Abstract
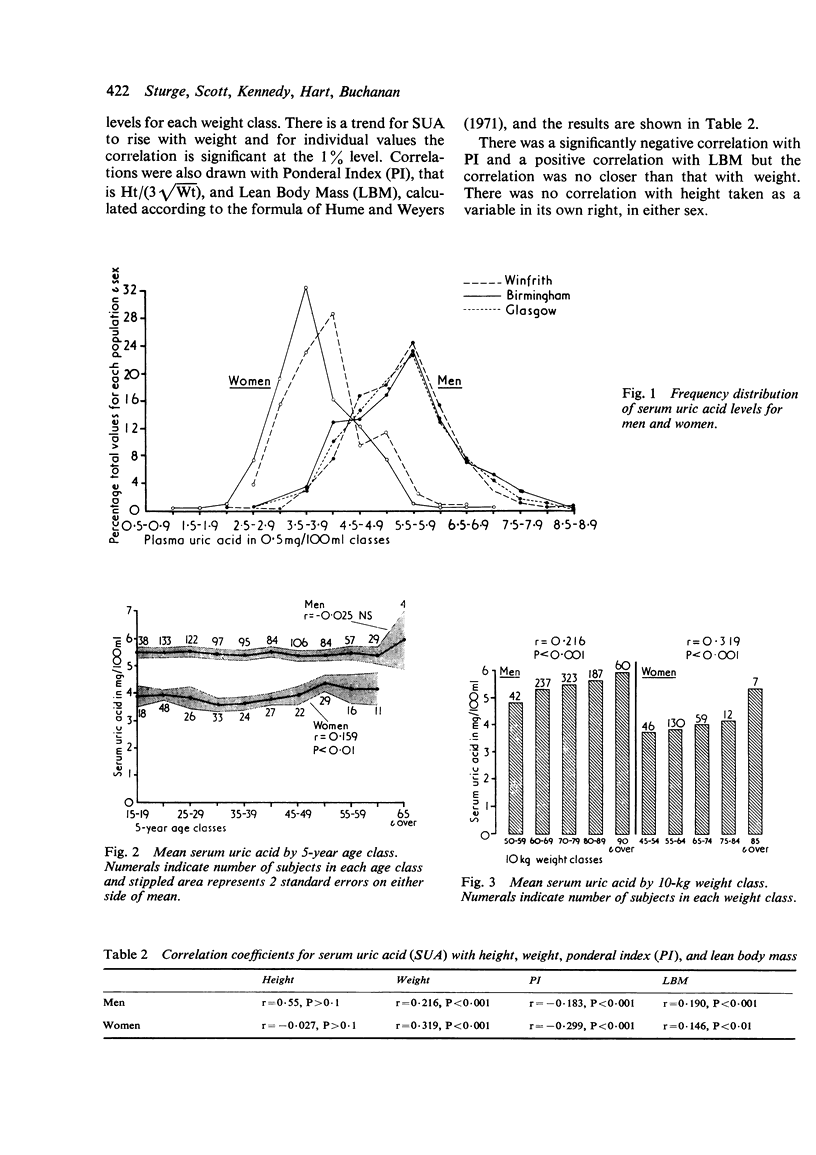
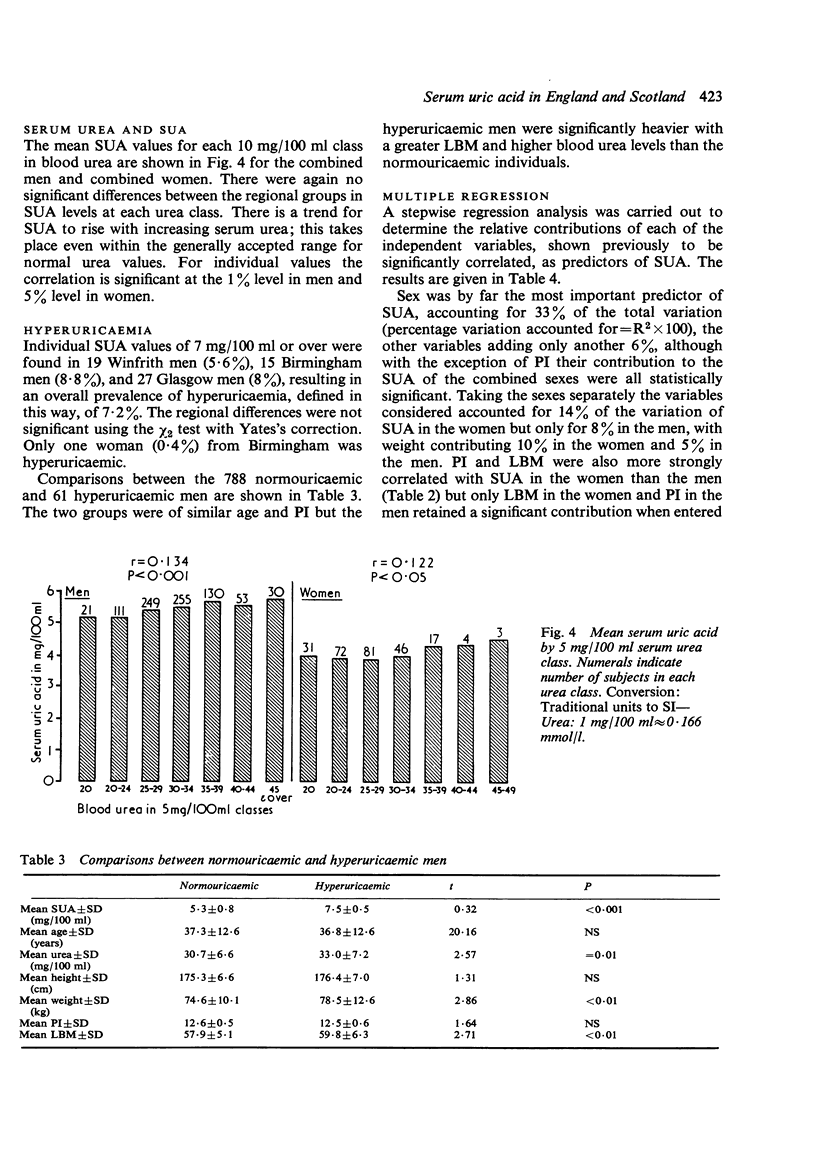
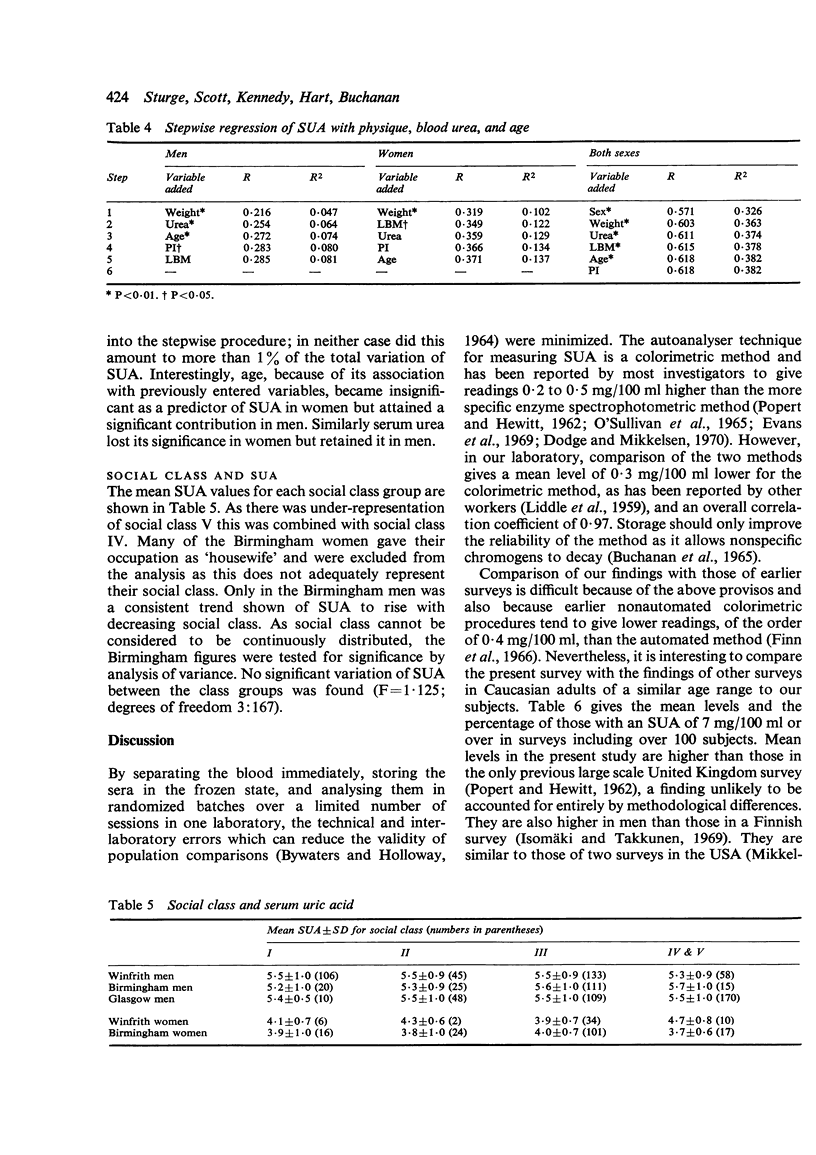
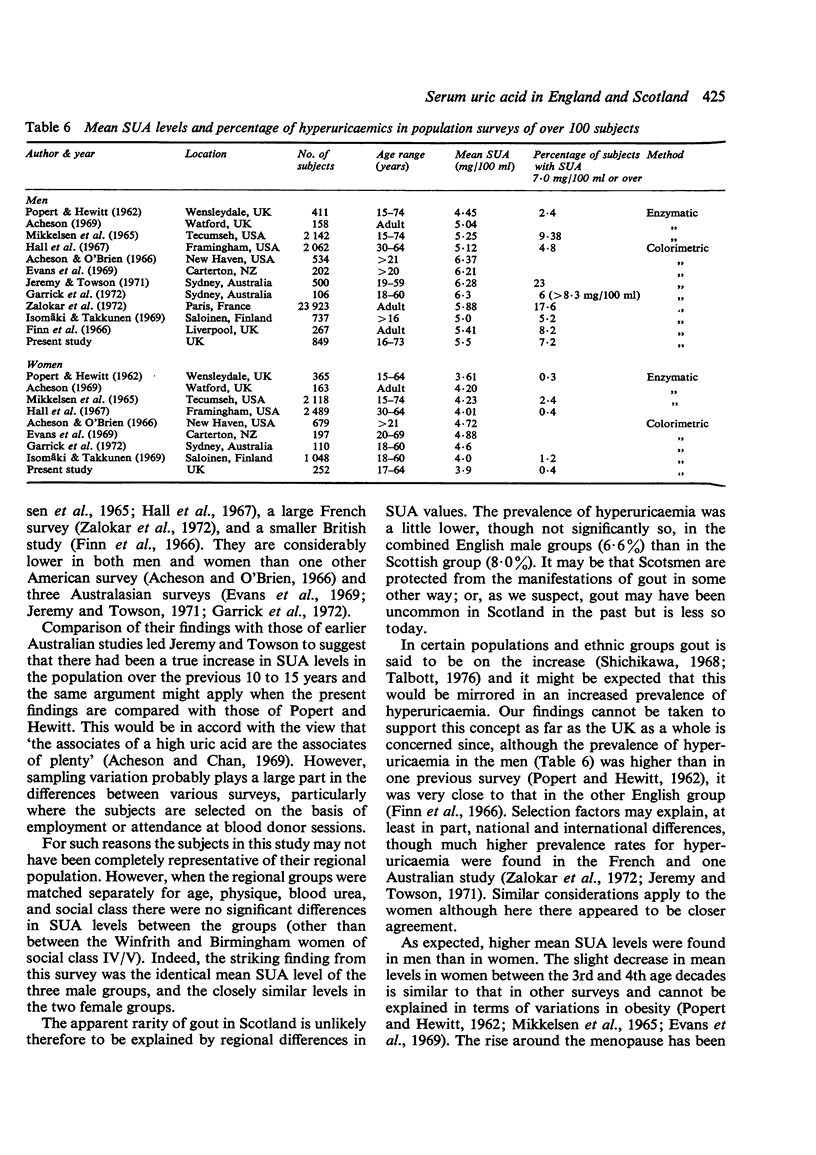
Serum uric acid (SUA) was measured in 512 men and 254 women from two English regions and in 337 men from one Scottish region. Mean SUA levels were the same in the men (5-5 mg/100 ml) and similar in the women (3-9 and 4-1 mg/100 ml). The apparent rarity of gout in Scotsmen cannot be explained by regional differences in SUA levels or in the prevalence of hyperuricaemia (defined as SUA of 7-0 mg/100 ml or over) which was present in 6-6% of the English men and 8% of the Scots. SUA was positively correlated with weight and serum urea, and with age in women, but no variation was found with social class. Body weight was the most important predictor of SUA in both men and women and superior to measurements involving correction for height, such as ponderal index and calculated lean body mass.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson R. M., Chan Y. K. New Haven survey of joint diseases. The prediction of serum uric acid in a general population. J Chronic Dis. 1969 Jan;21(8):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(69)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson R. M., O'Brien W. M. Dependence of serum-uric-acid on haemoglobin and other factors in the general population. Lancet. 1966 Oct 8;2(7467):777–778. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90368-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson R. M. Social class gradients and serum uric acid in males and females. Br Med J. 1969 Oct 11;4(5675):65–67. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5675.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHANAN M. J., ISDALE I. C., ROSE B. S. SERUM URIC ACID ESTIMATION CHEMICAL AND ENZYMATIC METHODS COMPARED. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 May;24:285–288. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYWATERS E. G., HOLLOWAY V. P. MEASUREMENT OF SERUM URIC ACID IN GREAT BRITAIN IN 1963. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 May;23:236–239. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson C., Tibblin E. Serum uric acid levels in women. An epidemiological survey with special reference to women with high serum uric acid values. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Jul-Aug;196(1-2):93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge H. J., Mikkelsen W. M. Observations on the distribution of serum uric acid levels in participants of the Tecumseh, Michigan, Community Health Studies. A comparison of results of one method used at two different times and of two methods used simultaneously. J Chronic Dis. 1970 Sep;23(3):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(70)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. G., Morrison R. B. The Carterton study. 5. Serum uric acid levels of a sample of New Zealand European adults. N Z Med J. 1969 Nov;70(450):306–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn R., Tweedie M. C., Jones P. O., Hall S. M., Dinsdale O. F., Bourdillon R. E. Frequency-distribution curve of uric acid in the general population. Lancet. 1966 Jul 23;2(7456):185–187. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92473-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French J. G., Dodge H. J., Kjelsberg M. O., Mikkelsen W. M., Schull W. J. A study of familial aggregation of serum uric acid levels in the population of Tecumseh, Michigan, 1959-1960. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Jul;86(1):214–224. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick R., Ewan C. E., Bauer G. E., Neale F. C. Serum uric acid in normal and hypertensive Australian subjects. Aust N Z J Med. 1972 Nov;2(4):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1972.tb03936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. P., Barry P. E., Dawber T. R., McNamara P. M. Epidemiology of gout and hyperuricemia. A long-term population study. Am J Med. 1967 Jan;42(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume R., Weyers E. Relationship between total body water and surface area in normal and obese subjects. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Apr;24(3):234–238. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.3.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomäki H. A., Takkunen H. Gout and hyperuricemia in a Finnish rural population. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1969;15(2):112–120. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1969.15.issue-1-4.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeremy R., Towson J. Serum urate levels and gout in Australian males. Med J Aust. 1971 May 22;1(21):1116–1118. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1971.tb88075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDLE L., SEEGMILLER J. E., LASTER L. The enzymatic spectrophotometric method for determination of uric acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Dec;54:903–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKKELSEN W. M., DODGE H. J., VALKENBURG H. THE DISTRIBUTION OF SERUM URIC ACID VALUES IN A POPULATION UNSELECTED AS TO GOUT OR HYPERURICEMIA: TECUMSEH, MICHIGAN 1959-1960. Am J Med. 1965 Aug;39:242–251. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Scott J. T. Effect of weight-loss on plasma and urinary levels of uric acid. Lancet. 1972 Dec 9;2(7789):1223–1224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'SULLIVAN J. B., FRANCIS J. O., KANTOR N. COMPARISON OF A COLORIMETRIC (AUTOMATED) WITH AN ENZYMATIC (MANUAL) URIC ACID PROCEDURE. Clin Chem. 1965 Mar;11:427–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPERT A. J., HEWITT J. V. Gout and hyperuricaemia in rural and urban populations. Ann Rheum Dis. 1962 Jun;21:154–163. doi: 10.1136/ard.21.2.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbott J. H. It happened on the way to the XIII International Congress on Rheumatology in Kyoto and after I had arrived. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6 Suppl):699–708. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalokar J., Lellouch J., Claude J. R., Kuntz D. Serum uric acid in 23,923 men and gout in a subsample of 4257 men in France. J Chronic Dis. 1972 May;25(5):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(72)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


