Abstract
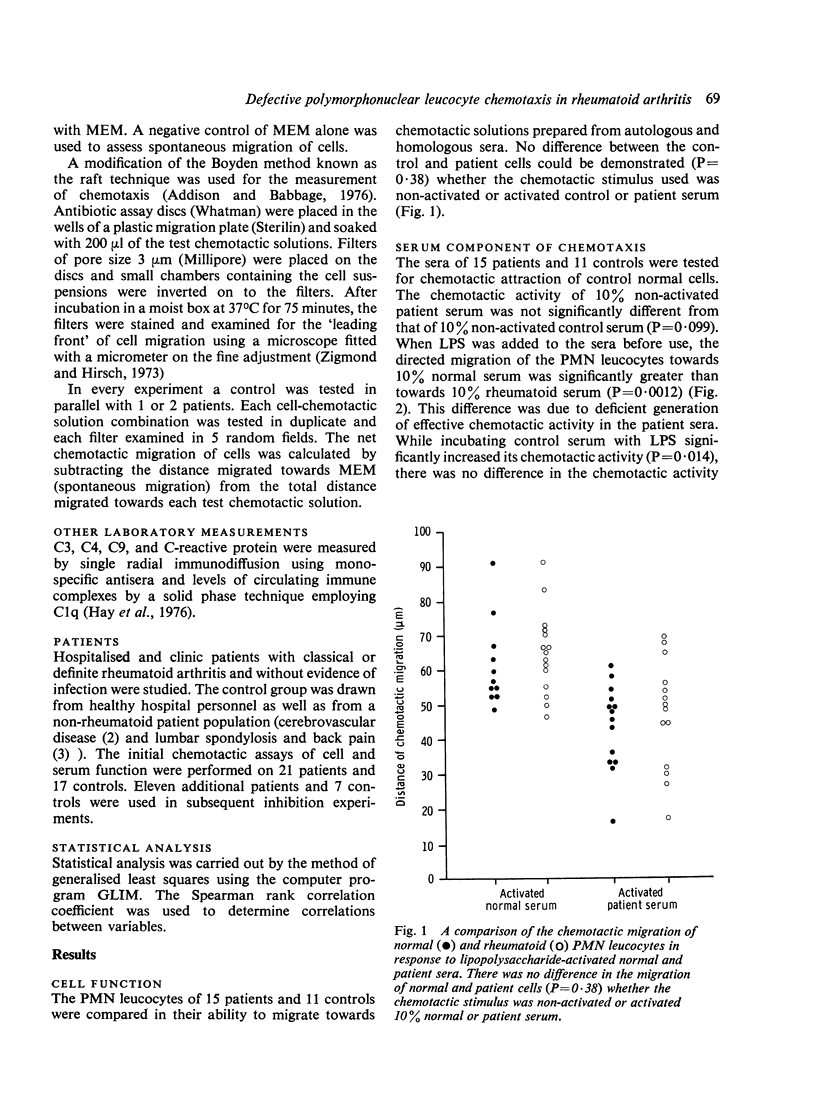
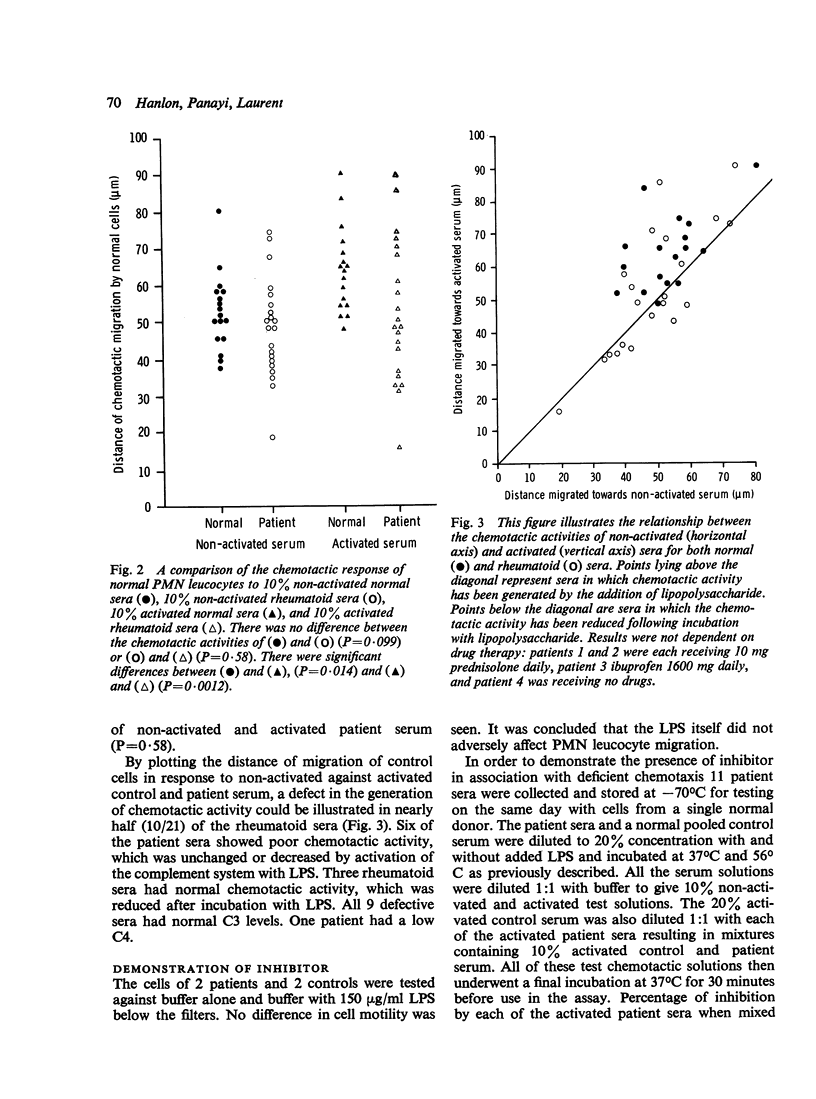
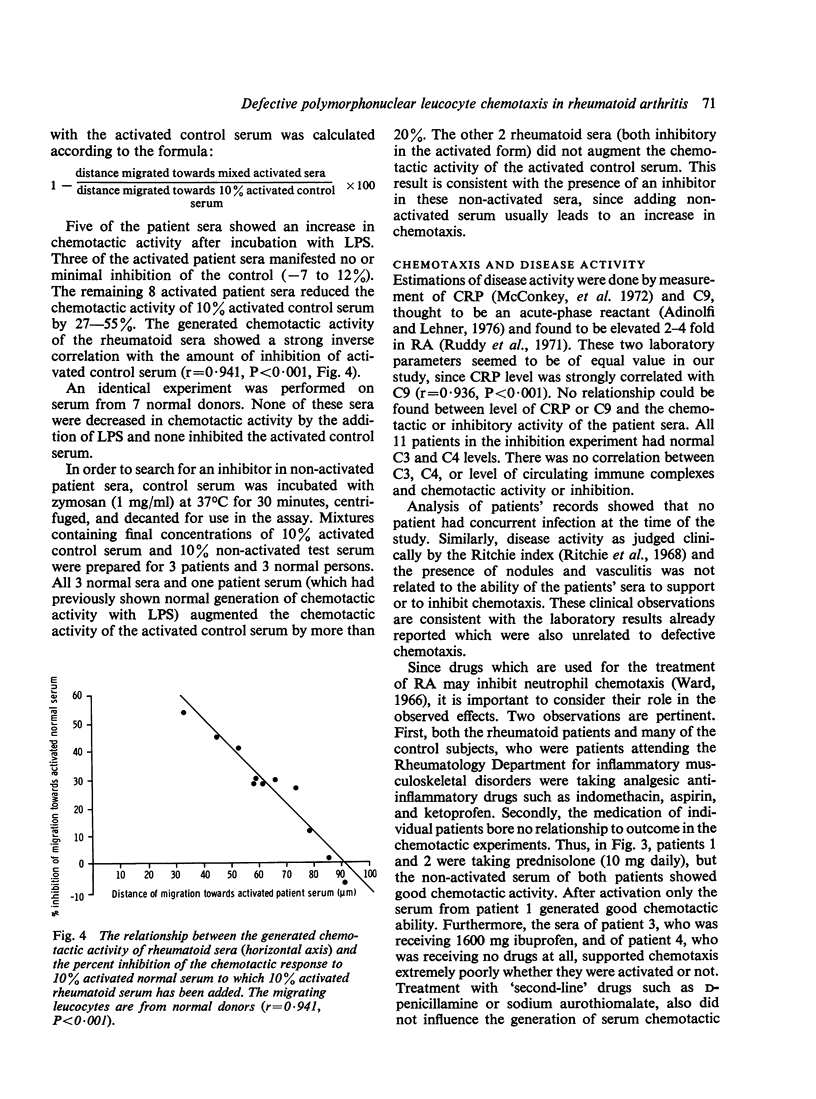
Cellular and/or serum components of polymorphonuclear leucocyte chemotaxis were assessed in 21 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. No difference in the chemotactic migration of control and patient cells in response to a number of chemotactic solutions could be detected (P = 0.38). Deficient generation of chemotactic activity in patient sera (P = 0.58) as compared to control sera (P = 0.014) after incubation of the sera with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide, resulted in a significant difference in the chemotactic activity of the control and rheumatoid serum preparations for polymorphonuclear leucocytes (P = 0.0012). This defect was associated with the presence of a serum inhibitor of chemotaxis, the potency of which was inversely correlated with the level of chemotactic activity generated in the rheumatoid sera (r = -0.941, P less than 0.001).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison I. E., Babbage J. W. A raft technique for chemotaxis: a versatile method suitable for clinical studies. J Immunol Methods. 1976;10(4):385–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J., Mowat A. G., Kirk J. A. A simplified method for the measurement of chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from human blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Mar;77(3):501–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenberg J. L., Ward P. A. Chemotactic factor inactivator in normal human serum. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1200–1206. doi: 10.1172/JCI107287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Kimball H. R., Decker J. L. Neutrophil chemotaxis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Mar;33(2):167–172. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeo A. N., Andersen B. R. Defective chemotaxis associated with a serum inhibitor in cirrhotic patients. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 6;286(14):735–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204062861401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epps D. E., Williams R. C., Jr Serum chemotactic inhibitory activity: heat activation of chemotactic inhibition. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):741–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.741-749.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J. Defective responsiveness to ascorbic acid of neutrophil random and chemotactic migration in Felty's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Dec;35(6):510–515. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.6.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for the detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):396–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderazo E. G., Ward P. A., Woronick C. L., Kubik J., DeGraff A. C., Jr Leukotactic dystunction in sarcoidosis. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Apr;84(4):414–419. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-4-414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey B., Crockson R. A., Crockson A. P. The assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. A study based on measurements of the serum acute-phase reactants. Q J Med. 1972 Apr;41(162):115–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson P. J., Hazleman B. L., Barnett I. G., MacLennan I. C., Mowat A. G. Factors relating to circulating immune complexes in rheumatoid arthirits. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):314–320. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Everson L. K., Schur P. H., Austen K. F. Hemolytic assay of the ninth complement complement component: elevation and depletion in rheumatic diseases. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):259s–275s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C., Dupree E., Goldman A. S., Lord R. A. A serum inhibitor of leukotaxis in a child with recurrent infections. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jun;79(6):878–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G., Ward P. A. Two distinct chemotactic factor inactivators in human serum. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):843–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Palmer D. L., Williams R. C., Jr Characterization of serum inhibitors of neutrophil chemotaxis associated with anergy. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):189–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Strickland R. G., Williams R. C., Jr Inhibitors of leukocyte chemotaxis in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Berenberg J. L. Defective regulation of inflammatory mediators in Hodgkin's disease. Supernormal levels of chemotactic-factor inactivator. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 10;290(2):76–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401102900203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Goralnick S., Bullock W. E. Defective leukotaxis in patients with lepromatous leprosy. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jun;87(6):1025–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Ozols J. Characterization of the protease activity in the chemotactic factor inactivator. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):123–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI108440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. The chemosuppression of chemotaxis. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):209–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


