Abstract
HLA B27 is associated with a number of forms of arthritis, including ankylosing spondylitis. It has been suggested that the disease is caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae and that the bacterium evokes an odd immune response because it cross-reacts with HLA B27. This proposed cross-reactivity was investigated in a number of ways. The results consistently failed to confirm evidence from cross reaction, even in antisera with activity against both HLA B27-positive lymphocytes and klebsiella. It is suggested that the anomalous anti-klebsiella response of rabbits immunised with pools of HLA B27-positive leucocytes may be caused by antigenic bacterial fragments on the cells of infected individuals.
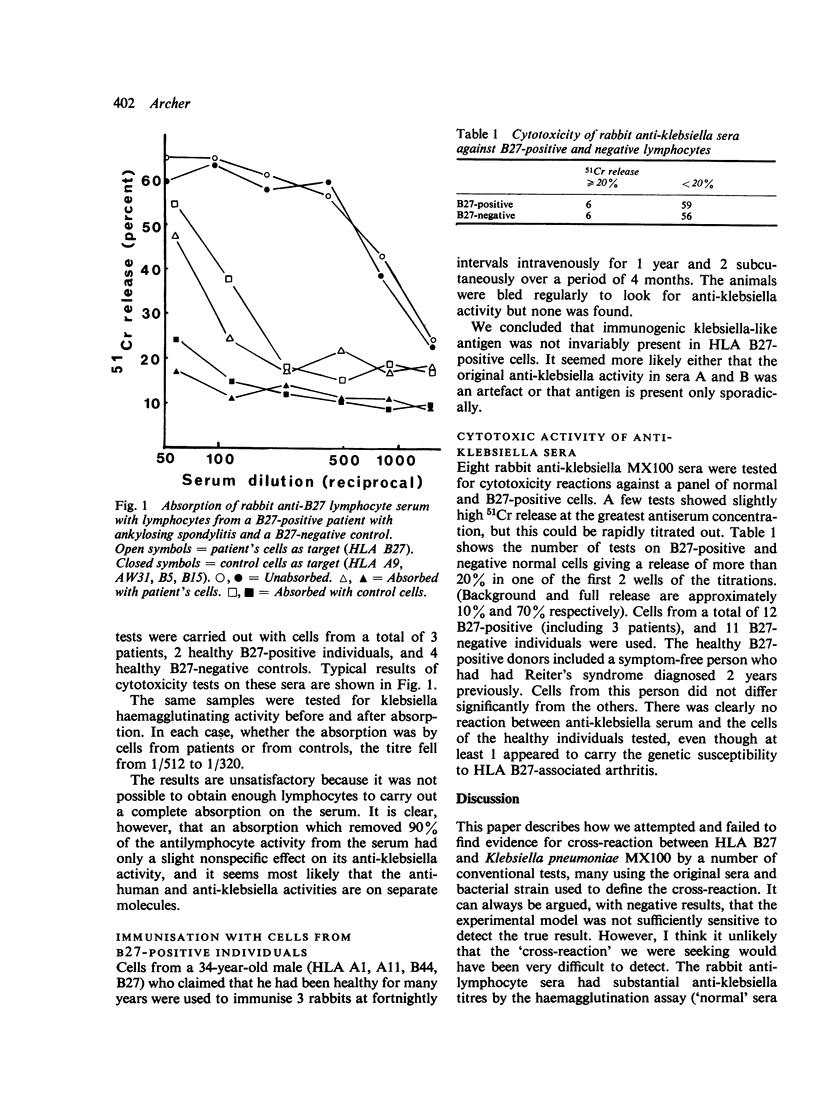
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYUM A. SEPARATION OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS. Nature. 1964 Nov 21;204:793–794. doi: 10.1038/204793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastmond C. J., Willshaw H. E., Burgess S. E., Shinebaum R., Cooke E. M., Wright V. Frequency of faecal Klebsiella aerogenes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and controls with respect to individual features of the disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Apr;39(2):118–123. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.2.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer R. W., Cawdell D. R., Cowling P., Ebringer A. Sequential studies in ankylosing spondylitis. Association of Klebsiella pneumoniae with active disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Apr;37(2):146–151. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.2.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer R., Cooke D., Cawdell D. R., Cowling P., Ebringer A. Ankylosing spondylitis: klebsiella and HL-A B27. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1977 Aug;16(3):190–196. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/16.3.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas de St Groth, Webster R. G. Disquisitions of Original Antigenic Sin. I. Evidence in man. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):331–345. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas de St Groth, Webster R. G. Disquisitions on Original Antigenic Sin. II. Proof in lower creatures. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):347–361. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy A. F., Alexander K., Bashir H. V., Edmonds J. A factor(s) in Klebsiella culture filtrates specifically modifies an HLA-B27 associated cell-surface component. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):782–784. doi: 10.1038/283782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodinka L., Gömör B., Merétey K., Zahumenszky Z., Géher P., Telegdy L., Bozsóky S. HLA-B27-associated spondylarthritis in chronic brucellosis. Lancet. 1978 Mar 4;1(8062):499–499. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi T., Mäkelä O. Strain differences in the fine specificity of mouse anti-hapten antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Jun;3(6):323–330. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seager K., Bashir H. V., Geczy A. F., Edmonds J., de Vere-Tyndall A. Evidence for a specific B27-associated cell surface marker on lymphocytes of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):68–70. doi: 10.1038/277068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. E., Brewerton D. A. Faecal carriage of klebsiella by patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Feb;39(1):37–44. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Avakian H., Cowling P., Ebringer A., Wooley P., Panayi G., Ebringer R. Ankylosing spondylitis, HLA-B27 and Klebsiella. I. Cross-reactivity studies with rabbit antisera. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980 Feb;61(1):85–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



