Abstract
In the title compound, C10H7NO2S, the dihedral angle between the benzimidazole and malonaldehyde group is 1.41 (2)°. An intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed between the NH group and one of the adjacent carbonyl O atoms. In addition, the NH group forms an intermolecular hydrogen bond to a symmetry equivalent of this carbonyl O atom, connecting the molecules into centrosymmetric dimers. The structure also contains C—H⋯O intermolecular interactions.
Related literature
For biological activities of benzothiazole derivatives, see: Mortimer et al. (2006 ▶); Yoshida et al. (2005 ▶); Vicini et al. (2003 ▶).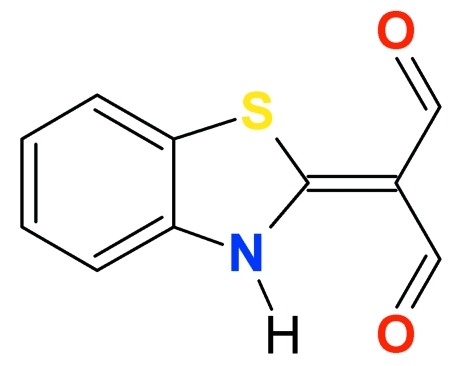
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H7NO2S
M r = 205.23
Monoclinic,
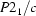
a = 8.3927 (10) Å
b = 5.0972 (8) Å
c = 20.739 (2) Å
β = 100.098 (8)°
V = 873.4 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 3.05 mm−1
T = 133 K
0.12 × 0.12 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.711, T max = 0.942
10660 measured reflections
1569 independent reflections
1475 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.082
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.067
wR(F 2) = 0.165
S = 1.02
1569 reflections
128 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (van der Sluis & Spek, 1990 ▶; Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030248/hg5064sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030248/hg5064Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030248/hg5064Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N6—H6⋯O11 | 0.88 | 2.13 | 2.731 (3) | 125 |
| N6—H6⋯O11i | 0.88 | 2.13 | 2.926 (3) | 151 |
| C3—H3⋯O14ii | 0.95 | 2.43 | 3.297 (4) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 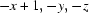 ; (ii)
; (ii) 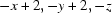 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Benzothiazole and its derivatives are good candidates that have fluorescent properties and possess diverse biological properties, such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antitumor. (Mortimer et al. (2006); Yoshida et al. (2005); Vicini et al. (2003)). In the present paper, we report the synthesis of 1,3-benzothiazol-2(3H)-ylidenemalonaldehyde using the Vilsmeier reaction. This molecule can be used as a precursor for the synthesis of a variety of fluorescent molecules. The crystal structure of the title compound is characterized by bifurcated hydrogen bonds between the amine and aldehyde groups. The donor atom N6 gives the mean interactions with 2 acceptor atom O11. One is intramolecular (x, y, z) but the other one is intermolecular (1 - x, -y, -z). These interactions form a coplanar dimer around the centre in 1/2, 1/2, 0.5. Atom C3 in the molecule at (x, y, z) acts as a hydrogen-bond donor via atom H3 to atom O14 in the molecule at (2 - x, 2 - y, -z)
Experimental
To N,N-dimethylformamide (2 ml) cooled in an ice bath was added dropwise phosphorus oxychloride (1.6 ml, 17.4 mmol) with stirring at below 5 °C. After this addition, a solution of 2-methybenzothiazole (2.9 mmol, 0.432 g) in DMF (2 ml) was added dropwise. The cooling bath was removed and the reaction mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 12 h. The resulting solution was added to ice-cooled water and made alkaline with NaOH (aq.) solution. The resulting precipitate was collected by filtration after 24 h, dried in air, recrystallized from ethanol, to give 1,3-benzothiazol-2(3H)-ylidenemalonaldehyde as colourless crystals.
Refinement
Carbon and Nitrogen H-atoms were located from Fourier Fourier synthesis and placed in calculated positions (C—H 0.95 Å, N—H 0.88 Å) and included in the refinement in the riding model approximation with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N).
Figures
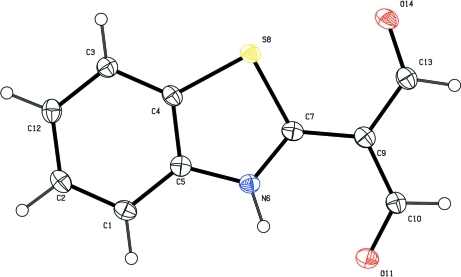
Fig. 1.
ORTEP diagram of the title molecule with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoid are drawn at 30% probability level.
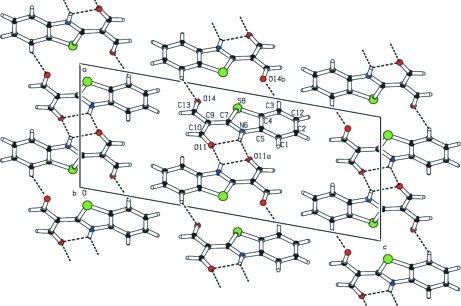
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the b axis. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds intra and intermolecular interactions.
Crystal data
| C10H7NO2S | F(000) = 424 |
| Mr = 205.23 | Dx = 1.561 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54180 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1475 reflections |
| a = 8.3927 (10) Å | θ = 7.5–71.9° |
| b = 5.0972 (8) Å | µ = 3.05 mm−1 |
| c = 20.739 (2) Å | T = 133 K |
| β = 100.098 (8)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 873.4 (2) Å3 | 0.12 × 0.12 × 0.02 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 1569 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus rotating anode | 1475 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| confocal | Rint = 0.082 |
| ω scans | θmax = 71.9°, θmin = 7.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.711, Tmax = 0.942 | k = −4→5 |
| 10660 measured reflections | l = −25→25 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.067 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.165 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.098P)2 + 1.503P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1569 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 128 parameters | Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.6870 (3) | 0.3667 (6) | 0.16032 (14) | 0.0291 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.6162 | 0.2210 | 0.1600 | 0.035* | |
| C2 | 0.7501 (3) | 0.4952 (7) | 0.21783 (13) | 0.0311 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.7216 | 0.4366 | 0.2578 | 0.037* | |
| C3 | 0.8986 (3) | 0.7993 (6) | 0.16137 (14) | 0.0272 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.9706 | 0.9434 | 0.1619 | 0.033* | |
| C4 | 0.8343 (3) | 0.6732 (6) | 0.10311 (13) | 0.0256 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.7315 (3) | 0.4596 (6) | 0.10291 (13) | 0.0255 (6) | |
| N6 | 0.6804 (3) | 0.3641 (5) | 0.03972 (11) | 0.0248 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.6145 | 0.2294 | 0.0313 | 0.030* | |
| C7 | 0.7391 (3) | 0.4926 (6) | −0.00706 (13) | 0.0248 (6) | |
| S8 | 0.86490 (8) | 0.74932 (13) | 0.02434 (3) | 0.0253 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.7044 (3) | 0.4279 (6) | −0.07455 (13) | 0.0267 (7) | |
| C10 | 0.6013 (3) | 0.2122 (6) | −0.09676 (14) | 0.0267 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.5856 | 0.1748 | −0.1423 | 0.032* | |
| O11 | 0.5306 (2) | 0.0694 (4) | −0.06329 (9) | 0.0303 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.8543 (4) | 0.7080 (6) | 0.21876 (14) | 0.0308 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.8955 | 0.7919 | 0.2592 | 0.037* | |
| C13 | 0.7714 (3) | 0.5777 (6) | −0.12103 (14) | 0.0303 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.7447 | 0.5248 | −0.1655 | 0.036* | |
| O14 | 0.8605 (3) | 0.7691 (4) | −0.10910 (11) | 0.0343 (6) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0248 (13) | 0.0302 (18) | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0004 (12) | 0.0085 (11) | 0.0039 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0296 (14) | 0.037 (2) | 0.0280 (14) | 0.0031 (13) | 0.0094 (11) | 0.0059 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0231 (13) | 0.0296 (17) | 0.0300 (14) | 0.0009 (12) | 0.0079 (11) | −0.0012 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0205 (12) | 0.0312 (17) | 0.0266 (13) | 0.0034 (11) | 0.0087 (10) | 0.0026 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0197 (12) | 0.0278 (17) | 0.0294 (14) | 0.0042 (11) | 0.0052 (10) | −0.0001 (11) |
| N6 | 0.0200 (11) | 0.0268 (15) | 0.0287 (11) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0071 (8) | −0.0004 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0176 (12) | 0.0264 (17) | 0.0318 (14) | 0.0032 (11) | 0.0084 (10) | 0.0007 (11) |
| S8 | 0.0225 (4) | 0.0277 (5) | 0.0274 (5) | −0.0021 (2) | 0.0090 (3) | 0.0003 (2) |
| C9 | 0.0213 (13) | 0.0307 (18) | 0.0295 (14) | 0.0040 (11) | 0.0082 (10) | 0.0010 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0218 (13) | 0.0316 (18) | 0.0277 (14) | 0.0040 (11) | 0.0070 (11) | 0.0002 (11) |
| O11 | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0315 (13) | 0.0341 (10) | −0.0017 (8) | 0.0083 (8) | 0.0019 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0295 (15) | 0.0367 (19) | 0.0263 (14) | 0.0045 (12) | 0.0053 (11) | −0.0022 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0276 (14) | 0.0352 (19) | 0.0303 (14) | 0.0030 (13) | 0.0109 (11) | 0.0003 (12) |
| O14 | 0.0333 (12) | 0.0377 (15) | 0.0353 (12) | −0.0053 (9) | 0.0151 (9) | 0.0016 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (4) | N6—C7 | 1.334 (4) |
| C1—C5 | 1.392 (4) | N6—H6 | 0.8800 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C7—C9 | 1.418 (4) |
| C2—C12 | 1.391 (4) | C7—S8 | 1.735 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C9—C13 | 1.421 (4) |
| C3—C12 | 1.388 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.425 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.391 (4) | C10—O11 | 1.228 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.388 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C4—S8 | 1.741 (3) | C13—O14 | 1.228 (4) |
| C5—N6 | 1.393 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C1—C5 | 117.2 (3) | C5—N6—H6 | 122.6 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 121.4 | N6—C7—C9 | 124.4 (3) |
| C5—C1—H1 | 121.4 | N6—C7—S8 | 112.0 (2) |
| C1—C2—C12 | 121.8 (3) | C9—C7—S8 | 123.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.1 | C7—S8—C4 | 90.23 (13) |
| C12—C2—H2 | 119.1 | C7—C9—C13 | 120.5 (3) |
| C12—C3—C4 | 117.9 (3) | C7—C9—C10 | 120.4 (3) |
| C12—C3—H3 | 121.0 | C13—C9—C10 | 119.1 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 121.0 | O11—C10—C9 | 126.9 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.7 (3) | O11—C10—H10 | 116.5 |
| C5—C4—S8 | 111.4 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 116.5 |
| C3—C4—S8 | 127.8 (2) | C3—C12—C2 | 120.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—C1 | 121.6 (3) | C3—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—N6 | 111.4 (2) | C2—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C1—C5—N6 | 126.9 (3) | O14—C13—C9 | 126.2 (3) |
| C7—N6—C5 | 114.9 (2) | O14—C13—H13 | 116.9 |
| C7—N6—H6 | 122.6 | C9—C13—H13 | 116.9 |
| C5—C1—C2—C12 | −0.2 (4) | C9—C7—S8—C4 | −179.5 (2) |
| C12—C3—C4—C5 | −1.2 (4) | C5—C4—S8—C7 | 0.0 (2) |
| C12—C3—C4—S8 | 178.5 (2) | C3—C4—S8—C7 | −179.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C1 | 1.1 (4) | N6—C7—C9—C13 | 179.4 (2) |
| S8—C4—C5—C1 | −178.7 (2) | S8—C7—C9—C13 | −1.0 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—N6 | 179.7 (3) | N6—C7—C9—C10 | −0.3 (4) |
| S8—C4—C5—N6 | −0.1 (3) | S8—C7—C9—C10 | 179.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—C5—C4 | −0.3 (4) | C7—C9—C10—O11 | 2.1 (4) |
| C2—C1—C5—N6 | −178.7 (3) | C13—C9—C10—O11 | −177.7 (3) |
| C4—C5—N6—C7 | 0.2 (3) | C4—C3—C12—C2 | 0.7 (4) |
| C1—C5—N6—C7 | 178.7 (3) | C1—C2—C12—C3 | 0.0 (5) |
| C5—N6—C7—C9 | 179.4 (2) | C7—C9—C13—O14 | −0.4 (5) |
| C5—N6—C7—S8 | −0.2 (3) | C10—C9—C13—O14 | 179.3 (3) |
| N6—C7—S8—C4 | 0.1 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N6—H6···O11 | 0.88 | 2.13 | 2.731 (3) | 125. |
| N6—H6···O11i | 0.88 | 2.13 | 2.926 (3) | 151. |
| C3—H3···O14ii | 0.95 | 2.43 | 3.297 (4) | 152. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z; (ii) −x+2, −y+2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG5064).
References
- Mortimer, C. G., Wells, G., Crochard, J.-P., Stone, E. L., Bradshaw, T. D., Stevens, M. G. F. & Westwell, A. D. (2006). J. Med. Chem. 49, 179–185. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear. Rigaku/MSC Inc., The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sluis, P. van der & Spek, A. L. (1990). Acta Cryst. A46, 194–201.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vicini, P., Gernonikaki, A., Incerti, M., Busonera, B., Poni, G., Cabras, C. A. & Colla, P. L. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 11, 4785–4789. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Yoshida, M., Hayakawa, I., Hayashi, N., Agatsuma, T., Oda, Y., Tanzawa, F., Iwasaki, S., Koyama, K., Furukawa, H., Kurakata, Y. & Sugano, Y. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15, 3328–3332. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030248/hg5064sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030248/hg5064Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030248/hg5064Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report