Abstract
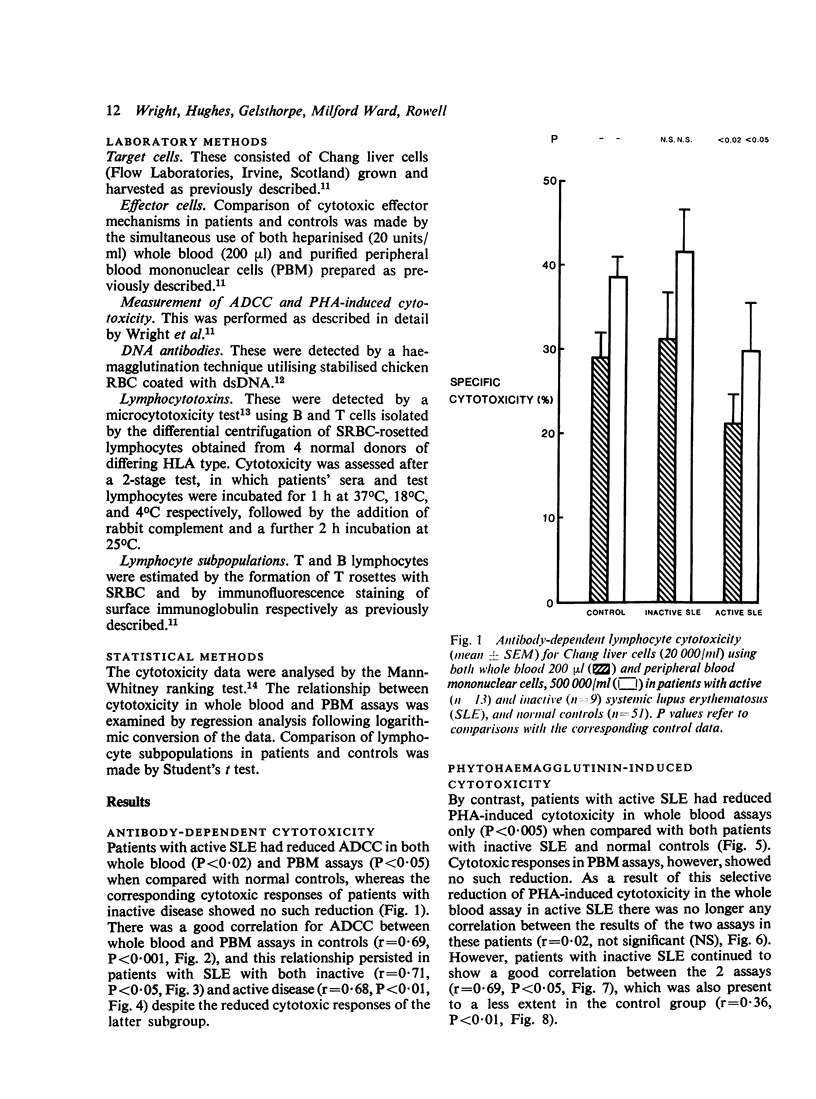
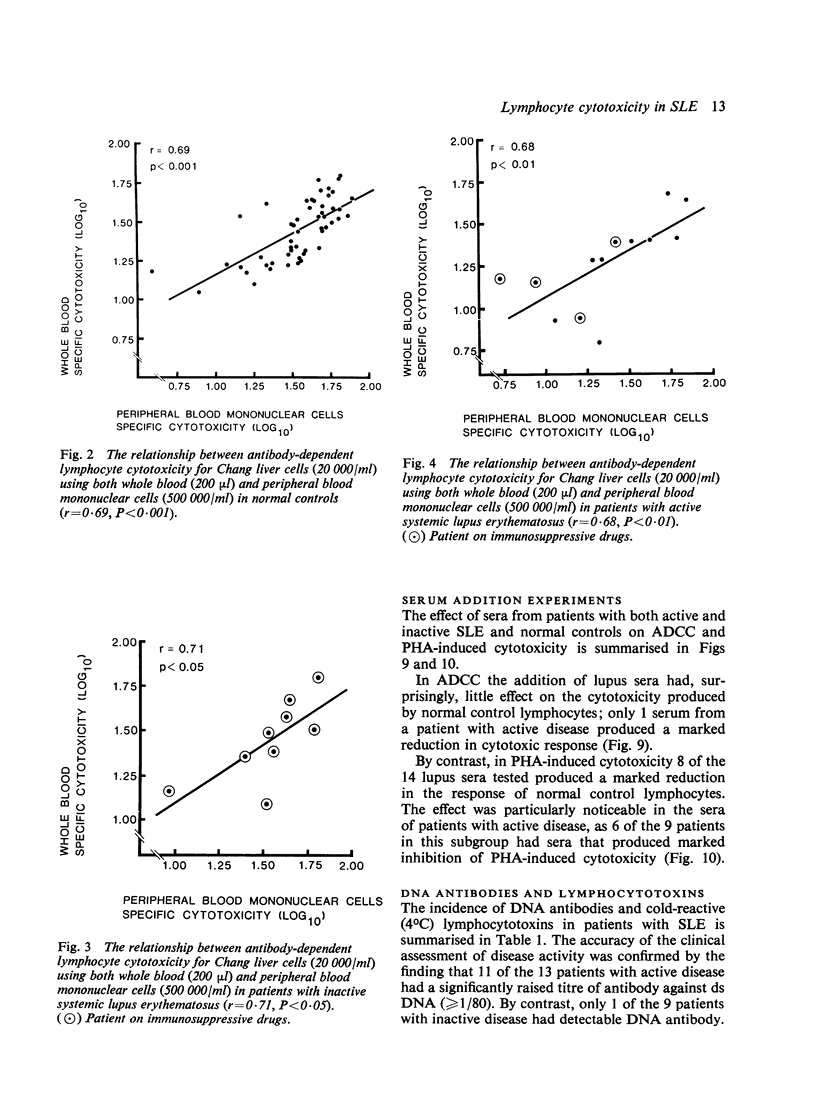
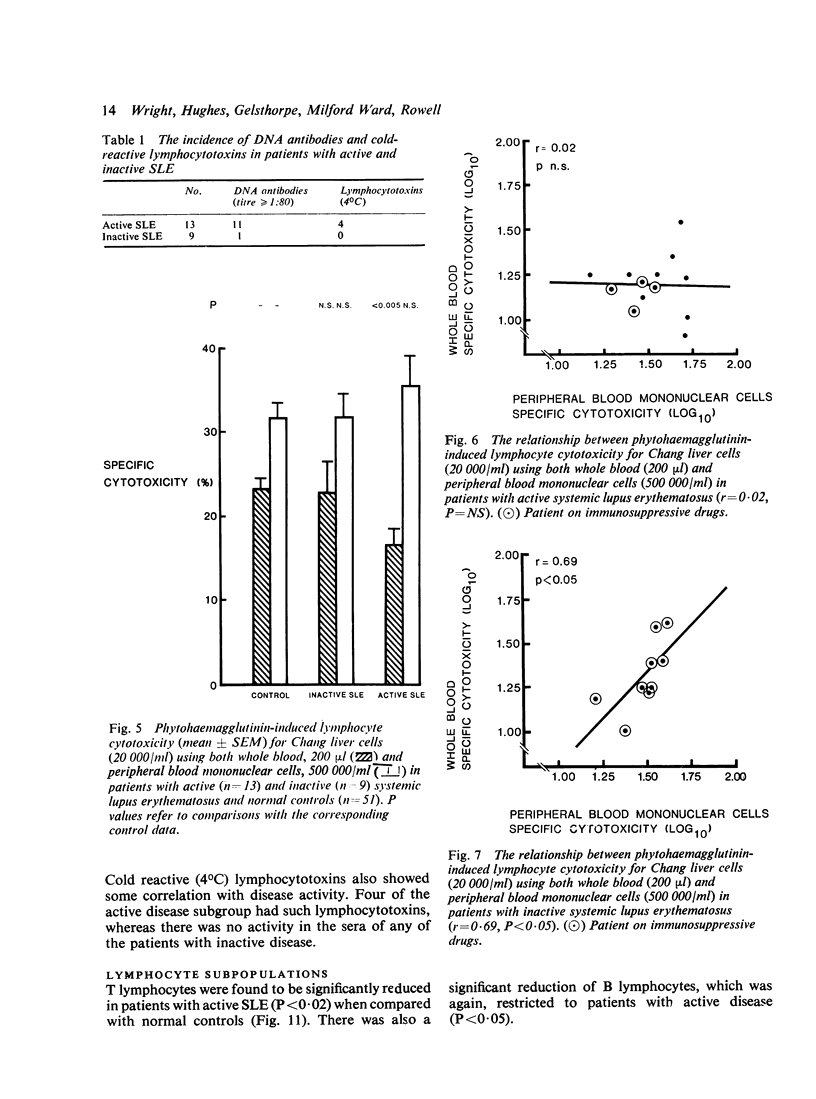
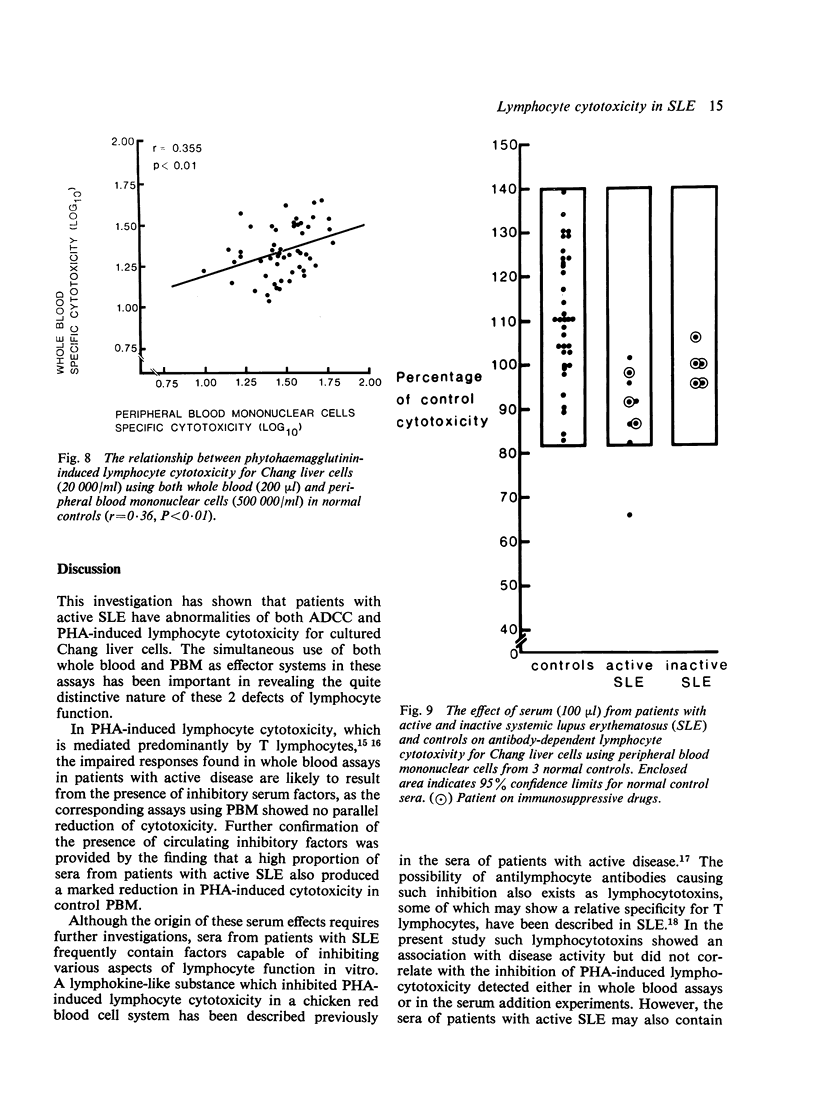
An investigation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity in 22 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), using both whole blood and purified peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBM) to measure antibody-dependent (ADCC) and phytohaemagglutinin (PHA)-induced lymphocyte cytotoxicity for Chang liver cells, has revealed 2 distinct abnormalities in patients with active disease. PHA-induced cytotoxicity was found to be selectively reduced in whole blood assays only (P less than 0.05), whereas ADCC was impaired in both whole blood (P = 0.02) and PBM (P less than 0.05) assays, when comparison was made with 52 normal controls. The addition of patients' sera to corresponding assays utilizing control PBM confirmed that the impaired PHA-induced cytotoxicity resulted from circulating inhibitory serum factors. Surprisingly little effect, however, was exerted on ADCC assays. These findings suggest that there is a reduction in numbers and/or functional capacity of Fc-receptor cells in active SLE, which may have pathogenetic implications.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amlot P. L., Unger A. Binding of phytohaemagglutinin to serum substances and inhibition of lymphocyte transformation in Hodgkin's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):520–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. M., Harding B., Mirick G. R., Schneider J., Quismorio F. P., Friou G. J. Selective decrease in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in systemic lupus erythematosus and progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Nov;34(2):235–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelsthorpe K., Doughty R. W. An easily produced micro-cytotoxic test plate with a further modification of the standard micro-cytotoxic technique for lymphocyte typing. Med Lab Technol. 1971 Jan;28(1):22–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey P., Edwards A., Edwards J. Characterization of mononuclear effector cells in human blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):104–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Garrett M. A. Lymphocyte reactivity to mitogens in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):92–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P., Holt S., Rowell N. R., Dodd J. K. Relationship of phytohaemagglutinin-induced lymphocyte transformation to disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Apr;35(2):97–105. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liburd E. M., Pazderka V., Russell A. S., Dossetor J. B. Fibroblast lysis by lymphocytes from normal persons and SLE patients on short-term cultures. Immunology. 1976 Nov;31(5):767–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lies R. B., Messner R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Relative T-cell specificity of lymphocytotoxins from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 May-Jun;16(3):369–375. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Lindström F. D., Williams R. C., Jr Peripheral blood lymphocyte cell surface markers during the course of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3046–3056. doi: 10.1172/JCI107503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalevicz R., Many A., Ramot B., Trainin N. The in vitro effect of thymic humoral factor and levamisole on peripheral blood lymphocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jan;31(1):111–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruíz-Argüelles A., Díaz-Jouanen E., Alarcón-Segovia D. PHA-induced cellular cytotoxicity. Inhibition by a nonimmunoglobulin factor present in sera from patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jan;22(1):59–65. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Suppressor-cell antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. Possible mechanism for suppressor-cell dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):536–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI109333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):954–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI109396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Chin W., Friou G. J., Cooper S. M., Harding B., Hill R. L., Quismorio F. P. Reduced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayanova T. G., Sura V. V., Svet-Moldavsky G. J. Destruction of human cells in tissue culture by lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1966 Feb 26;1(7435):452–454. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91456-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsinger P. D. Lymphocyte responsiveness in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jan-Feb;19(1):88–92. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Froland S. S., Michaelsen T. E. Characterization of subpopulations of human lymphoid cells participating in phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A-induced cytotoxicity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(4):488–497. doi: 10.1159/000231243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. K., Hughes P., Rowell N. R., Sneddon I. B. Antibody-dependent and phytohaemagglutinin-induced lymphocyte cytotoxicity in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):175–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


