Carozzi VA, Canta A, Oggioni N, Ceresa C, Marmiroli P, Konvalinka J, Zoia C, Bossi M, Ferrarese C, Tredici G, Cavaletti G (2008) Expression and distribution of ‘high affinity’ glutamate transporters GLT1, GLAST, EAAC1 and of GCPII in the rat peripheral nervous system. Journal of Anatomy, 213(5):539–46. 10.1111/j.1469‐7580.2008.00984.x
In the article which appeared in the Journal of Anatomy entitled ‘Expression and distribution of ‘high affinity’ glutamate transporters GLT1, GLAST, EAAC1 and of GCPII in the rat peripheral nervous system’, the authors wish to correct a mistake. In the Figure 1 of the paper, the bands referring to brain lanes of EAAC1 and GLAST were wrong. The authors apologise for this mistake. However, the results reported in Table 1 are still correct, and thus the conclusions of the original paper remain valid.
FIGURE 1.
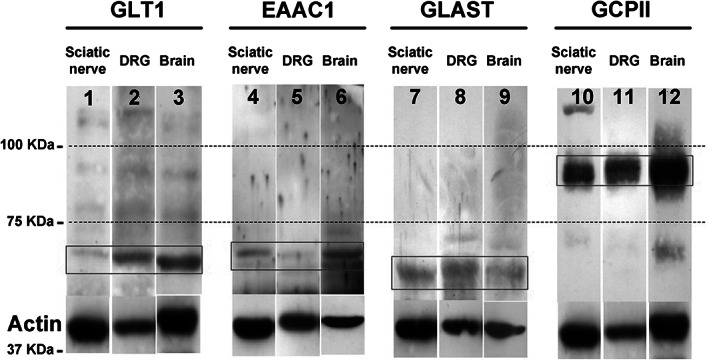
Immunoblotting (11% SDS‐PAGE). Affinity‐purified primary antibody against GLT1 (lanes 1–3), EAAC1 (lanes 4–6), GLAST (lanes 7–9) and GCPII (lanes 10–12) were used. The amount of total protein samples loaded per lane was 40 μg. All three glutamate transporters and GCPII were expressed in both the sciatic nerve and DRG, at the same expected molecular weight as the positive control represented by brain homogenate (GLT1 = 68 kDa, EAAC1 = 70 kDa, GLAST = 60 kDa and GCPII = 85 kDa). Actin (42 kDa) was used for the normalized quantitative densitometric analysis of the bands.
Figure 1 has been corrected as follows:


