Abstract
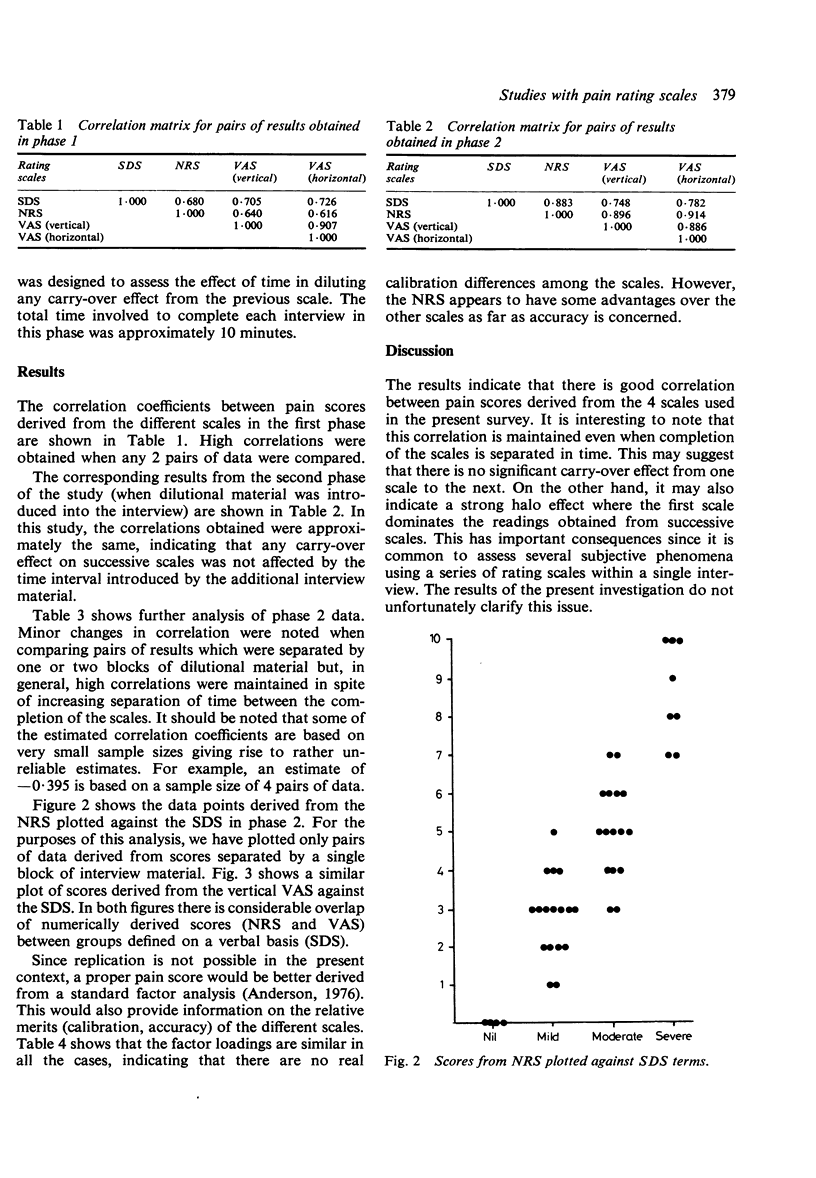
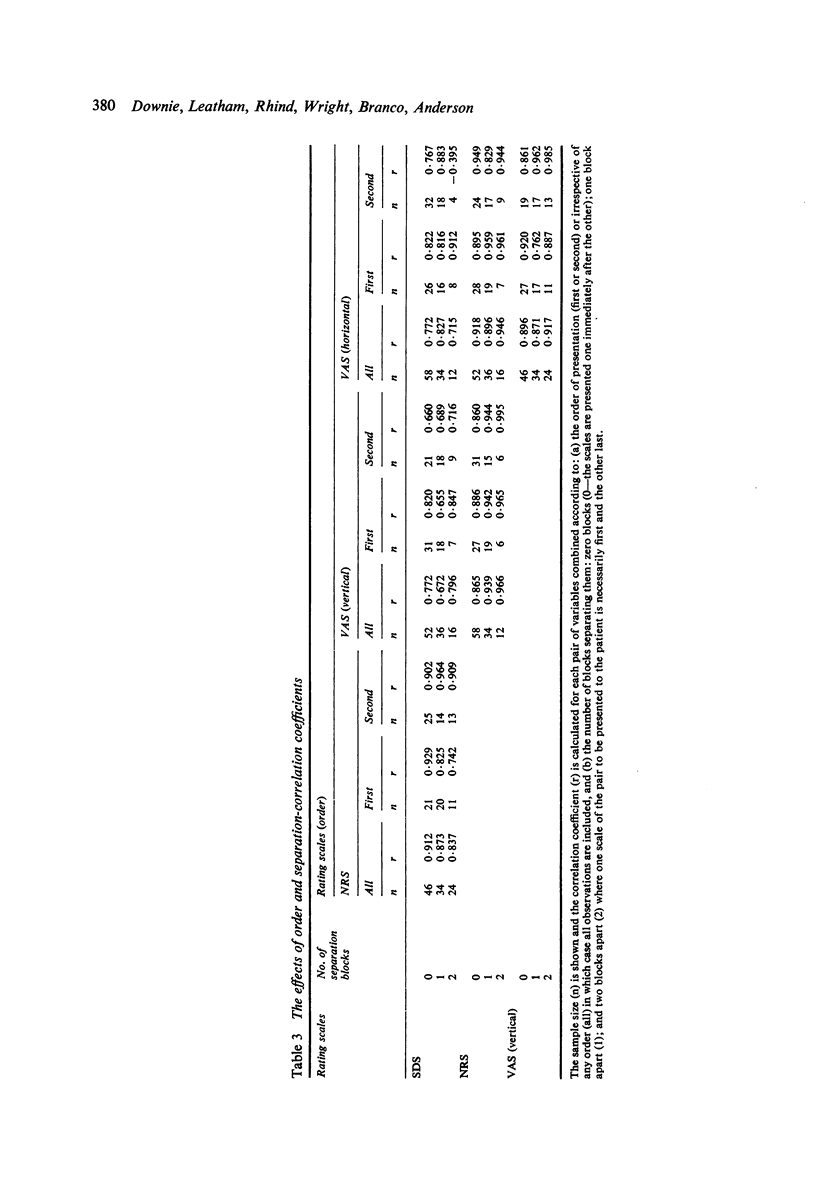
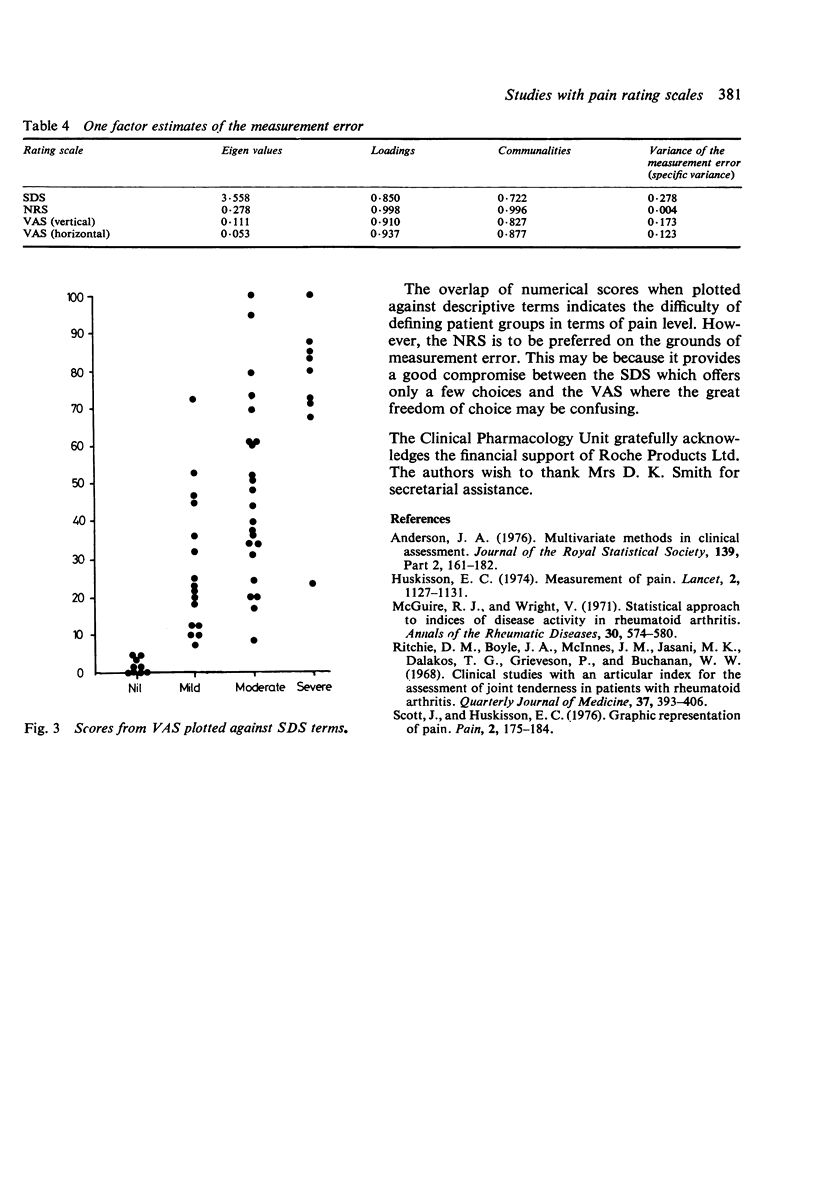
Good correlation has been shown between pain scores derived from 4 different rating scales. The correlation was maintained when presentation of the scales was separated by a series of questions and by physical examination. There is good evidence that the 4 scales are measuring the same underlying pain variable as they calibrate well. There is also evidence that an 11-point (0-10) numerical rating scale performs better than both a 4-point simple descriptive scale or a continuous (visual analogue) scale.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- McGuire R. J., Wright V. Statistical approach to indices of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Nov;30(6):574–580. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.6.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Huskisson E. C. Graphic representation of pain. Pain. 1976 Jun;2(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


