Abstract
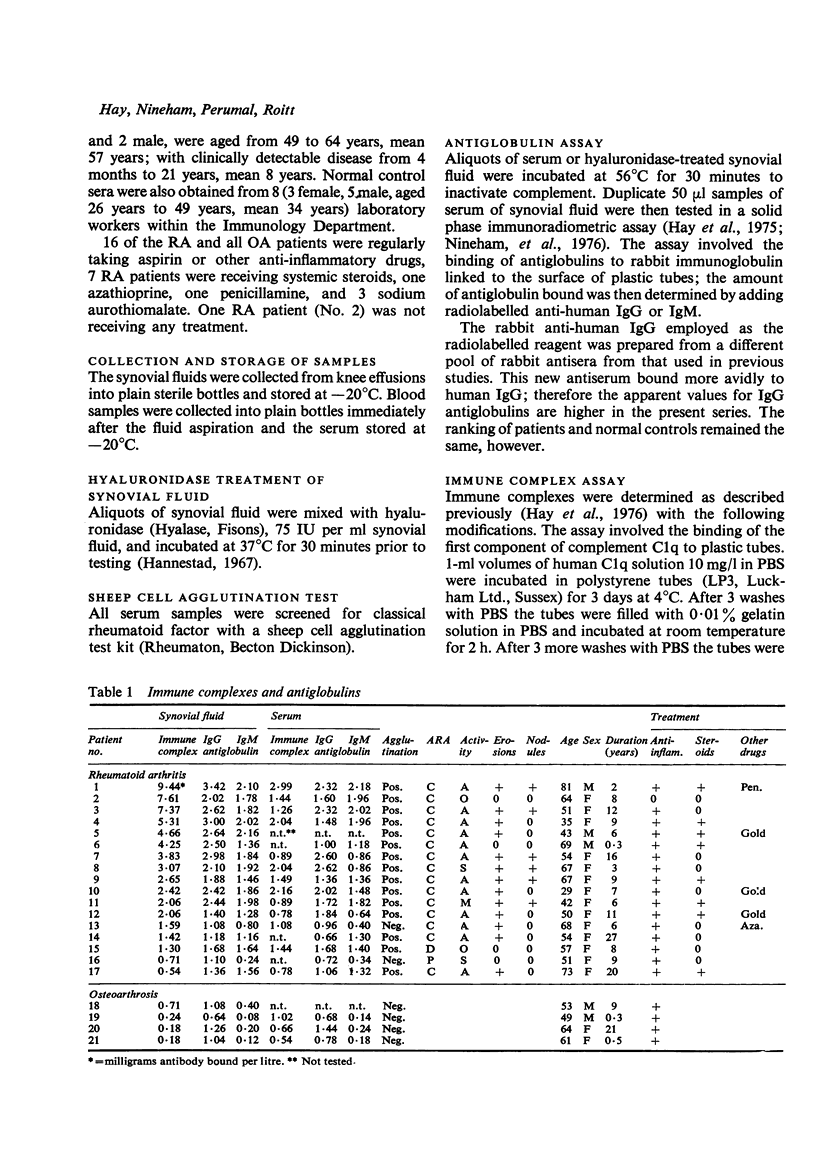
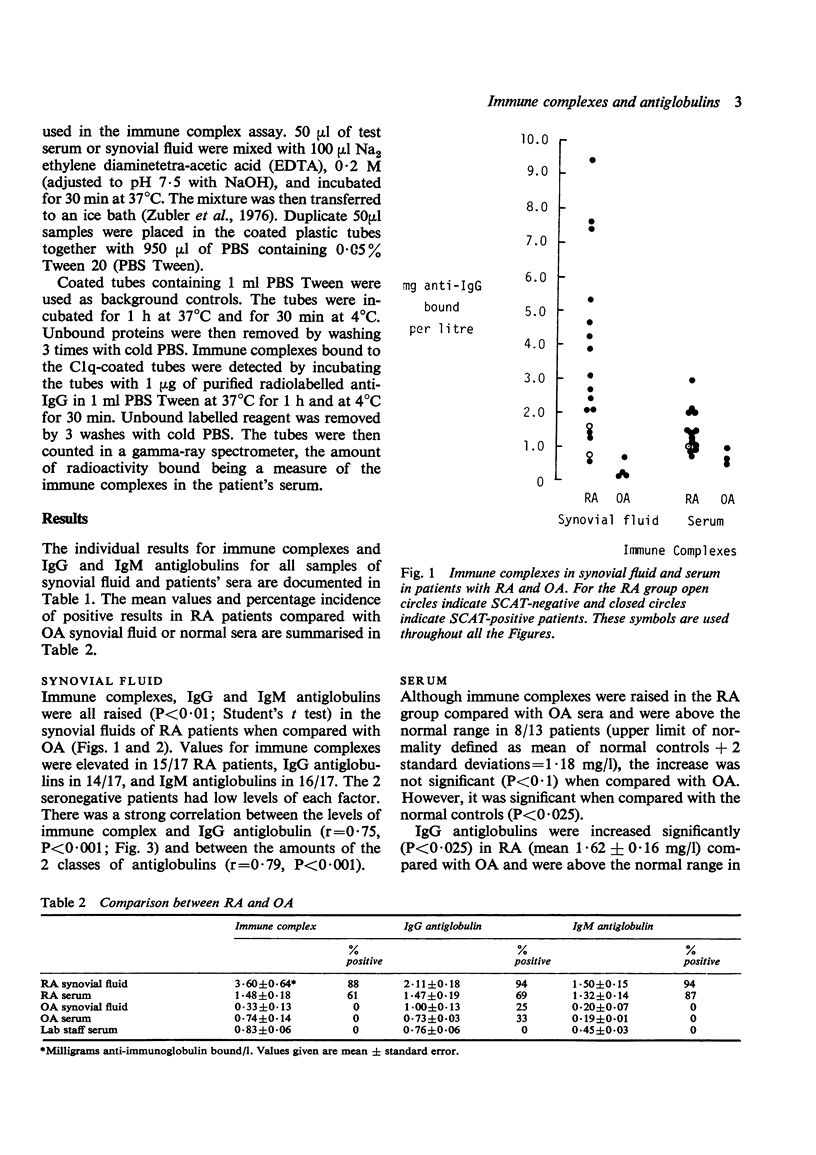
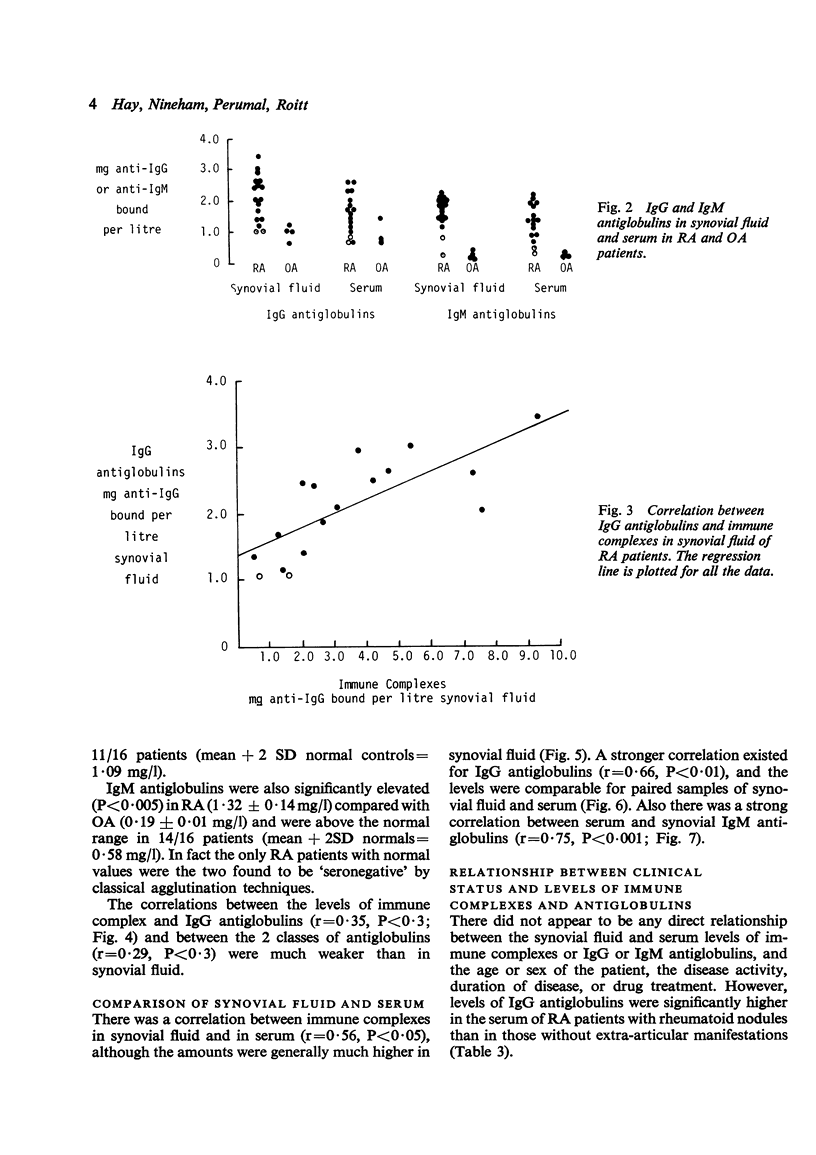
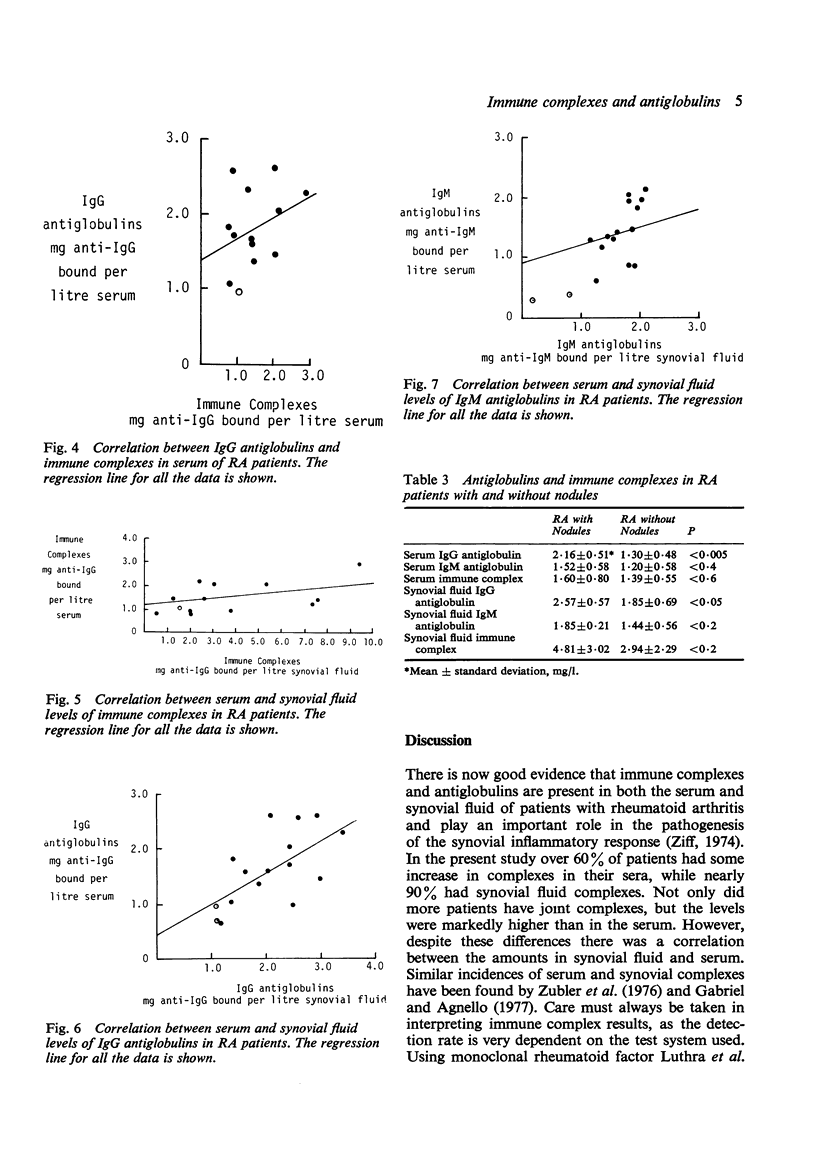
Solid phase radioimmunometric methods have been used to assay immune complexes and IgG and IgM antiglobulins in paired samples of synovial fluid and serum from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or osteoarthrosis. Over 60% of RA patients had some increase in complexes in their sera, while nearly 90% had synovial fluid complexes. Moreover, the levels of complexes within the joint were much higher than in the serum. Both IgG and IgM antiglobulins were raised in most RA patients.The levels of IgG antiglobulins--and to a less extent IgM antiglobulins--were nearly always higher in synovial fluid than in the corresponding serum sample.A strong correlation was found between the levels of immune complex and IgG antiglobulin. A marked association was seen between the presence of subcutaneous nodules and increased IgG antiglobulins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gabriel A., Jr, Agnello V. Detection of immune complexes. The use of radioimmunoassays with Clq and monoclonal rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):990–1001. doi: 10.1172/JCI108722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K. Presence of aggregated gamma-G-globulin in certain rheumatoid synovial effusions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jul;2(4):511–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for detection of IgG and IgM antiglobulins in seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 26;3(5977):203–204. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5977.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for the detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):396–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunder G. G., McDuffie F. C. Hypocomplementemia in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1973 Apr;54(4):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., FUDENBERG H. H., TOMASI T. B. Gamma globulin complexes in rheumatoid arthritis and certain other conditions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:117–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI104224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra H. S., McDuffie F. C., Hunder G. G., Samayoa E. A. Immune complexes in sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Radioimmunoassay with monocylonal rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):458–466. doi: 10.1172/JCI108112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Immunglobulin classes, subclasses and complexes of IgG rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid plasma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nineham L. J., Hay F. C., Roitt I. M. Laboratory diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: a solid phase radioassay for IgG and IgM antiglobulins. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Dec;29(12):1121–1126. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.12.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowoslawski A., Brzosko W. J. Immunopathology of rheumatoid arthritis. II. The rheumatoid nodule (the rheumatoid granuloma). Pathol Eur. 1967;2(3):302–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Zubler R. H., Gabay R., Joliat G., Karagevrekis C. H., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating complement breakdown products in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation between plasma C3d, circulating immune complexes, and clinical activity. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):862–868. doi: 10.1172/JCI108708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
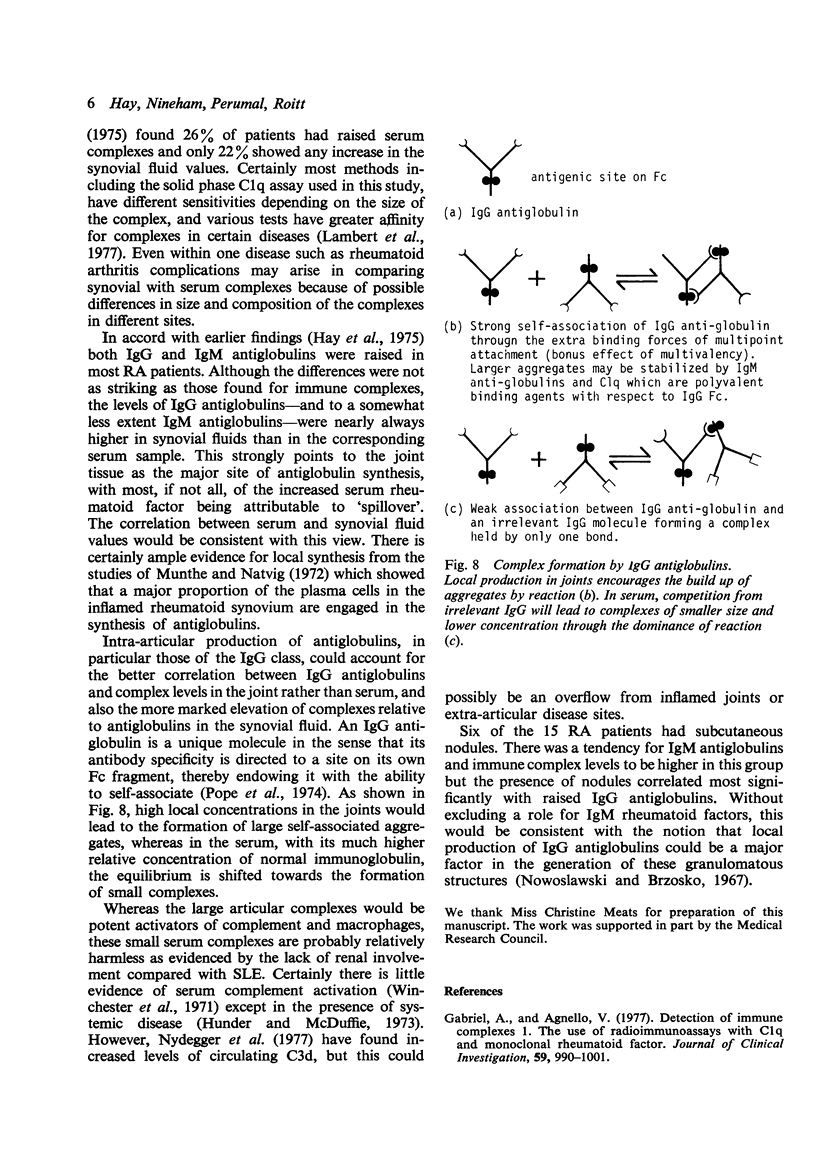
- Pope R. M., Teller D. C., Mannik M. The molecular basis of self-association of antibodies to IgG (rheumatoid factors) in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):517–521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M., Lloyd K. N., Corbett M. Elevated IgG antiglobulins in patients with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1970 Jan 3;1(7636):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90524-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G., Agnello V. Occurrence of -globulin complexes in serum and joint fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients: use of monoclonal rheumatoid factors as reagents for their demonstration. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):286s–295s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Nydegger U., Perrin L. H., Fehr K., McCormick J., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating and intra-articular immune complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of 125I-Clq binding activity with clinical and biological features of the disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1308–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI108399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


