Abstract
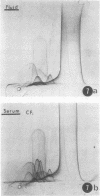
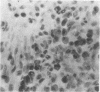
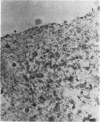
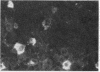
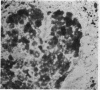
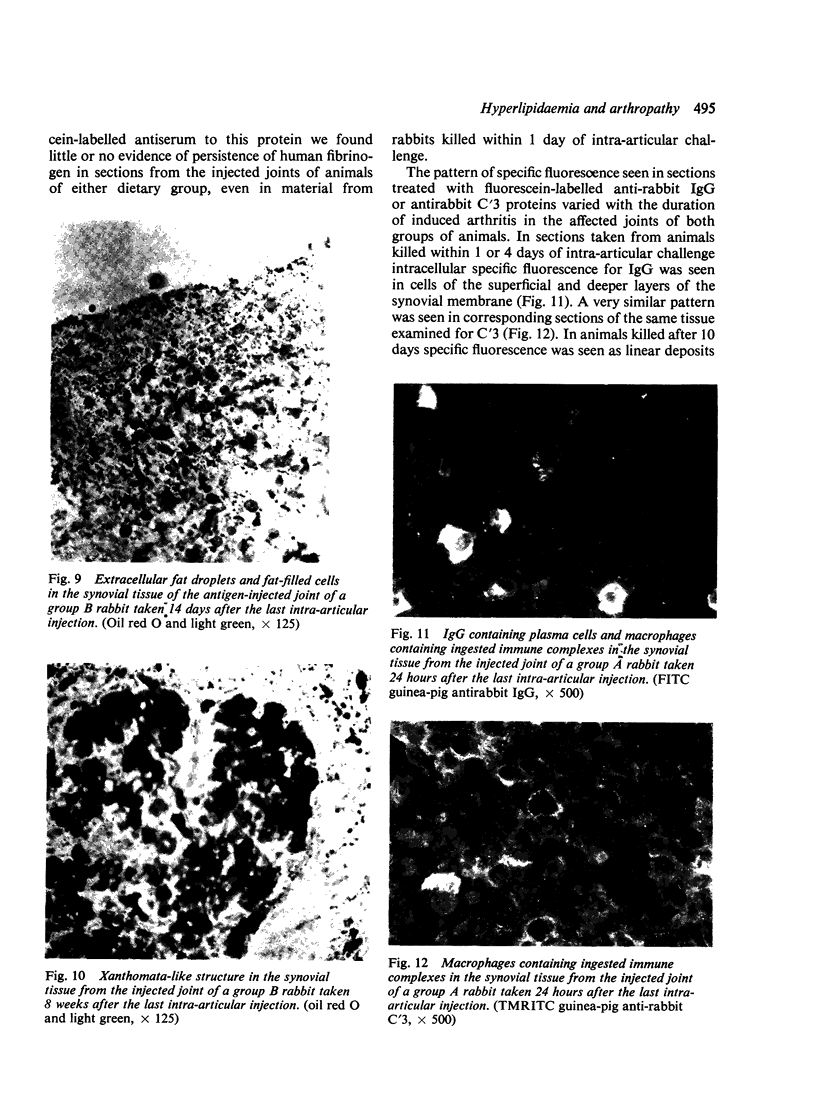
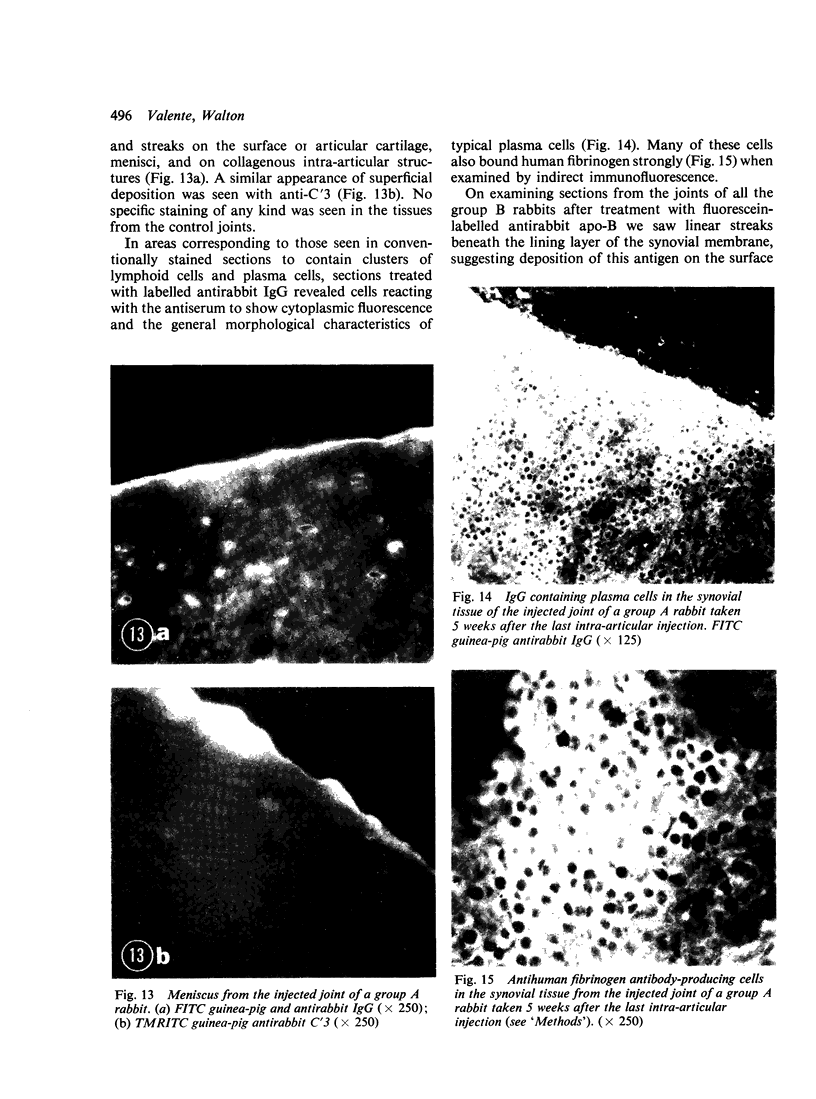
In order to investigate the known associations between hyperlipidaemia and various rheumatic complaints, immune arthritis and hyperlipidaemia have been induced concurrently in rabbits. The results obtained show that: (1) Rabbit apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins (LpB), which are normally virtually excluded from joint fluid, gain access to the inflamed joint in the serous effusion and serve as intrinsic indicators of altered local permeability to macromolecules. (2) Much of the LpB entering the joint space is taken up by the phagocytic cells and, following intracellular hydrolysis, leaves a lipid residue. In some chronically affected joints these residues are modified so as to give rise to crystalline cholesterol and its esters. Such crystals may serve as a chronic irritant in the joint. (3) In addition intact LpB is found sequestered in the superficial layers of intra-articular collagenous structures of the challenged joint in a distribution identical with that of similarly sequestered immune complexes and complement, suggesting altered permeability of these intra-articular structures also.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON A. J. THE FORMATION OF CHONDROMUCOPROTEIN-FIBRINOGEN AND CHONDROMUCOPROTEIN-BETA-LIPOPROTEIN COMPLEXES. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:460–469. doi: 10.1042/bj0880460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Ziff M., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. II. Preferential localization of antigen-antibody complexes to collagenous tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A., Glynn L. E. Is persisting antigen responsible for the chronicity of experimental allergic arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):34–38. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn L. E. The chronicity of inflammation and its significance in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Mar;27(2):105–121. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker R. J., Hawker L. M. A rapidly produced 125I labelled autologous fibrinogen: in vitro properties and preliminary metabolic studies in man. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jun;29(6):495–501. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.6.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister J. R., Mannik M. Antigen retention in joint tissues in antigen-induced synovitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Apr;16(4):615–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Smiley J. D., Ziff M. Electron microscopic demonstration of immunoglobulin deposition in rheumatoid cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):563–576. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E. Mechanism of trapping of immune complexes in joint collagenous tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Dec;22(3):473–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Somerville J. A. Permeability of human synovial membrane to plasma proteins. Relationship to molecular size and inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Sep-Oct;14(5):560–570. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullagh K. G., Ehrhart L. A. Increased arterial collagen synthesis in experimental canine atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1974 Jan-Feb;19(1):13–28. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(74)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. J., Bradby G. V., Walton K. W. Fibrous long-spacing collagen in human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1978 Nov;31(3):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(78)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propp R. P., Alper C. A. Rabbit C3 isolation and characterization of reactions in vitro and during in vivo antigen-antibody interaction. Immunology. 1969 Nov;17(5):695–707. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondier J., Cayla J., Roux H., Turpin G. Hyperlipidémies et manifestations de la sphère rhumatologique. Sem Hop. 1977 Apr 9;53(14-15):813–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkin P. A. Synovial permeability in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jul;22(7):689–696. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W., Morris C. J. Studies on the passage of plasma proteins across arterial endothelium in relation to atherogenesis. Prog Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;13:138–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W., Thomas C., Dunkerley D. J. The pathogenesis of xanthomata. J Pathol. 1973 Apr;109(4):271–289. doi: 10.1002/path.1711090402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKNER J., UDDIN J., GANTNER G. E., Jr, DORNER R. W. CHOLESTEROL CRYSTALS IN SYNOVIAL FLUID. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Mar;60:436–446. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-3-436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]