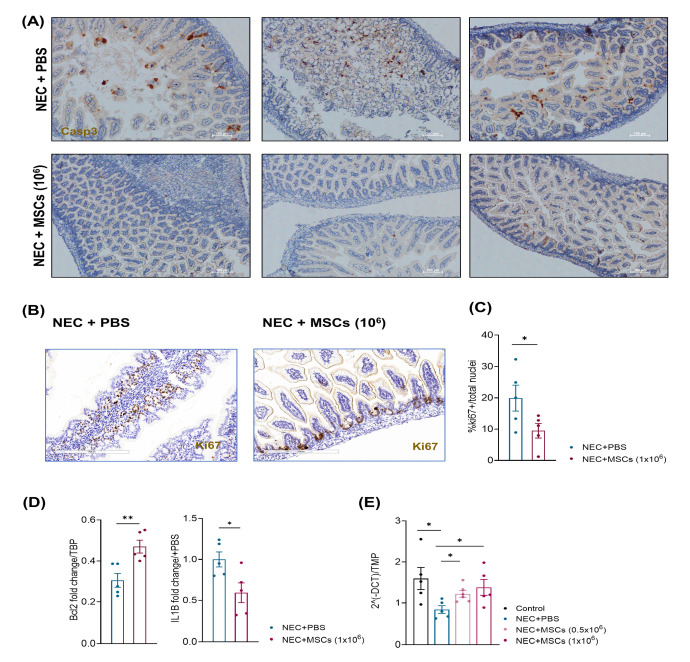
Figure 5.
hBM-MSCs reduced apoptosis and stimulated tissue regeneration in a neonatal mouse NEC model. (A) Representative Caspase-3 staining on histological intestinal sections from mice belonging to the NEC + PBS and NEC + hBM-MSCs (1 × 106) experimental groups. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B,C) Representative Ki67 staining and its relative quantification on histological intestinal sections from mice belonging to the NEC + PBS and NEC + hBM-MSCs (1 × 106) experimental groups (n = 5) Scale bar: 200 µm. (D) Relative gene expression of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl2 and the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1B. (E) Relative gene expression of the tight junction component ZO-1 in the four indicated experimental groups. Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma 2; hBM-MSCs: human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells; IL-1B: Interleukin 1b; NEC: necrotizing enterocolitis; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; ZO-1: zonula occludens-1. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.