Abstract
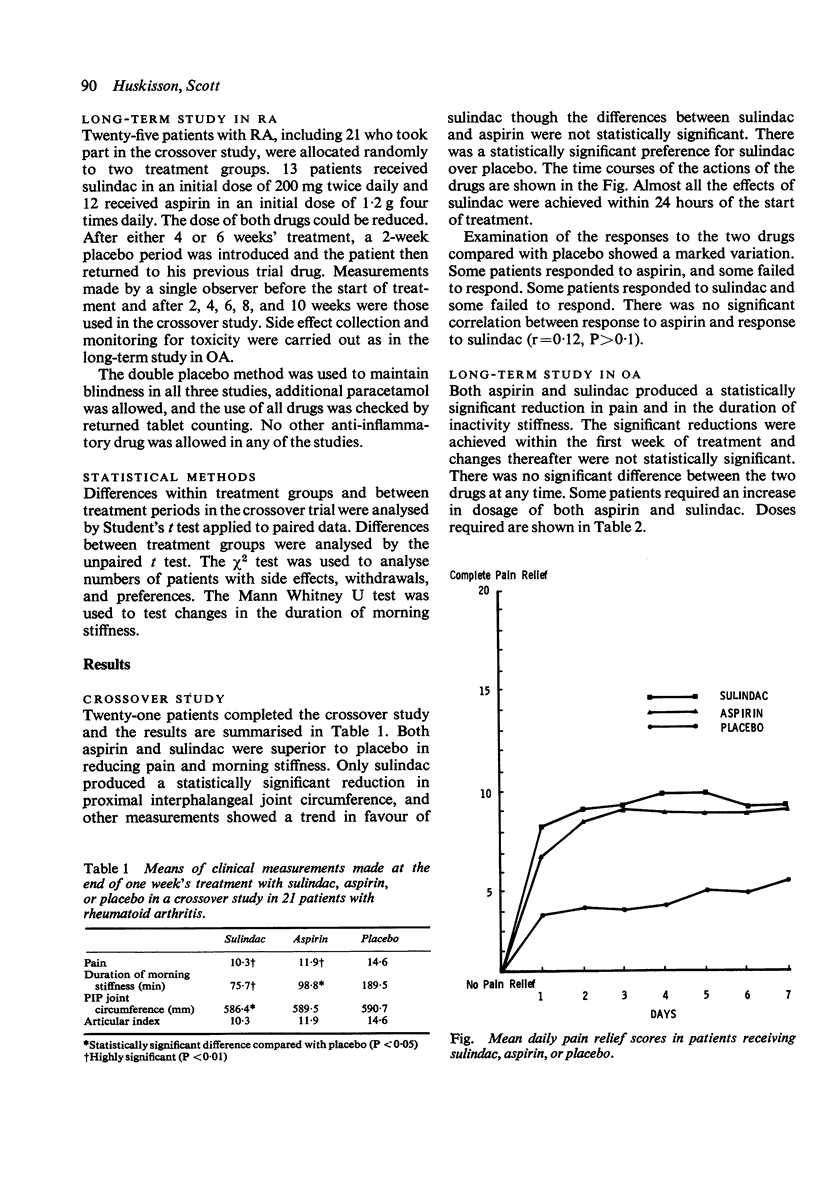
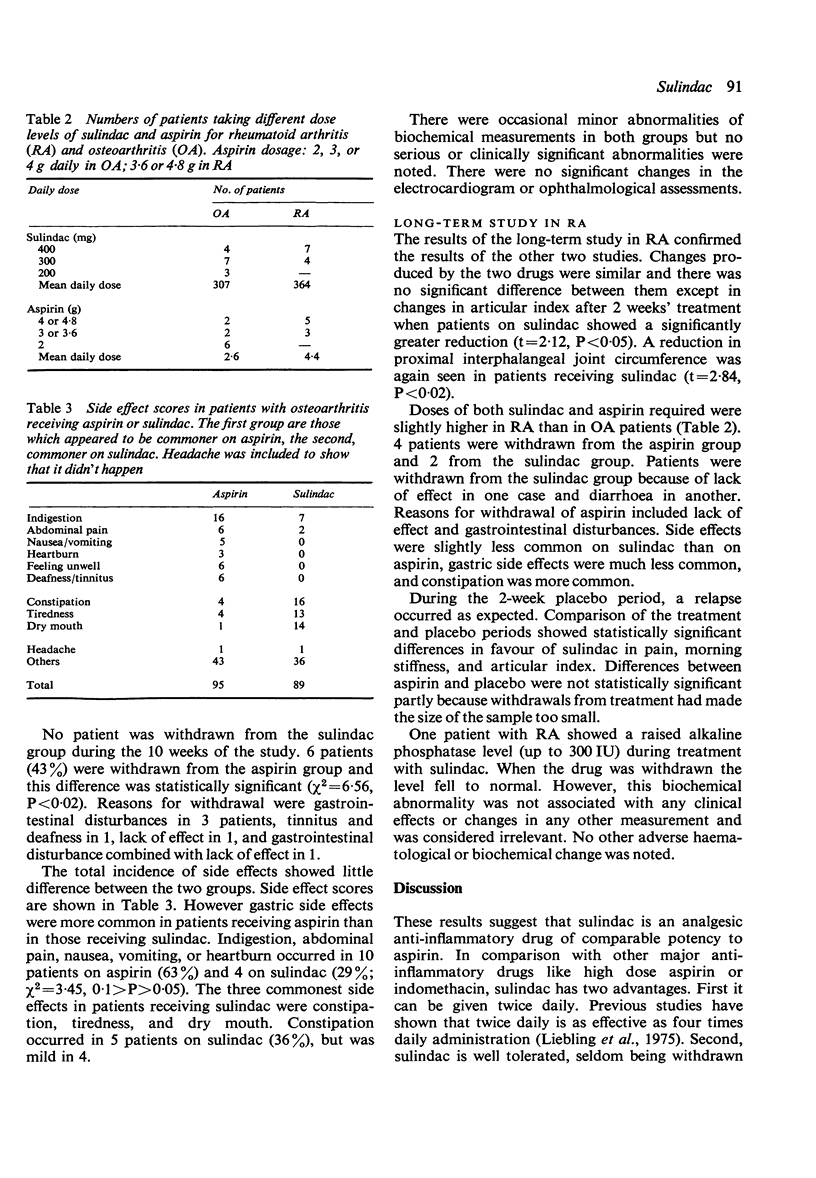
Trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis showed sulindac to be an analgesic with anti-inflammatory properties and at least as effective as aspirin. It was effective within 24 hours in doses of 300-400 mg daily. It had the advantages of twice daily administration and a lower incidence of gastric side effects than aspirin. Constipation, usually mild, occurred in 20-30% of cases. Like other anti-inflammatory drugs, it was effective in only a proportion of the patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boardman P. L., Hart F. D. Clinical measurement of the anti-inflammatory effects of salicylates in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1967 Nov 4;4(5574):264–268. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5574.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieppe P. A., Burry H. C., Grahame R., Perera T. Sulindac in osteoarthrosis of the hip. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1976 May;15(2):112–115. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/15.2.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribnau F. W., Lissone D. A. Ervaringen tijdens een dubbelblind onderzoek met MK 231 versus indomethacine bij lijders aan spondylitis ankylopoetica. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1975 Jul 12;119(28):1135–1135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucker H. B., Stauffer S. C., White S. D., Rhodes R. E., Arison B. H., Umbenhauer E. R., Bower R. J., McMahon F. G. Physiologic disposition and metabolic fate of a new anti-inflammatory agent, cis-5-fluro-2-methyl-1-(p-(methylsulfinyl)-benzylidenyl)-indene-3-acetic acid in the rat, dog, rhesus monkey, and man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1973 Nov-Dec;1(6):721–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


