Abstract
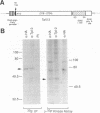
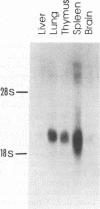
Tpl-2 is a gene encoding a protein kinase which is primarily expressed in normal spleen, thymus, and lung tissue and is activated by provirus insertion in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomas during the late stages of oncogenesis. Tpl-2 is composed of eight exons and spans a 35-kb genomic DNA region. The provirus integrates reproducibly in the last intron and in the same transcriptional orientation as the Tpl-2 gene. This genetic change leads to the expression of enhanced steady-state levels of a truncated Tpl-2 RNA transcript which is predicted to encode a protein with an altered C-terminal domain. Tpl-2 is transcribed from two alternating promoters, P1 and P2. The RNA transcripts originating in the two promoters harbor different 5' untranslated regions derived from the alternate noncoding exons IA and IB. Utilization of the P2 promoter, which gives rise to exon IB containing Tpl-2 RNA transcripts, was detected primarily in tumor cells. The Tpl-2 protein was expressed in COS-1 cells as an N-terminal fusion with a 12-amino-acid hemagglutinin tag. Immunoprecipitation of transfected COS-1 cell lysates with antihemagglutinin or anti-Tpl-2 antibodies, followed by incubation with [gamma-32P]ATP, confirmed that Tpl-2 possesses protein kinase activity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bear S. E., Bellacosa A., Lazo P. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Hanson C., Levan G., Tsichlis P. N. Provirus insertion in Tpl-1, an Ets-1-related oncogene, is associated with tumor progression in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymic lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7495–7499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellacosa A., Testa J. R., Staal S. P., Tsichlis P. N. A retroviral oncogene, akt, encoding a serine-threonine kinase containing an SH2-like region. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):274–277. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone G. L., Winguth S. D. Immunoprecipitation of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:688–700. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint A. J., Paladini R. D., Koshland D. E., Jr Autophosphorylation of protein kinase C at three separated regions of its primary sequence. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):408–411. doi: 10.1126/science.2377895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilks C. B., Bear S. E., Grimes H. L., Tsichlis P. N. Progression of interleukin-2 (IL-2)-dependent rat T cell lymphoma lines to IL-2-independent growth following activation of a gene (Gfi-1) encoding a novel zinc finger protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1759–1768. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V., Allis C. D. Enzyme activity dot blots for assaying protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:85–90. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00128-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice M. J., Gilbert D. J., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Buchberg A. M., Ceci J. D., Matsuda Y., Chapman V. M., Patriotis C., Makris A. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 18 reveals extensive linkage conservation with human chromosomes 5 and 18. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1281–1288. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90047-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Circumstances and mechanisms of inhibition of translation by secondary structure in eucaryotic mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5134–5142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Regulation of translation in eukaryotic systems. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:197–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., Klein-Szanto A. J., Tsichlis P. N. T-cell lymphoma lines derived from rat thymomas induced by Moloney murine leukemia virus: phenotypic diversity and its implications. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3948–3959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3948-3959.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makris A., Patriotis C., Bear S. E., Tsichlis P. N. Structure of a Moloney murine leukemia virus-virus-like 30 recombinant: implications for transduction of the c-Ha-ras proto-oncogene. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1286–1291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1286-1291.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. A series of mammalian expression vectors and characterisation of their expression of a reporter gene in stably and transiently transfected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1068–1068. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriotis C., Makris A., Bear S. E., Tsichlis P. N. Tumor progression locus 2 (Tpl-2) encodes a protein kinase involved in the progression of rodent T-cell lymphomas and in T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2251–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. D., Pech M., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. The 5' untranslated sequence of the c-sis/platelet-derived growth factor 2 transcript is a potent translational inhibitor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):284–292. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Sithanandam G., Copeland T. D., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U. R., Morrison D. K. 95-kilodalton B-Raf serine/threonine kinase: identification of the protein and its major autophosphorylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3733–3742. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Selective inactivation of the exonuclease activity of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase by in vitro mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6447–6458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung R. S., Taguchi T., Patriotis C., Makris A., Tsichlis P. N., Levan K. K., Levan G., Tartof K., Hino O., Knudson A. G. New markers, D16FC1 and Tp12, differentiate between rat chromosomes 16 and 17. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1993;62(2-3):149–152. doi: 10.1159/000133459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]