test, potential sampling error and analysis can be affected by improper specimen handling and storage [39]. The mainstays of management includes disaccharide dietary restriction and/or enzyme replacement.
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
Pancreatic disorders are not uncommon in IBD [40]. Patients with IBD can develop acute pancreatitis from gallstones or medications, there is a strong association between Type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis and UC and there is an increased prevalence of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) in IBD. The reported prevalence of EPI may be overestimated as diarrhea can lead to falsely low fecal elastase due to dilution effect [41]. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) refers to maldigestion and malabsorption of nutrients as a consequence of reduced pancreatic enzyme output. Data regarding EPI in IBD is scarce and conflicting. In a cross-sectional study, EPI was demonstrated in patients with IBD based on fecal elastase test using a cut off of ≤ 200 μg/g. EPI was found in 22% of UC and 14% of CD patients and OR for patients with IBD was 10.5 (95%CI 2.5–44.8) compared to controls, based on screening by fecal elastase [41]. The proposed pathophysiology for EPI in IBD includes pancreatic autoantibodies, duodenal involvement resulting in ampullary obstruction, duodenal reflux, and extensive small bowel resection leading to reduced hormone secretion [42, 43]. Common symptoms of EPI include abdominal bloating, chronic diarrhea, steatorrhea, and chronic abdominal pain. Steatorrhea is characteristic of severe pancreatic exocrine insufficiency and typically occurs when 90 percent of glandular function has been lost. To evaluate for steatorrhea, a coefficient of fat absorption (CFA) is the considered gold standard. The patient should maintain a strict diet containing 100 g of fat per day over 5 days, then collect feces in the last 3 days of the 5 days period. A CFA < 93% is considered pathological [44]. The initial evaluation for EPI includes a fecal elastase level and nutritional laboratory markers including fat soluble vitamins, proteins, and micronutrients. An IgG4 level can also be obtained if there is concern for autoimmune pancreatitis. The presence of symptoms of malabsorption, nutritional deficiencies, and a low fecal elastase makes the diagnosis of EPI very likely [45]. The pretest probability of EPI is very high in patients with chronic calcifying pancreatitis on imaging [44]. The mainstay of management is a trial of exogenous pancreatic enzymes.
Immune Mediated Syndromes
Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGID) are chronic, inflammatory conditions characterized by GI symptoms and increase in eosinophil predominant inflammation in the GI tract, in the absence of secondary causes of eosinophilia [46]. The best known EGID is eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE), but non-EoE EGIDs can involve the stomach, small bowel, and/or colon. Non-EOE EGIDs are rare and affect less than 10 in 10,000 people [47]. In IBD, eosinophils (eos) typically represent a small percentage of infiltrating leukocytes [48]. Patients with IBD and IBS-D harbor significantly increased mucosal eosinophils and appear to respond to a hypoallergenic diet and budesonide therapy [49]. EGID is characterized by increased mucosal eosinophils, distributed in sheets that can involve the mucosa, muscle layer or serosa. Patient presentation ranges from vague abdominal symptoms to serious complications including mucosal ulceration, intestinal obstruction, pyloric stenosis, strictures, protein losing enteropathy, bowel perforation, anemia, and ascites. EGID limited to the mucosa can lead to diarrhea, abdominal pain and signs of malabsorption or protein losing enteropathy. The muscular form is characterized by intestinal strictures with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting due to intestinal obstruction. The serosal form can present with an eosinophilic rich ascites and peritonitis [50]. Other clinical features include peripheral eosinophilia, which is present in over 70% of patients with eosinophilic enteritis and during flares. IgE levels can also be elevated in more than 50% of patients with EGID. There are no clear guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of non-EoE EGIDs. In general, ≥ 30 eos in ≥ 5 high power field (hpf) is considered positive for gastric biopsies and ≥ 30 eos in 3 hpf is considered positive for duodenal biopsy. A minimum of 12 biopsies should be collected per subject during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), 4 in each the gastric antrum, gastric body and duodenum [51]. Eosinophilia secondary to more common conditions such as parasitic infections, food hypersensitivies, drug reactions, and malignancies must be excluded. Imaging should be obtained if there are obstructive symptoms or peritoneal signs or suspicion of ascites. Treatment is based on evidence from case reports and small case series. First line therapy includes empirical food elimination diets and systemic glucocorticoids. Most case series report good efficacy with corticosteroids, with clinical remission obtain in 50–90% of patients with eosinophilic enteritis. Treatment should be started at 0.5 to 1 mg/kg for a few weeks followed by a tapering dose over a 6–8 week period [52]. For those who become corticosteroid dependent, budesonide or azathioprine can be used. Relapsing or refractory disease may respond to immunosuppressive agents and biologic agents. Potential role of monoclonal antibodies (e.g., dupilumab) is the subject of active research in IBD-IBS overlap.
Mast Cell Activation Syndrome
Mast cell activation disorders include a spectrum of conditions including cutaneous or systemic mastocytosis, associated with clonal expansion of mast cells (MC) and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), a non-clonal condition defined by episodic and/or chronic symptoms of MC activation with elevation of MC mediators [53]. Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) is a common but underrecognized cause of GI symptoms and can be mistaken as functional GI disorders. The prevalence of MCAS in IBD is unknown and there is limited data on the role for mast cells in IBD [54]. In one study, there was no significant difference in the number of intra-mucosal mast cells (MCs) in the colon among IBS, IBD, and normal control groups [55]. Gelbmann et al. described accumulation of mast cells in strictures of patients with CD, suggesting a role in fibrosis [56]. Nevertheless, MCAS is a common and underrecognized cause of GI symptoms that may overlap with IBD. The defining symptom characteristics of MCAS include involvement of the skin, airway, and GI tract. Common skin manifestations include flushing, hives, and pruritis. Airway or nasal passageway symptoms include throat scratching, chest tightness, and rhinitis. Common GI manifestations include nausea, heartburn, abdominal bloating, abdominal pain, and altered bowel movements [57]. When MCs are located within the muscular layer of the GI tract, they can lead to symptoms of GI dysmotility such as constipation [58]. MCAS should be considered in patients who are not responding to conventional IBS therapies who also have a personal history or family history of atopy including allergic rhinitis, asthma, and eczema. MCAS is associated with other syndromes including hypermobile EDS and POTS [59, 60]. Diagnosis for MCAS include the major criteria of characteristic MC activation symptoms in 2 or more systems plus one or more minor criteria. Minor criteria include (1) elevation in blood and/or urine tests relatively specific to MC, (2) clinical improvement with MC-directed medical therapy, and (3) ≥ 20 MCs per HPF in extracutaneous tissue (luminal GI tract or bladder biopsies) [57]. Initial diagnostic testing includes serum tryptase and chromogranin A, plasma prostaglandin D2 and histamine and urine testing with 24 h and/or random urine N-methylhistamine, leukotriene E4 and 2,3-dinor-11-beta-prostaglandin-F2-alpha. In general, testing within 1–6 h of an acute MC activation attack and prior to initiation of MCAS therapy is helpful. Negative serologies do not exclude a diagnosis and serum tryptase is only elevated in 15% of patients with MCAS [61, 62]. When serum tryptase is > 20 ng/mL, work-up for systemic mastocytosis is indicated. Treatment involves trigger avoidance (i.e., stress, heat, and alcohol), dietary interventions with low histamine and gluten free diet and medications to control MC mediator production and action [57]. First line pharmacologic agents include non-sedating H1 histamine receptor antagonist and H2 histamine receptor antagonist once to twice per day. If this only provides partial relief, second line pharmacologic therapy includes montelukast, a leukotriene receptor antagonist twice daily and/or oral cromolyn sodium, an MC stabilizer. Cromolyn sodium can be introduced earlier for patients with severe GI symptoms. The starting dose is 100 mg four times taking and should be taken 30 min before meals and at bedtime. Third line therapy includes ketotifen, a second generation H1 antagonists with anti-inflammatory effects. This can be found at compounding pharmacies and usual dosing is 1–4 mg BID. A multidisciplinary approach including an allergist and hematologist may be required in optimal management of patients with MCAS.
Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Nonceliac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) is a condition where gluten ingestion leads to intestinal and extra-intestinal symptoms. The reported prevalence of NCGS and wheat sensitivity ranges between 0.49 and 14.9% [63]. The pathophysiology of NCGS is not fully understood, however NCGS seems to be triggered by activation of the innate immune system rather than the adaptive immune system. Markers such as toll-like receptor 2 have been shown to be increased, which is consistent with innate immunity, whereas makers of adaptive immunity such as interleukin-6 and interleukin-21 are not expressed at high levels [64] . Unlike Celiac disease, NCGS is not associated with small bowel enteropathy or abnormal celiac serologies [65]. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, irregular bowel movements, fatigue, joint pain, migraines, and brain fog. The gold standard diagnosis is a placebo controlled crossover challenge, which has been used in clinical trials, but is impractical in clinical settings [66]. In general, clinical symptoms with a gluten containing diet in the absence of serologic or histologic findings of Celiac disease or wheat allergy are suggestive of NCGS. Despite not having Celiac disease or a wheat allergy, patients with NCGS improve symptomatically with a gluten free diet.
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Hypermobile Ehlers Danlos syndrome (hEDS) is a multi-system and heritable disorder of connective tissue characterized by joint hypermobility, GI symptoms, autonomic dysfunction, chronic pain syndromes, and structural abnormalities such as visceroptosis and pelvic organ prolapse and urinary dysfunction [67]. In one cohort, joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS)/hEDS was present in 32% of patients with CD (8 of 25) compared to 21% of patients with UC (8 of 38) [68]. Another study found that joint hypermobility, using the Beighton score, is observed more frequently in CD (n = 37, 70.7%) compared to patients with UC (n = 10, 35.7%), (P = 0.0063) and healthy controls (n = 17, 25.4%) (P < 0.001) [69]. In a retrospective review of patients with EDS, of which 71% had JHS, 55% complained of GI symptoms with the most common symptoms being abdominal pain (56%), nausea (44%), constipation (42%), heartburn (38%), IBS-like symptoms (30%), vomiting (25%), and diarrhea (23%) [70]. The increased connective tissue laxity and weakness also results in multiple structural abnormalities including hiatal hernia, visceroptosis, pelvic organ prolapse, and colon redundancy [71]. The diagnosis of hEDS is made clinically and there is no genetic etiology to test for. A detailed criteria has been outlined for hEDS diagnosis and includes presence of (1) generalized joint hypermobility, (2) systemic manifestations or a generalized connective tissue disorder, and (3) exclusion of unusual skin fragility, other heritable and acquired connective tissue disorders and alternative diagnosis that include joint hypermobility [72]. Generalized joint hypermobility can be determined by a Beighton score of ≥ 5 points out of 9 for pubertal men and women up to age 50 and ≥ 4 for those > 50 years of age (Table 1). hEDS can be challenging to manage and should involve a multidisciplinary approach. For GI manifestations, patients with defecatory complaints should be referred for anorectal physiological assessment and considered for biofeedback and/or pelvic floor therapy. Promotility agents can be helpful in patients with hEDS with GI dysmotility.
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a disorder of the autonomic nervous system characterized by orthostatic intolerance. POTS is more frequent in women (female:male ratio 4.5:1) and most cases occur between ages 15 and 25 [73]. POTS can often overlap with EDS and MCAS [74]. The prevalence of POTS in IBD is unknown. The pathophysiology of POTS is multifactorial and includes, impaired sympathetic vasoconstriction, hyperadrenergic states, hypovolemia, and physical deconditioning [73]. In adults, the condition is defined as an elevation of the heart rate of at least 30 beats per minute (bpm) within 10 min after standing upright, or a heart rate ≥ 120 bpm after standing in the absence of orthostatic hypotension [75]. In addition to orthostatic tachycardia, patients may display symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion (lightheadedness, blurred vision, cognitive difficulties, weakness) and sympathetic hyperactivity (palpitations, chest pain, and tremulousness). Independent of EDS, POTS is associated with GI symptoms due to dysmotility of the stomach, small bowel, and colon [76, 77]. Common GI symptoms include, nausea, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain [78]. Additionally, patients with POTS and GI symptoms can have abnormal, either rapid or slow gastric emptying, on scintigraphic evaluation [76]. The evaluation and management of POTS should be multidisciplinary. The basic evaluation should include cardiac evaluation to exclude other causes of inappropriate sinus tachycardia, autonomic reflex testing (i.e., tilt table test) and measurement of supine and standing plasma catecholamine levels. Management includes avoidance of exacerbating factors (i.e., heat exposure, physical exertion, heavy meals, prolonged recumbency, medications (diuretics, vasodilators, sympathomimetics), maintenance of intravascular volume with increased water and sodium intake, physical reconditioning and pharmacotherapy (fludrocortisone, midodrine, beta blockers, and/or pyridostigmine). The added benefit of pyridostigmine is that it may potentiate muscarinic receptor activation in the GI tract and has promotility features that may improve gastric emptying and constipation symptoms. Additionally, as a cholinesterase inhibitor, it may potentiate vagal effects.
Intra-abdominal Adhesions
Intra-abdominal adhesions are fibrous bands of scar tissue that form between loops of bowel and adjacent structures [79]. They form primarily after abdominal surgery but can also form as a result of endometriosis, inflammation or radiation therapy. While the majority of post-operative adhesions are asymptomatic, symptomatic adhesions can present with chronic bloating, abdominal cramping, altered bowel habits, chronic abdominal pain, and nausea. Other clinical features include bowel obstruction, SIBO, female infertility, and dyspareunia. Intra-abdominal adhesions are relevant to patients with IBD because the surgeries that carry the highest risk of adhesion related hospital readmissions are open total proctocolectomy (15.4%), total colectomy (8.8%), and ileostomy (10.6%) [80]. Additionally, Crohn’s disease, proctocolectomy, total colectomy, ileostomy, age younger than 60 years old, procedures involving the small intestine, colon are all risk factors for adhesion formation. Outside of a bowel obstruction where a clear transition point can be identified, diagnosis using imaging is challenging. An X-ray barium study with small bowel follow through may be able to suggest adhesions when acute angulation(s) of the bowels are identified. When clinical suspicion for symptomatic adhesions is high, a laparoscopy can be both diagnostic and therapeutic. Non-invasive treatment options include manual physical therapy as this may be beneficial for both breaking apart adhesions and preventing adhesion formation [81]. Thus far, only in vivo studies on rats have shown manual therapy to attenuate formation of adhesions [82]. In a systematic review on effects of soft tissue mobilization on surgical and non-surgical abdominal adhesion related symptoms, all of the studies that used pain as an outcome reported decreased pain after treatment. There were also improvements seen in infertility as well [83]. Fiber supplementation, high fiber diets, and stimulant type anti-constipation agents should be avoided because they can worsen symptoms. A low residue diet is better tolerated in patients with symptomatic adhesions. Lastly, a trial of anti-spasmodic medications such as peppermint based products, dicyclomine or hyoscyamine may also be helpful [84].
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is an inflammatory disease characterized by ectopic endometrial tissue at extrauterine sites [85]. Endometriosis should be part of the differential diagnosis for abdominal pain in pre-menopausal women. In a systematic review, epidemiological studies found a positive association between endometriosis and IBD. The proportion of IBD in patients with endometriosis varied from 2 to 3.4%, compared to 0–1% of the control group [85]. A large nationwide Danish cohort study reported a 50% increase in the risk of IBD in women with endometriosis in comparison with women in the general population [86, 87]. In a nationwide Danish cohort study, women with surgically verified endometriosis had an increased risk of IBD overall, UC (standardized incidence ration (SIR) = 1.8; 95% CI 1.4 to 2.3) and CD (SIR = 1.7; 95% CI 1.2 to 2.5) [86]. The most common site of extragenital endometriosis are the GI and urinary tracts. GI endometriosis is found in 3.8 to 37% of endometriosis with most being found on the rectosigmoid, followed by the rectum, ileum, appendix and cecum [88, 89]. GI symptoms are 8 times more common in women with endometriosis compared to those without disease [90, 91]. Endometriosis may even present with IBD-like symptoms of chronic abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, fecal urgency, and rectal bleeding. Common gastrointestinal symptoms in endometriosis include chronic abdominal pain, constipation, bloating, flatulence, fecal urgency, painful defecation, and rectal bleeding. Other symptoms of endometriosis include dysmenorrhea, lower abdominal or pelvic pain, deep dyspareunia, and infertility [92]. The abdominal and pelvic pain can be acyclical. In terms of diagnosis, there are no accurate biomarkers for endometriosis. Physical exam may demonstrate pain and tenderness on bimanual examination or on rectal examination. Imaging plays a key role in evaluation of endometriosis. If there is high clinical suspicion a transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) can diagnose endometriosis with high specificity (92–100%) and sensitivity (71–98%) [92, 93]. TVUS is the first line imaging modality, however ultrasound is limited in detecting small (< 1 cm) or superficial peritoneal lesions and for assessing depth of infiltration. MRI pelvis with contrast is able to detect superficial peritoneal and deep infiltrating lesions. Laparoscopic surgical evaluation is the gold standard for detection and diagnosis of endometriosis. Treatment includes hormonal therapies, surgical removal of endometrial implants, and pain management [94].
Rectal Evacuation Disorders
Rectal evacuation disorders consist of both functional and structural disorders than can cause inability to evacuate stool from the rectum. Functional defecatory disorders are characterized by paradoxical contraction or inadequate relaxation of pelvic floor muscles (i.e., dyssynergic defecation) and/or inadequate propulsive force during attempted defecation [95]. Dyssynergic defecation (DD) is highly prevalent in patients with IBD and defecatory symptoms and is responsive to biofeedback therapy [96, 97]. In a systematic review and meta-analysis, DD in patients without IPAA (n = 182) ranged from 45 to 97% and in those with IPAA (n = 260) ranged from 24 to 75%. The prevalence of DD in patients with IPAA with and without pouchitis ranged from 17 to 67% and 29% to 50%, respectively. In terms of proposed pathophysiology, persistent defecatory symptoms are thought to be related to long-term neuromuscular sequelae of prolonged inflammation or surgical complications. Additionally, maladaptive behaviors to cope with painful and frequent defecation may contribute [98]. DD can present with a wide array of symptoms including constipation, alternating bowel habits, fecal incontinence, diarrhea, and rectal discomfort [96]. The evaluation for DD includes a digital rectal examination and anorectal manometry with balloon expulsion test. Unfortunately, there are no validated diagnostic criteria for DD in IBD. Rome IV has a suggested diagnostic criteria, however this requires patients to meet the diagnostic criteria for functional constipation and/or constipation predominant IBS, however DD in IBD presents with a wide array of symptoms aside from constipation. Additionally, data on what constitutes abnormal and normal values in IPAA on ARM and BET is lacking and altered post-surgical anatomy can make interpretation more challenging [98, 99]. Biofeedback is the first line therapy for DD and involves interactive retraining of the pelvic floor muscles and anal sphincters to restore a normal pattern of defecation. Despite the variability in the definition of DD used in IBD research, biofeedback has been shown to be effective in IBD [96, 97]. In a systematic review and meta-analysis, there was a good response rate to biofeedback in both IPAA and non-IPAA patients. The pooled response rate to biofeedback therapy in patients without IPAA was 70% (95% CI, 55–84%; I2 = 95%; P < 0.01), and was 86% (95% CI, 67–98%; I2 = 61%; P = 0.05) in those with IPAA [97]. Additionally, biofeedback has been shown to improve quality of life and reduced GI-related health care resource utilization [96]. While DD is prevalent in IBD, it is important to recognize that structural issues can also explain persistent defecatory symptoms. Examples of structural rectal evacuation disorders include enterocele, rectocele, rectal prolapse, pelvic organ prolapse, intussusception, and strictures. These issues can be identified by MR or XR defecography, which provide a dynamic assessment of defecatory function. Depending on the severity of these abnormalities, the patient may benefit from biofeedback or need evaluation with colorectal surgeon and/or urogynecology. Defecography is also a useful diagnostic test for evaluating functional defecatory disorders of the pouch and can provide valuable information regarding pouch emptying dynamics and also assess for underlying structural abnormalities [100].
Conclusion
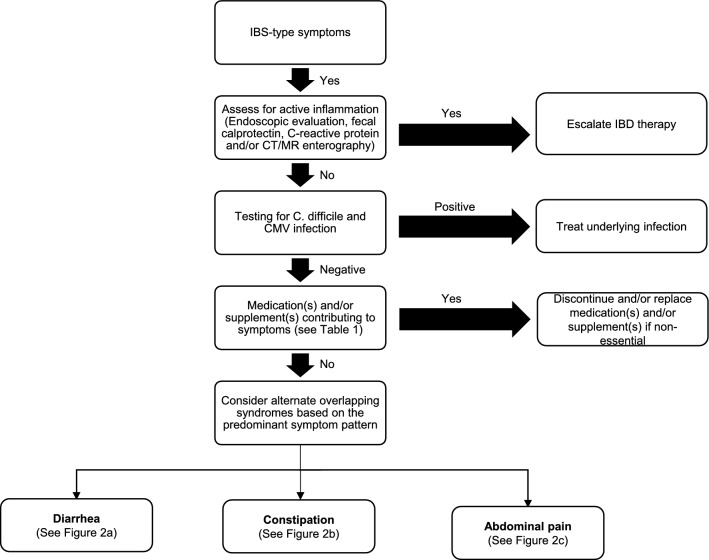
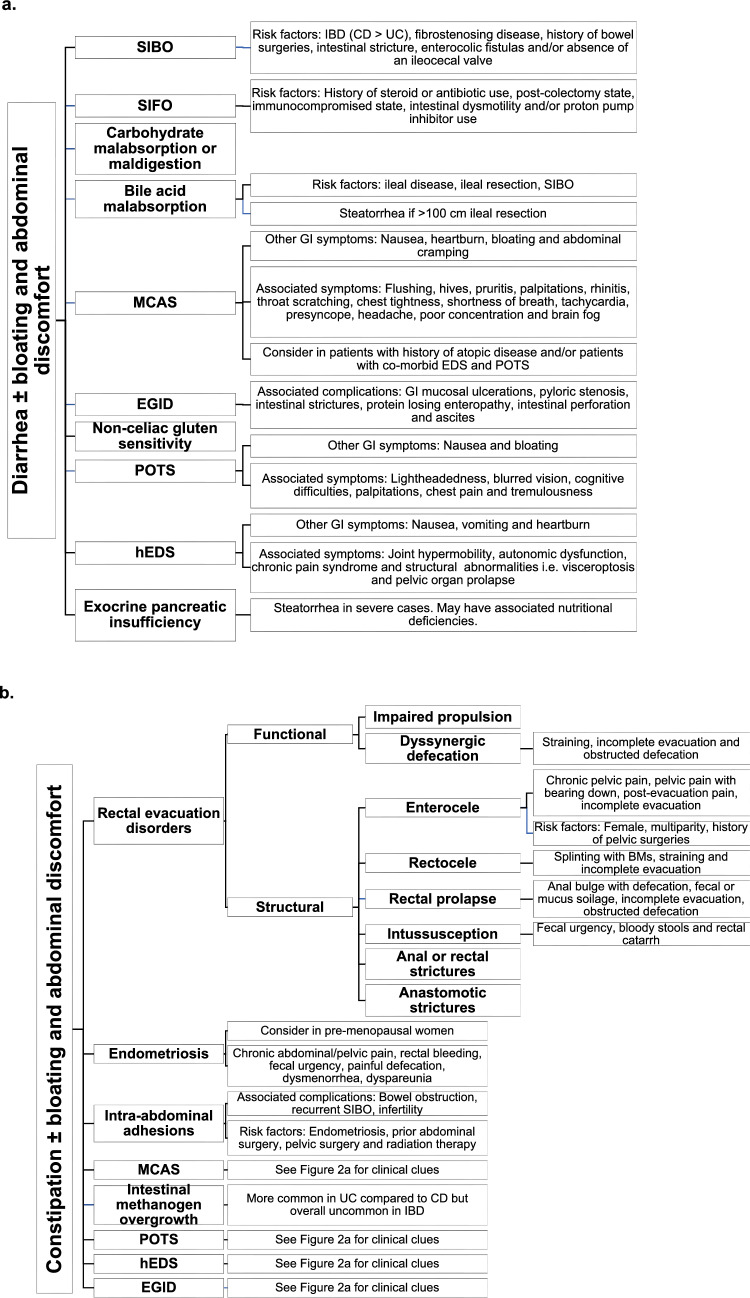
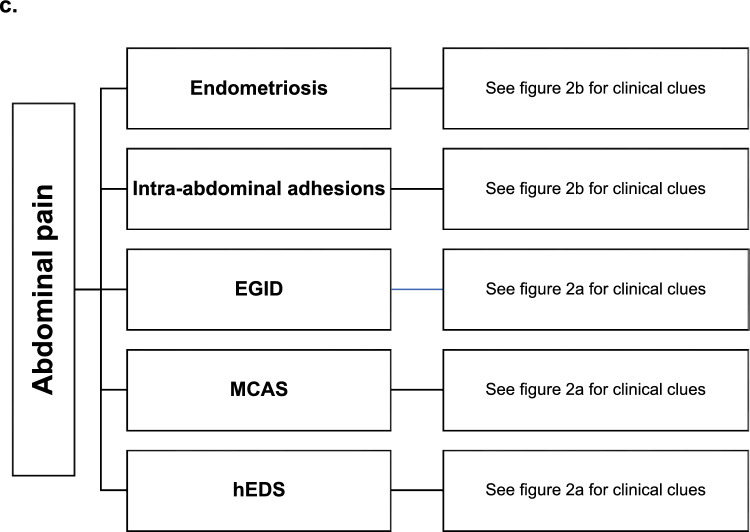
Patients with IBD in apparent clinical remission who present with IBS-like symptoms pose a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge for clinicians. Persistent GI symptoms can be attributed to a wide range of etiologies including overlapping gastrointestinal conditions or other systemic syndromes with GI manifestations. Several overlapping etiologies can also co-exist at the same time, such as SIBO and SIFO, BAM and SIBO with EDS, POTS and MCAS. After ruling out inflammation and infectious etiologies (Fig. 1), medication and/or supplement related side effects and adverse drug reactions should be explored (Table 1). For example, some patients with UC receiving 5 amino salicylic acid (5-ASA) containing therapies can develop an acute 5-ASA intolerance syndrome characterized by fever, diarrhea, and abdominal pain [101]. A detailed history and physical examination, can guide evaluation, minimize unnecessary or redundant testing and prevent delays in diagnosis (Fig. 1). The differential diagnosis can be narrowed down based on key elements of the patient history, particularly the predominant symptom pattern: diarrhea, constipation, and/or abdominal pain (Fig. 2), associated clinical signs and symptoms and predisposing conditions. Despite the high prevalence of patients with IBD and with persistent unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms, evidence for the prevalence, diagnosis and treatment of motility disorders and other overlapping gastrointestinal and systemic conditions in this population is critically lacking. Further studies are needed to address the current gaps in knowledge.
Fig. 1.
Initial evaluation of IBS-like symptoms in quiescent IBD
Fig. 2.
a Differential diagnosis and clinical clues for diarrhea predominant symptoms in quiescent IBD. b. Differential diagnosis and clinical clues for constipation predominant symptoms in quiescent IBD. c. Differential diagnosis and clinical clues for abdominal pain in quiescent IBD.CD Crohn’s disease; UC ulcerative colitis; SIBO small intestinal bacterial overgrowth; SIFO small intestinal fungal overgrowth; MCAS mast cell activation syndrome; EGID eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders; POTS postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome; hEDS hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome; cm centimeter; BMs bowel movements
Author’s contribution
JL wrote the manuscript. AR contributed to project conception and manuscript revision. All authors have approved the final draft submitted.
Funding
The John and Geraldine Cusenza Family Foundation. Open access funding provided by SCELC, Statewide California Electronic Library Consortium.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
Jane Lim: No conflicts of interest to disclose. Ali Rezaie: Consultant/speaker for and has received grant support from Bausch Health. He also has equity in Gemelli Biotech, with which Cedars-Sinai Medical Center has licensing agreements.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Fairbrass KM, Costantino SJ, Gracie DJ, Ford AC. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome-type symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in remission: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abdalla MI, Sandler RS, Kappelman MD, Martin CF, Chen W, Anton K, et al. Prevalence and impact of inflammatory bowel disease-irritable bowel syndrome on patient-reported outcomes in CCFA partners. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017;23:325–331. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000001017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pimentel M, Saad RJ, Long MD, Rao SSC. ACG clinical guideline: small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:165–178. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee JM, Lee KM, Chung YY, Lee YW, Kim DB, Sung HJ, et al. Clinical significance of the glucose breath test in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30:990–994. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wanzl J, Grohl K, Kafel A, Nagl S, Muzalyova A, Golder SK, et al. Impact of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and other gastrointestinal disorders-a retrospective analysis in a tertiary single center and review of the literature. J Clin Med. 2023 doi: 10.3390/jcm12030935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ghoshal UC, Yadav A, Fatima B, Agrahari AP, Misra A. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a case-control study. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2022;41:96–103. doi: 10.1007/s12664-021-01211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shah A, Morrison M, Burger D, Martin N, Rich J, Jones M, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49:624–635. doi: 10.1111/apt.15133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rezaie A, Buresi M, Lembo A, Lin H, McCallum R, Rao S, et al. Hydrogen and methane-based breath testing in gastrointestinal disorders: the North American consensus. The American journal of gastroenterology. 2017;112:775–784. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2017.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cangemi DJ, Lacy BE, Wise J. Diagnosing small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: a comparison of lactulose breath tests to small bowel aspirates. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:2042–2050. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06484-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gu P, Patel D, Lakhoo K, Ko J, Liu X, Chang B, et al. Breath Test Gas patterns in inflammatory bowel disease with concomitant irritable bowel syndrome-like symptoms: a controlled large-scale database linkage analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65:2388–2396. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05967-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pimentel M, Constantino T, Kong Y, Bajwa M, Rezaei A, Park S. A 14-day elemental diet is highly effective in normalizing the lactulose breath test. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49:73–77. doi: 10.1023/B:DDAS.0000011605.43979.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ghoshal UC, Sachdeva S, Ghoshal U, Misra A, Puri AS, Pratap N, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus on small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in gastrointestinal disorders: an initiative of the Indian neurogastroenterology and motility association. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2022;41:483–507. doi: 10.1007/s12664-022-01292-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pimentel M, Morales W, Lezcano S, Sun-Chuan D, Low K, Yang J. Low-dose nocturnal tegaserod or erythromycin delays symptom recurrence after treatment of irritable bowel syndrome based on presumed bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2009;5:435–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gandhi A, Shah A, Jones MP, Koloski N, Talley NJ, Morrison M, et al. Methane positive small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes. 2021;13:1933313. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1933313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pimentel M, Lin HC, Enayati P, van den Burg B, Lee HR, Chen JH, et al. Methane, a gas produced by enteric bacteria, slows intestinal transit and augments small intestinal contractile activity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G1089–G1095. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00574.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Takakura W, Pimentel M, Rao S, Villanueva-Millan MJ, Chang C, Morales W, et al. A single fasting exhaled methane level correlates with fecal methanogen load, clinical symptoms and accurately detects intestinal methanogen overgrowth. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:470–477. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dridi B, Fardeau ML, Ollivier B, Raoult D, Drancourt M. The antimicrobial resistance pattern of cultured human methanogens reflects the unique phylogenetic position of archaea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(9):2038–2044. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Low K, Hwang L, Hua J, Zhu A, Morales W, Pimentel M. A combination of rifaximin and neomycin is most effective in treating irritable bowel syndrome patients with methane on lactulose breath test. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44:547–550. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181c64c90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Erdogan A, Rao SS. Small intestinal fungal overgrowth. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2015;17:16. doi: 10.1007/s11894-015-0436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schulze J, Sonnenborn U. Yeasts in the gut: from commensals to infectious agents. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009;106:837–842. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2009.0837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rao SSC, Tan G, Abdulla H, Yu S, Larion S, Leelasinjaroen P. Does colectomy predispose to small intestinal bacterial (SIBO) and fungal overgrowth (SIFO)? Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018;9:146. doi: 10.1038/s41424-018-0011-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liu S, Zhao W, Lan P, Mou X. The microbiome in inflammatory bowel diseases: from pathogenesis to therapy. Protein Cell. 2021;12:331–345. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00745-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sokol H, Leducq V, Aschard H, Pham HP, Jegou S, Landman C, et al. Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut. 2017;66:1039–1048. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li XV, Leonardi I, Putzel GG, Semon A, Fiers WD, Kusakabe T, et al. Immune regulation by fungal strain diversity in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2022;603:672–678. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04502-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Iliev ID, Funari VA, Taylor KD, Nguyen Q, Reyes CN, Strom SP, et al. Interactions between commensal fungi and the C-type lectin receptor dectin-1 influence colitis. Science. 2012;336:1314–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.1221789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ferwerda B, Ferwerda G, Plantinga TS, Willment JA, van Spriel AB, Venselaar H, et al. Human dectin-1 deficiency and mucocutaneous fungal infections. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1760–1767. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0901053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Glocker EO, Hennigs A, Nabavi M, Schaffer AA, Woellner C, Salzer U, et al. A homozygous CARD9 mutation in a family with susceptibility to fungal infections. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1727–1735. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Taylor PR, Tsoni SV, Willment JA, Dennehy KM, Rosas M, Findon H, et al. Dectin-1 is required for beta-glucan recognition and control of fungal infection. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:31–38. doi: 10.1038/ni1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.McGovern DP, Gardet A, Torkvist L, Goyette P, Essers J, Taylor KD, et al. Genome-wide association identifies multiple ulcerative colitis susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010;42:332–337. doi: 10.1038/ng.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Franke A, Balschun T, Sina C, Ellinghaus D, Hasler R, Mayr G, et al. Genome-wide association study for ulcerative colitis identifies risk loci at 7q22 and 22q13 (IL17REL) Nat Genet. 2010;42:292–294. doi: 10.1038/ng.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bogatyrev SR, Leite G, Pimentel M, Mathur R, Hosseini A, Rashid M, et al. Increased fungal loads detected in duodenal aspirates using multiplexed digital polymerase chainr eaction are associated with more severe upper respiratory symptoms and abdominal pain. [Abstract]. In press 2023.
- 32.Friedman M, Ramsay DB, Borum ML. An unusual case report of small bowel Candida overgrowth as a cause of diarrhea and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:679–680. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9604-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Allegretti JR, Kassam Z, Chan WW. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: should screening be included in the pre-fecal microbiota transplantation evaluation? Dig Dis Sci. 2018;63:193–197. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4864-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Camilleri M. Bile Acid diarrhea: prevalence, pathogenesis, and therapy. Gut Liver. 2015;9:332–339. doi: 10.5009/gnl14397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Min YW, Rezaie A, Pimentel M. Bile acid and gut microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022;28:549–561. doi: 10.5056/jnm22129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vijayvargiya P, Camilleri M. Update on bile acid malabsorption: finally ready for prime time? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2018;20:10. doi: 10.1007/s11894-018-0615-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sauter GH, Munzing W, von Ritter C, Paumgartner G. Bile acid malabsorption as a cause of chronic diarrhea: diagnostic value of 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one in serum. Dig Dis Sci. 1999;44:14–19. doi: 10.1023/A:1026681512303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Barrett JS, Irving PM, Shepherd SJ, Muir JG, Gibson PR. Comparison of the prevalence of fructose and lactose malabsorption across chronic intestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;30:165–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Burke M. Carbohydrate intolerance and disaccharidase measurement - a mini-review. Clin Biochem Rev. 2019;40:167–174. doi: 10.33176/AACB-19-00025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ramos LR, Sachar DB, DiMaio CJ, Colombel JF, Torres J. Inflammatory bowel disease and pancreatitis: a review. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10:95–104. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Maconi G, Dominici R, Molteni M, Ardizzone S, Bosani M, Ferrara E, et al. Prevalence of pancreatic insufficiency in inflammatory bowel diseases Assessment by fecal elastase-1. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:262–70. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9852-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fousekis FS, Theopistos VI, Katsanos KH, Christodoulou DK. Pancreatic involvement in inflammatory bowel disease: a review. J Clin Med Res. 2018;10:743–751. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3561w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Massironi S, Fanetti I, Vigano C, Pirola L, Fichera M, Cristoferi L, et al. Systematic review-pancreatic involvement in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55:1478–1491. doi: 10.1111/apt.16949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lohr JM, Dominguez-Munoz E, Rosendahl J, Besselink M, Mayerle J, Lerch MM, et al. United European gastroenterology evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of chronic pancreatitis (HaPanEU) United European Gastroenterol J. 2017;5:153–199. doi: 10.1177/2050640616684695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dominguez-Munoz JE. Diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2018;34:349–354. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Abonia JP, Alexander JA, Arva NC, Atkins D, et al. International consensus recommendations for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease nomenclature. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:2474–2484 e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.02.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Walker MM, Potter M, Talley NJ. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis and other eosinophilic gut diseases distal to the oesophagus. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:271–280. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Walsh RE, Gaginella TS. The eosinophil in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991;26:1217–1224. doi: 10.3109/00365529108998617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tozlu M, Cash B, Younes M, Ertan A. Dilemma in post-IBD patients with IBS-D symptoms: a 2020 overview. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15:5–8. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1829469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Klein NC, Hargrove RL, Sleisenger MH, Jeffries GH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 1970;49:299–319. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197007000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Rothenberg ME, Hirano I, Chehade M, Peterson KA, et al. Determination of biopsy yield that optimally detects eosinophilic gastritis and/or duodenitis in a randomized trial of lirentelimab. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:535–545 e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Abou Rached A, El Hajj W. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: Approach to diagnosis and management. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016;7:513–523. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Castells M, Butterfield J. Mast cell activation syndrome and mastocytosis: initial treatment options and long-term management. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7:1097–1106. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2019.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Boeckxstaens G. Mast cells and inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015;25:45–49. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2015.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fan L, Wong M, Fan XS, Hong Y, Sun K, Jiang C, et al. Quantitative analysis of intramucosal mast cells in irritable bowel syndrome: a comparison with inflammatory bowel disease in remission. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021;55:244–249. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gelbmann CM, Mestermann S, Gross V, Kollinger M, Scholmerich J, Falk W. Strictures in Crohn's disease are characterised by an accumulation of mast cells colocalised with laminin but not with fibronectin or vitronectin. Gut. 1999;45:210–217. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.2.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Weinstock LB, Pace LA, Rezaie A, Afrin LB, Molderings GJ. Mast cell activation syndrome: a primer for the gastroenterologist. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:965–982. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bassotti G, Villanacci V, Nascimbeni R, Cadei M, Manenti S, Sabatino G, et al. Colonic mast cells in controls and slow transit constipation patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:92–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Beckers AB, Keszthelyi D, Fikree A, Vork L, Masclee A, Farmer AD, et al. Gastrointestinal disorders in joint hypermobility syndrome/Ehlers-Danlos syndrome hypermobility type: a review for the gastroenterologist. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 doi: 10.1111/nmo.13013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.DiBaise JK, Harris LA, Goodman B. Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and the GI tract: a primer for the gastroenterologist. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:1458–1467. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Afrin LB, Fox RW, Zito SL, Choe L, Glover SC. Successful targeted treatment of mast cell activation syndrome with tofacitinib. Eur J Haematol. 2017;99:190–193. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Molderings GJ, Brettner S, Homann J, Afrin LB. Mast cell activation disease: a concise practical guide for diagnostic workup and therapeutic options. J Hematol Oncol. 2011;4:10. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-4-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cardenas-Torres FI, Cabrera-Chavez F, Figueroa-Salcido OG, Ontiveros N. Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: an update. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 doi: 10.3390/medicina57060526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sapone A, Lammers KM, Casolaro V, Cammarota M, Giuliano MT, De Rosa M, et al. Divergence of gut permeability and mucosal immune gene expression in two gluten-associated conditions: celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. BMC Med. 2011;9:23. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Naik RD, Seidner DL, Adams DW. Nutritional consideration in celiac disease and nonceliac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2018;47:139–154. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2017.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Volta U, Caio G, De Giorgio R, Henriksen C, Skodje G, Lundin KE. Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: a work-in-progress entity in the spectrum of wheat-related disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;29:477–491. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2015.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Mastoroudes H, Giarenis I, Cardozo L, Srikrishna S, Vella M, Robinson D, et al. Prolapse and sexual function in women with benign joint hypermobility syndrome. BJOG. 2013;120:187–192. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.12082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Fikree A, Aktar R, Grahame R, Hakim AJ, Morris JK, Knowles CH, et al. Functional gastrointestinal disorders are associated with the joint hypermobility syndrome in secondary care: a case-control study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27:569–579. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Vounotrypidis P, Efremidou E, Zezos P, Pitiakoudis M, Maltezos E, Lyratzopoulos N, et al. Prevalence of joint hypermobility and patterns of articular manifestations in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2009;2009:924138. doi: 10.1155/2009/924138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zarate N, Farmer AD, Grahame R, Mohammed SD, Knowles CH, Scott SM, et al. Unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms and joint hypermobility: is connective tissue the missing link? Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;22:252–e78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Thwaites PA, Gibson PR, Burgell RE. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: what the gastroenterologist needs to know. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;37:1693–709. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Malfait F, Francomano C, Byers P, Belmont J, Berglund B, Black J, et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017;175:8–26. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Benarroch EE. Postural tachycardia syndrome: a heterogeneous and multifactorial disorder. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:1214–25. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.08.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kohn A, Chang C. The relationship between hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (hEDS), postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020;58:273–97. doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08755-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, Benditt DG, Benarroch E, Biaggioni I, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res. 2011;21:69–72. doi: 10.1007/s10286-011-0119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Loavenbruck A, Iturrino J, Singer W, Sletten DM, Low PA, Zinsmeister AR, et al. Disturbances of gastrointestinal transit and autonomic functions in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27:92–8. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Wang LB, Culbertson CJ, Deb A, Morgenshtern K, Huang H, Hohler AD. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2015;359:193–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.10.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Thieben MJ, Sandroni P, Sletten DM, Benrud-Larson LM, Fealey RD, Vernino S, et al. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: the Mayo clinic experience. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007;82:308–13. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)61027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Moris D, Chakedis J, Rahnemai-Azar AA, Wilson A, Hennessy MM, Athanasiou A, et al. Postoperative abdominal adhesions: clinical significance and advances in prevention and management. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017;21:1713–22. doi: 10.1007/s11605-017-3488-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Parker MC, Wilson MS, Menzies D, Sunderland G, Clark DN, Knight AD, et al. The SCAR-3 study: 5-year adhesion-related readmission risk following lower abdominal surgical procedures. Colorectal Dis. 2005;7:551–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2005.00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Pichetshote N, Rezaie A. Bloating and abdominal distension: exploring hidden depths and insights. Currrent Treatment Options in Gastroenterology. 2020;18:337–52. doi: 10.1007/s11938-020-00288-w. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bove GM, Chapelle SL, Hanlon KE, Diamond MP, Mokler DJ. Attenuation of postoperative adhesions using a modeled manual therapy. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0178407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wasserman JB, Copeland M, Upp M, Abraham K. Effect of soft tissue mobilization techniques on adhesion-related pain and function in the abdomen: a systematic review. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2019;23:262–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2018.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Tabibian N, Swehli E, Boyd A, Umbreen A, Tabibian JH. Abdominal adhesions: a practical review of an often overlooked entity. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2017;15:9–13. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Chiaffarino F, Cipriani S, Ricci E, Roncella E, Mauri PA, Parazzini F, et al. Endometriosis and inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020;252:246–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.06.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Jess T, Frisch M, Jorgensen KT, Pedersen BV, Nielsen NM. Increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease in women with endometriosis: a nationwide Danish cohort study. Gut. 2012;61:1279–83. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.de Silva PS, Hansen HH, Wehberg S, Friedman S, Norgard BM. Risk of ectopic pregnancy in women with inflammatory bowel disease: a 22-year nationwide cohort study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16:83–89 e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.06.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Young S, Burns MK, DiFrancesco L, Nezhat A, Nezhat C. Diagnostic and treatment guidelines for gastrointestinal and genitourinary endometriosis. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2017;18:200–9. doi: 10.4274/jtgga.2017.0143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Veeraswamy A, Lewis M, Mann A, Kotikela S, Hajhosseini B, Nezhat C. Extragenital endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:449–66. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0b013e3181e0ea6e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Maroun P, Cooper MJ, Reid GD, Keirse MJ. Relevance of gastrointestinal symptoms in endometriosis. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;49:411–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2009.01030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Schink M, Konturek PC, Herbert SL, Renner SP, Burghaus S, Blum S, et al. Different nutrient intake and prevalence of gastrointestinal comorbidities in women with endometriosis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;70:10–26402. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2019.2.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yu V, McHenry N, Proctor S, Wolf J, Nee J. Gastroenterologist primer: endometriosis for gastroenterologists. Dig Dis Sci. 2023 doi: 10.1007/s10620-022-07674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Hudelist G, English J, Thomas AE, Tinelli A, Singer CF, Keckstein J. Diagnostic accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound for non-invasive diagnosis of bowel endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011;37:257–63. doi: 10.1002/uog.8858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Becker CM, Bokor A, Heikinheimo O, Horne A, Jansen F, Kiesel L, et al. ESHRE guideline: endometriosis. Hum Reprod Open. 2022;2022:hoac009. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoac009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Rao SS, Bharucha AE, Chiarioni G, Felt-Bersma R, Knowles C, Malcolm A, et al. Functional anorectal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Perera LP, Ananthakrishnan AN, Guilday C, Remshak K, Zadvornova Y, Naik AS, et al. Dyssynergic defecation: a treatable cause of persistent symptoms when inflammatory bowel disease is in remission. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:3600–5. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2850-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Rezaie A, Gu P, Kaplan GG, Pimentel M, Al-Darmaki AK. Dyssynergic defecation in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2018;24:1065–73. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izx095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Quinn KP, Tse CS, Lightner AL, Pendegraft RS, Enders FT, Raffals LE. Nonrelaxing pelvic floor dysfunction is an underestimated complication of ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:1242–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Quinn KP, Lightner AL, Faubion WA, Raffals LE. A comprehensive approach to pouch disorders. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;25:460–71. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Stellingwerf ME, Maeda Y, Patel U, Vaizey CJ, Warusavitarne J, Bemelman WA, et al. The role of the defaecating pouchogram in the assessment of evacuation difficulty after restorative proctocolectomy and pouch-anal anastomosis. Colorectal Dis. 2016;18:O292–300. doi: 10.1111/codi.13431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Mikami Y, Tsunoda J, Suzuki S, Mizushima I, Kiyohara H, Kanai T. Significance of 5-aminosalicylic acid intolerance in the clinical management of ulcerative colitis. Digestion. 2023;104:58–65. doi: 10.1159/000527452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]