Abstract
Using the Intralipid lipid tolerance test we could not demonstrate any direct effect of serum triglyceride on uric acid or any influence of hyperuricaemia on triglyceride removal. This result supports previous studies suggesting that hyperuricaemia and hypertriglyceridaemia are linked through the association of obesity and alcohol excess rather than a direct cause and effect mechanism. It was possible to demonstrate significant reductions of serum triglyceride in patients with gout by reducing either their alcohol intake or body weight. Reduction of serum uric acid by probenecid had no effect on serum triglyceride or cholesterol. Similarly, allopurinol had no significant effect on serum triglyceride, but a significant fall of serum cholesterol was observed.
Full text
PDF
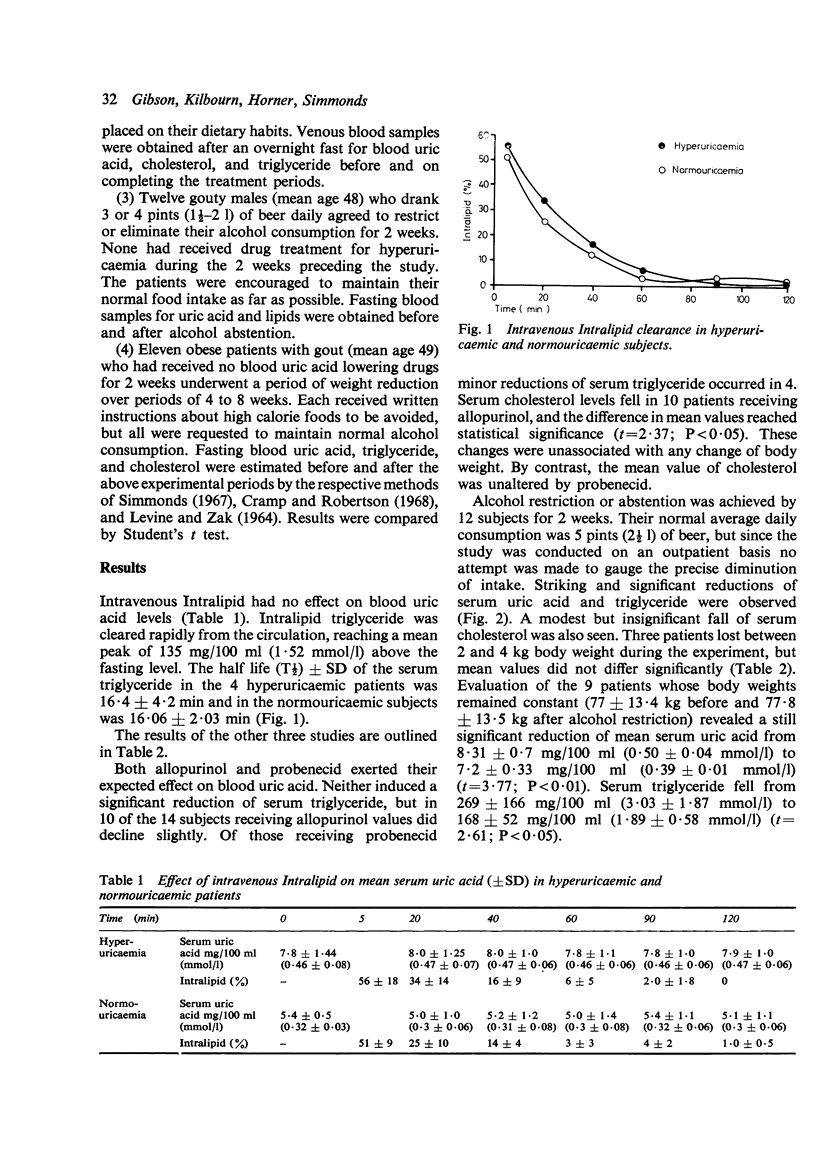
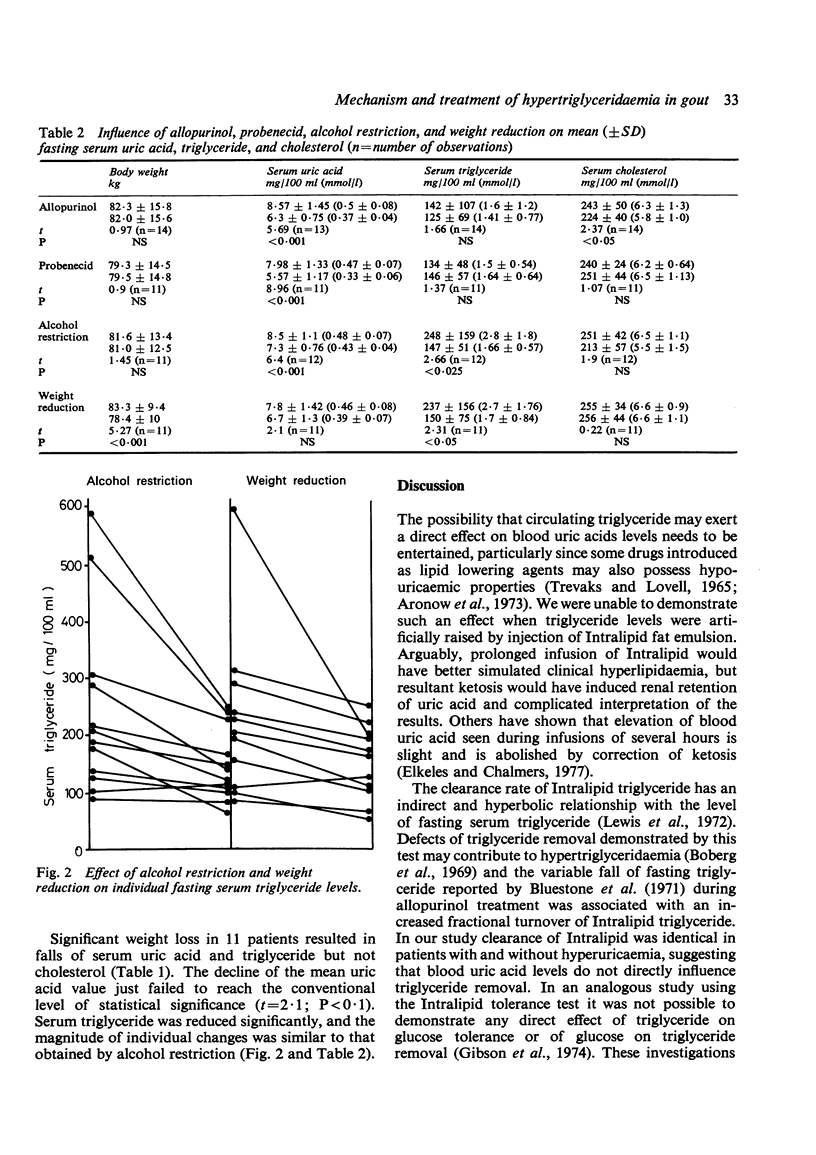


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronow W. S., Harding P. R., Khursheed M., Vangrow J. S., Papageorge's N. P. Effect of halofenate on serum uric acid. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 May-Jun;14(3):371–373. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973143371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraona E., Lieber C. S. Efcts of chronic ethanol feeding on serum lipoprotein metabolism in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):769–778. doi: 10.1172/JCI106290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Chait A., Lewis B. Familial hyperuricaemia and hypertriglyceridaemia. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Nov;32(6):497–500. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.6.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone R., Lewis B., Mervart I. Hyperlipoproteinaemia in gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Mar;30(2):134–137. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.2.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boberg J., Carlson L. A., Hallberg D. Application of a new intravenous fat tolerance test in the study of hypertriglyceridaemia in man. J Atheroscler Res. 1969 Mar-Apr;9(2):159–169. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(69)80051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., Dahms W. T., Greenway F. L., Marriott M., Molitch M., Atkinson R. Evaluation of the obese patient. 2. Clinical findings. JAMA. 1976 May 3;235(18):2008–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait A., Mancini M., February A. W., Lewis B. Clinical and metabolic study of alcoholic hyperlipidaemia. Lancet. 1972 Jul 8;2(7767):62–64. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91552-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramp D. G., Robertson G. The fluorometric assay of triglyceride by a semiautomated method. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):246–251. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington L. G., Scott J. T. Plasma lipid levels in gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Nov;31(6):487–489. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.6.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbarre F., Auscher C., Brouilhet H., de Géry A. Action de l'éthanol dans la goutte et sur le métabolisme de l'acide urique. Sem Hop. 1967 Feb 26;43(10):659–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkeles R. S., Chalmers R. A. Hypertriglyceridaemia and hyperuricaemia. Lancet. 1977 Jul 30;2(8031):252–252. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkeles R. S. The effect of hypolipidaemic therapy on serum uric acid concentration. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Sep;24(3):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson B. T. Alteration of urate metabolism by weight reduction. Aust N Z J Med. 1973 Aug;3(4):410–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1973.tb03115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson B. T., Knowles B. R. Triglyceride concentrations in primary gout and gout of chronic lead nephropathy. Metabolism. 1971 Aug;20(8):721–729. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(71)80001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN E. B., WALLACE S. L. HYPERTRIGLYCERIDEMIA IN GOUT. Circulation. 1964 Apr;29:SUPPL–SUPPL:513. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.29.4.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Fuller J. H., Grainger S. L., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Intralipid triglyceride and oral glucose tolerance. Diabetologia. 1974 Apr;10(2):97–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01219663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Grahame R. Gout and hyperlipidaemia. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jul;33(4):298–303. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.4.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90874-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Jr, DeBakey M. E., Foreyt J. P., Scott L. W., Thornby J. I. Dietary treatment of type IV hyperlipoproteinemia. JAMA. 1977 Mar 21;237(12):1212–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kral J. G., Lundholm K., Björntorp P., Sjöström L., Scherstén T. Hepatic lipid metabolism in severe human obesity. Metabolism. 1977 Sep;26(9):1025–1031. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE J. B., ZAK B. AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF SERUM TOTAL CHOLESTEROL. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Oct;10:381–384. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBER C. S., JONES D. P., LOSOWSKY M. S., DAVIDSON C. S. Interrelation of uric acid and ethanol metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1863–1870. doi: 10.1172/JCI104643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOSOWSKY M. S., JONES D. P., DAVIDSON C. S., LIEBER C. S. STUDIES OF ALCOHOLIC HYPERLIPEMIA AND ITS MECHANISM. Am J Med. 1963 Dec;35:794–803. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Boberg L., Mancini M., Carlson L. A. Determination of the intravenous fat tolerance test with intralipid by nephelometry. Atherosclerosis. 1972 Jan-Feb;15(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(72)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson J. H., Mello N. K. Alcohol-induced hyperlipidemia and beta lipoproteins. Science. 1973 Jun 29;180(4093):1372–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4093.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielants H., Veys E. M., de Weerdt A. Gout and its relation to lipid metabolism. I. Serum uric acid, lipid, and lipoprotein levels in gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Nov;32(6):501–505. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.6.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Hirsch E. Z. Mechanism of alcohol-induced hypertriglyceridemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Sep;66(3):357–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Scott J. T. Effect of weight-loss on plasma and urinary levels of uric acid. Lancet. 1972 Dec 9;2(7789):1223–1224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Reaven G. M., Farquhar J. W. Effects of weight reduction on obesity. Studies of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in normal and hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):64–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI107560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen R., Nikkilä E. A., Koskinen S., Penttinen K., Sarna S. Association of serum lipids and obesity with cardiovascular mortality. Br Med J. 1977 Nov 5;2(6096):1185–1187. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6096.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. T., Sturge R. A. The effect of weight loss on plasma and urinary uric acid and lipid levels. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;76B:274–277. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3285-5_41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen M. R., Nikkilä E. A. Nocturnal hypertriglyceridemia and hyperinsulinemia following moderate evening intake of alcohol. Acta Med Scand. 1977;202(3):173–177. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1977.tb16807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevaks G., Lovell R. R. Effect of atromid and its components on uric acid excretion and on gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Nov;24(6):572–575. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.6.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano K., Rhoads G., Kagan A. Epidemiology of serum uric acid among 8000 Japanese-American men in Hawaii. J Chronic Dis. 1977 Mar;30(3):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(77)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


