Abstract
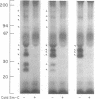
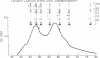
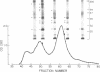
By using disuccinimidyl suberate, we have covalently cross-linked 125I-labeled somatomedin-C (Sm-C)/insulinlike growth factor I to specific binding proteins in human plasma. In unfractionated plasma samples from normal and acromegalic donors, 125I-Sm-C binding-protein complexes with relative molecular weights (Mr) of 160,000, 135,000, 110,000, 80,000, 50,000, 43,000-35,000, and 28,000-24,000 were consistently observed. In contrast, the 43,000-35,000-mol wt species were frequently the only specific complexes observed in hypopituitary plasma and were consistently more intensely labeled in such samples. Reduction of samples with beta-mercaptoethanol did not alter the electrophoretic pattern of these 125I-Sm-C binding-protein complexes. All Sm-C binding proteins, with the exception of the 43,000-35,000-mol wt complex, were adsorbed by concanavalin A-Sepharose. When acromegalic or normal plasma was fractionated on a Sephadex G-200 column and affinity labeled, the same complexes that were adsorbed by concanavalin A were found in fractions that eluted near the gamma-globulin peak. On the other hand, the 43,000-35,000-mol wt complex consistently eluted in size-appropriate fractions near the albumin peak. These data suggest that the growth hormone (GH)-dependent Sm-C binding protein, represented by the 160,000-mol wt complex, is in some way composed of smaller species, i.e., the 135,000-, 110,000-, 80,000-, 50,000-, and 28,000-24,000-mol wt complexes. Acid incubation of plasma prior to Sephadex G-200 chromatography results in the elimination of specific 125I-Sm-C binding-protein complexes which elute near gamma-globulin and a concurrent increase in the labeling intensity of the 28,000-24,000-mol wt complexes. We speculate, therefore, that each of the GH-dependent Sm-C binding-protein complexes represents an oligomer composed of 28,000-24,000-mol wt protomers. The 43,000-35,000-mol wt species is not dependent upon GH and appears to represent a different type of Sm-C binding protein.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binoux M., Hardouin S., Lassarre C., Hossenlopp P. Evidence for production by the liver of two IGF binding proteins with similar molecular weights but different affinities for IGF I and IGF II. Their relations with serum and cerebrospinal fluid IGF binding proteins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Sep;55(3):600–602. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-3-600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsi L., Rosenfeld R. G., Liu F., Hintz R. L. Somatomedin peptide distribution and somatomedin-binding protein content in cord plasma: comparison to normal and hypopituitary plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):223–228. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain P. G., Van Wyk J., Copeland K. C., Blethen S. L., Underwood L. E. Effect of in vitro action of serum proteases or exposure to acid on measurable immunoreactive somatomedin-C in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Feb;56(2):376–383. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-2-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Chatelain P. G., Van Wyk J. J. Liberation of immunoreactive somatomedin-C from its binding proteins by proteolytic enzymes and heparin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Feb;56(2):384–389. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-2-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. A., Blethen S. L. Somatomedin binding proteins in GH-deficient children with normal plasma somatomedin levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Mar;56(3):461–466. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-3-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen K. L., Nissley S. P. The serum half-life of somatomedin activity: evidence for growth hormone dependence. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Oct;83(2):243–258. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0830243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland K. C., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Induction of immunoreactive somatomedin C human serum by growth hormone: dose-response relationships and effect on chromatographic profiles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Apr;50(4):690–697. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-4-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Wilkins J. R. Affinity labeled somatomedin-C-binding proteins in rat sera. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1141–1144. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Ward A. P., Goldberg A. C., Trivedi B., Kapadia M. Characterization of somatomedin binding in human serum by ultracentrifugation and gel filtration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):916–921. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;51(1):12–19. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J., D'Ercole A. J. Estimation of somatomedin-C levels in normals and patients with pituitary disease by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):648–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI108816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grizzard J. D., D'Ercole A. J., Wilkins J. R., Moats-Staats B. M., Williams R. W. Affinity-labeled somatomedin-C receptors and binding proteins from the human fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;58(3):535–543. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-3-535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Andres R. Y., Humbel R. E. Evidence for the synthesis of a somatomedin similar to insulin-like growth factor I by chick embryo liver cells. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):245–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F. Demonstration of specific plasma protein binding sites for somatomedin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;45(5):988–995. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-5-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F., Rosenfeld R. G., Kemp S. F. Plasma somatomedin-binding proteins in hypopituitarism: changes during growth hormone therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):100–104. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis R. A., Moats-Staats B. M., Gualtieri R. T. Protein phosphorylation during spontaneous contraction of smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann U., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Growth-hormone dependence of non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) and of NSILA-carrier protein in rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Apr;87(4):716–727. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann U., Zapf J., Torretti B., Froesch E. R. Demonstration of a specific serum carrier protein of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jan;44(1):160–166. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-1-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Sequence analysis of somatomedin-C: confirmation of identity with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2215–2217. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauer D. J., Wagner F. W., Smith G. L. Purification and characterization of multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA) carrier protein. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(2):177–191. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. H., Schalch D. S. Structure of somatomedin-binding protein: alkaline pH-induced dissociation of an acid-stable, 60,000 molecular weight complex into smaller components. Endocrinology. 1982 Sep;111(3):801–805. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-3-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nessley S. P., Cohen K. L., Rechler M. M. Specific binding of a somatomedin-like polypeptide in rat serum depends on growth hormone. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):137–140. doi: 10.1038/263137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Passamani J., White R. M. Further characterization of growth hormone-dependent somatomedin-binding proteins in rat serum and demonstration of somatomedin-binding proteins produced by rat liver cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1979 Feb;104(2):536–546. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-2-536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Richards F. M. Chemical cross-linking: reagents and problems in studies of membrane structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:523–551. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch D. S., Tollefsen S. E., Klingensmith G. J., Gotlin R. W., Diehl M. J. Effects of human growth hormone administration on serum somatomedins, somatomedin carrier proteins, and growth rates in children with growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jul;55(1):49–55. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwander J. C., Hauri C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Synthesis and secretion of insulin-like growth factor and its binding protein by the perfused rat liver: dependence on growth hormone status. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):297–305. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Klapper D. G., Fellows R. E., Grissom F. E., Schlueter R. J. Purification of somatomedin-C from human plasma: chemical and biological properties, partial sequence analysis, and relationship to other somatomedins. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):790–797. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. M., Nissley S. P., Moses A. C., Rechler M. M., Johnsonbaugh R. E. The growth hormone dependence of a somatomedin-binding protein in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):49–57. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulinlike activity to human serum. Evidence for a carrier protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):638–645. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]