Abstract
Several studies have addressed the question of starvation effects on immune function by means of changes in lymphocyte subsets, cytokine induction or lymphocyte activation. Anorexia nervosa (AN) patients are severely malnourished and contradictory results have been obtained regarding the accompanying immunodeficiency, including its assignation as a part of the primary nervous disorder. In the present work, an extensive immunological function examination was carried out on 40 AN patients who were compared with a control group of 14 healthy girls. The AN patients were also classified according to their nutritional status (by the Body Mass Index: BMI), this being critical for a better understanding of these secondary immunodeficiency bases. Moreover, another immune system study was performed on five patients after refeeding. Lymphocyte subsets and function, cytokine induction and peripheral blood concentrations, and innate as well as humoral immunity were evaluated. Deregulation in the cytokine network, owing to the interaction of the central nervous (CNS) and immune systems, seems to be the initial immune alteration in AN immunodeficiency but it has not been disproved that the immunodeficiency is a direct consequence of the original psychiatric perturbation. Spontaneous high levels of circulating interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) have been observed; this is probably one of the causes of the anomalies found in the T-cell subpopulations (mainly the naive CD4+CD45RA+ reduction and the cytotoxic CD8+ increase) and T-cell activation status (mainly the down-regulation of the CD2 and CD69 activation pathways). This finally leads to an impairment, not only in T-cell function but also in T-cell to B-cell co-operation. The AN specificity of these results is confirmed by the fact that these immune alterations improve after refeeding and when nutritional status becomes less critical, which also suggests that AN immunodeficiency is indeed secondary to malnutrition.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Salmon M., Janossy G. The synergy between naive and memory T cells during activation. Immunol Today. 1991 Jun;12(6):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allende L. M., Corell A., Madroño A., Góngora R., Rodríguez-Gallego C., López-Goyanes A., Rosal M., Arnaiz-Villena A. Retinol (vitamin A) is a cofactor in CD3-induced human T-lymphocyte activation. Immunology. 1997 Mar;90(3):388–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.1997.00388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaiz-Villena A., Timon M., Corell A., Perez-Aciego P., Martin-Villa J. M., Regueiro J. R. Brief report: primary immunodeficiency caused by mutations in the gene encoding the CD3-gamma subunit of the T-lymphocyte receptor. N Engl J Med. 1992 Aug 20;327(8):529–533. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199208203270805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler H., Karp L., Notti I., Apter A., Tyano S., Djaldetti M., Weizman R. Cytokine production in anorexia nervosa. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1993 Jun;16(3):237–243. doi: 10.1097/00002826-199306000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla F. Anorexia nervosa and depression: a common biochemical pathogenesis? Funct Neurol. 1986 Apr-Jun;1(2):191–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. H., Cantrell D. A., Brattsand G., Crumpton M. J., Gullberg M. The CD2 antigen associates with the T-cell antigen receptor CD3 antigen complex on the surface of human T lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):551–553. doi: 10.1038/339551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese J. R., Kling M. A., Gold P. W. Alterations in immunocompetence during stress, bereavement, and depression: focus on neuroendocrine regulation. Am J Psychiatry. 1987 Sep;144(9):1123–1134. doi: 10.1176/ajp.144.9.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell C. W., Taylor H. M. A rapid, no-wash technic for immunophenotypic analysis by flow cytometry. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;86(5):600–607. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Dinarello C. A. Increased plasma interleukin-1 activity in women after ovulation. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.3871966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Kluger M. J. Endogenous pyrogen activity in human plasma after exercise. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):617–619. doi: 10.1126/science.6836306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cason J., Ainley C. C., Wolstencroft R. A., Norton K. R., Thompson R. P. Cell-mediated immunity in anorexia nervosa. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 May;64(2):370–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisp A. H. Anorexia nervosa 'feeding disorder', 'nervous malnutrition' or 'weight phobia'? World Rev Nutr Diet. 1970;12:452–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzer R., Kelley K. W. Stress and immunity: an integrated view of relationships between the brain and the immune system. Life Sci. 1989;44(26):1995–2008. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel P. E., Brown G. M., Stancer H. C., Moldofsky H. Hypothalamic-pituitary function in anorexia nervosa. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1975 Jun;32(6):739–744. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1975.01760240067005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golla J. A., Larson L. A., Anderson C. F., Lucas A. R., Wilson W. R., Tomasi T. B., Jr An immunological assessment of patients with anorexia nervosa. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Dec;34(12):2756–2762. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.12.2756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. L., Newberne P. M. Role of nutrition in immunologic function. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):188–302. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Góngora R., Corell A., Regueiro J. R., Carasol M., Rodríguez-Gallego C., Paz-Artal E., Timón M., Allende L., Arnaiz-Villena A. Peripheral blood reduction of memory (CD29+, CD45RO+, and "bright" CD2+ and LFA-1+) T lymphocytes in Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome. Hum Immunol. 1994 Nov;41(3):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(94)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
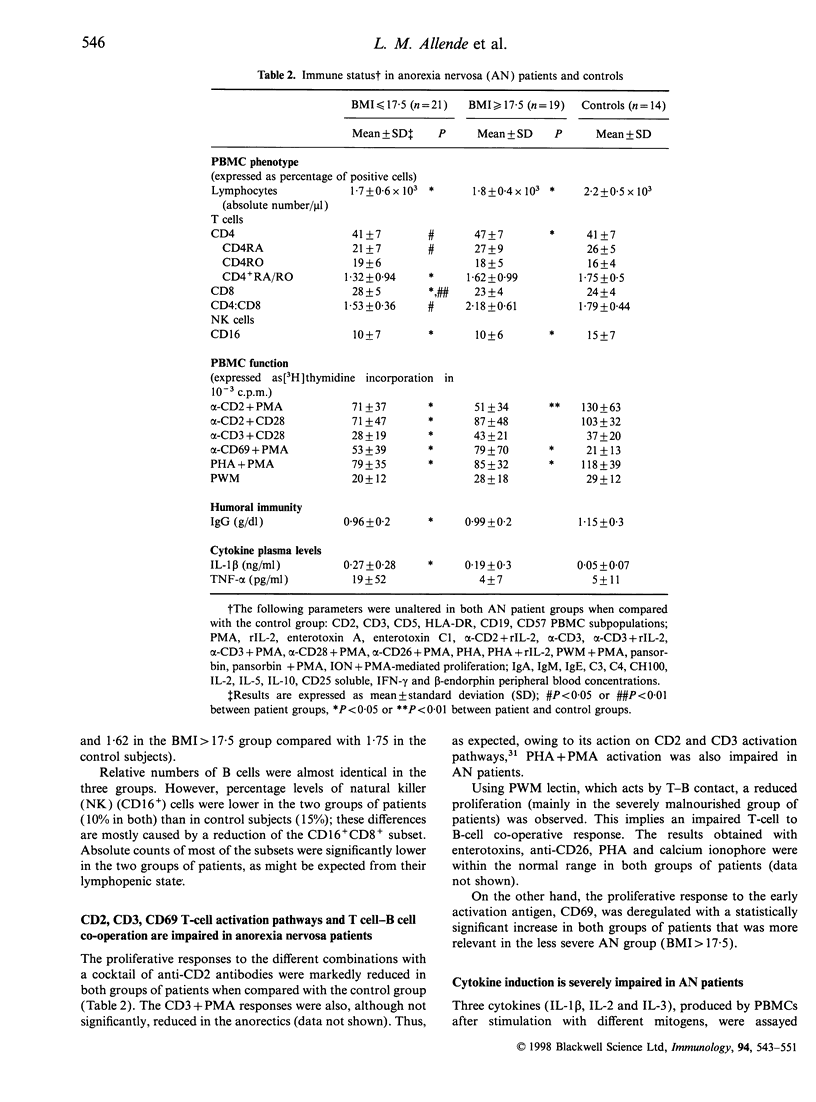
- Isler P., Vey E., Zhang J. H., Dayer J. M. Cell surface glycoproteins expressed on activated human T cells induce production of interleukin-1 beta by monocytic cells: a possible role of CD69. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1993 Jan-Feb;4(1):15–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. L. Anorexia nervosa and depression: another view. Am J Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;143(2):270–271. doi: 10.1176/ajp.143.2.aj1432270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A. R. On the meaning of laboratory values in anorexia nervosa. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Nov;52(11):748–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malipiero U. V., Frei K., Fontana A. Production of hemopoietic colony-stimulating factors by astrocytes. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3816–3821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manié S., Kubar J., Limouse M., Ferrua B., Ticchioni M., Breittmayer J. P., Peyron J. F., Schaffar L., Rossi B. CD3-stimulated Jurkat T cells mediate IL-1 beta production in monocytic THP-1 cells. Role of LFA-1 molecule and participation of CD69 T cell antigen. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1993 Jan-Feb;4(1):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcos A., Varela P., Santacruz I., Muñoz-Vélez A., Morandé G. Nutritional status and immunocompetence in eating disorders. A comparative study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1993 Nov;47(11):787–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray D. N., Watson R. R., Reyes M. A. Effect of renutrition on humoral and cell-mediated immunity in severely malnourished children. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Oct;34(10):2117–2126. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.10.2117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A., Ward A., Treasure J., Peakman M. T lymphocyte subpopulations in anorexia nervosa and refeeding. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997 Mar;82(3):282–289. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.4310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opara E. I., Meguid M. M., Yang Z. J., Chai J. K., Veerabagu M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and total parenteral nutrition-induced anorexia. Surgery. 1995 Oct;118(4):756–762. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(05)80046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Peters P. M., McCabe J., Crase D., Hansen S., Chen A. B., Liggitt D. Development of partial tolerance to the gastrointestinal effects of high doses of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rodents. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1587–1596. doi: 10.1172/JCI113245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata-Salamán C. R., Oomura Y., Kai Y. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 beta: suppression of food intake by direct action in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1988 May 10;448(1):106–114. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plebanski M., Elson C. J., Billington W. D. Dependency on interleukin-1 of primary human in vitro T cell responses to soluble antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2353–2358. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polack E., Nahmod V. E., Emeric-Sauval E., Bello M., Costas M., Finkielman S., Arzt E. Low lymphocyte interferon-gamma production and variable proliferative response in anorexia nervosa patients. J Clin Immunol. 1993 Nov;13(6):445–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00920020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Aciego P., Alarcón B., Arnaiz-Villena A., Terhorst C., Timón M., Segurado O. G., Regueiro J. R. Expression and function of a variant T cell receptor complex lacking CD3-gamma. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):319–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regueiro J. R., López-Botet M., De Landazuri M. O., Alcami J., Corell A., Martín-Villa J. M., Vicario J. L., Arnaiz-Villena A. An in vivo functional immune system lacking polyclonal T-cell surface expression of the CD3/Ti(WT31) complex. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):699–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socher S. H., Friedman A., Martinez D. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor induces acute reductions in food intake and body weight in mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1957–1962. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M., Keller S. E., Schleifer S. J. Stress and immunomodulation: the role of depression and neuroendocrine function. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):827s–833s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigersky R. A., Loriaux D. L., Andersen A. E., Lipsett M. B. Anorexia nervosa: behavioural and hypothalamic aspects. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Jul;5(2):517–535. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(76)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade S., Bleiberg F., Mossé A., Lubetzki J., Flavigny H., Chapuis P., Roche D., Lemonnier D., Dardenne M. Thymulin (Zn-facteur thymique serique) activity in anorexia nervosa patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Aug;42(2):275–280. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. G. CD28: a signalling perspective. Biochem J. 1996 Sep 1;318(Pt 2):361–377. doi: 10.1042/bj3180361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Ramsdell F., Alderson M. R. The activation antigen CD69. Stem Cells. 1994 Sep;12(5):456–465. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530120502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


