Abstract
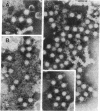
An experimental model of enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis (ET-NANBH) was established in tamarins (Saguinus mystax mystax) and cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis). First-passage animals were inoculated with two different stool suspensions obtained from human patients with well-defined ET-NANBH that originated from Burma and Pakistan, where epidemics of ET-NANBH occur. Both inocula contained 27- ato 34-nm-diameter viruslike particles (VLPs) that were specifically aggregated by acute-phase ET-NANBH sera. ET-NANBH was subpassaged in both tamarins and cynomolgus macaques by using pools of stool suspensions from first-passage animals. One additional passage of disease in cynomolgus macaques resulted in a significantly shortened incubation period and increased severity of disease. VLPs similar to those found in the human inocula were observed in stool specimens of first-, second-, and third-passage cynomolgus macaques and in first- and second-passage tamarins. Our findings indicate that cynomolgus macaques are particularly suitable experimental models for studies of human ET-NANBH. The 27- to 34-nm VLPs found in infected human and primate stools appear to be etiologically linked to disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balayan M. S., Andjaparidze A. G., Savinskaya S. S., Ketiladze E. S., Braginsky D. M., Savinov A. P., Poleschuk V. F. Evidence for a virus in non-A, non-B hepatitis transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Intervirology. 1983;20(1):23–31. doi: 10.1159/000149370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Maynard J. E. Etiology and natural history of post-transfusion and enterically-transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. 1986 Feb;6(1):56–66. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., McCaustland K. A., Cook E. H., Fields H. A., Frosner G. G., Maynard J. E. Dissociation of hepatitis A virus antigen-anti-HAV antibody complexes by 2-mercaptoethanol and dithiothreitol. J Med Virol. 1982;9(4):311–325. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Schable C. A., McCaustland K. A., Cook E. H., Murphy B. L., Fields H. A., Ebert J. W., Wheeler C., Maynard J. E. Hepatitis A virus: growth characteristics of in vivo and in vitro propagated wild and attenuated virus strains. J Med Virol. 1984;14(4):373–386. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cock K. M., Bradley D. W., Sandford N. L., Govindarajan S., Maynard J. E., Redeker A. G. Epidemic non-A, non-B hepatitis in patients from Pakistan. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Feb;106(2):227–230. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. A., McCaustland K. A., Bradley D. W., Maynard J. E. Purification of acute phase anti-hepatitis A virus (HAV) IgM and development of an IgM solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the detection of HAV. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jun 11;51(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravelle C. R., Hornbeck C. L., Maynard J. E., Schable C. A., Cook E. H., Bradley D. W. Hepatitis A: report of a common-source outbreak with recovery of a possible etiologic agent. II. Laboratory studies. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):167–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hla Myint, Myint Myint Soe, Tun Khin, Thein-Maung Myint, Khin Maung Tin A clinical and epidemiological study of an epidemic of non-A non-B hepatitis in Rangoon. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Nov;34(6):1183–1189. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane M. A., Bradley D. W., Shrestha S. M., Maynard J. E., Cook E. H., Mishra R. P., Joshi D. D. Epidemic non-A, non-B hepatitis in Nepal. Recovery of a possible etiologic agent and transmission studies in marmosets. JAMA. 1984 Dec 14;252(22):3140–3145. doi: 10.1001/jama.252.22.3140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuroo M. S., Duermeyer W., Zargar S. A., Ahanger M. A., Shah M. A. Acute sporadic non-A, non-B hepatitis in India. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Sep;118(3):360–364. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VISWANATHAN R. Epidemiology. Indian J Med Res. 1957 Jan;45(Suppl):1–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. C., Purcell R. H., Sreenivasan M. A., Prasad S. R., Pavri K. M. Epidemic and endemic hepatitis in India: evidence for a non-A, non-B hepatitis virus aetiology. Lancet. 1980 Oct 25;2(8200):876–879. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]