Abstract
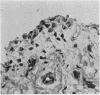
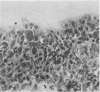
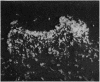
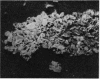
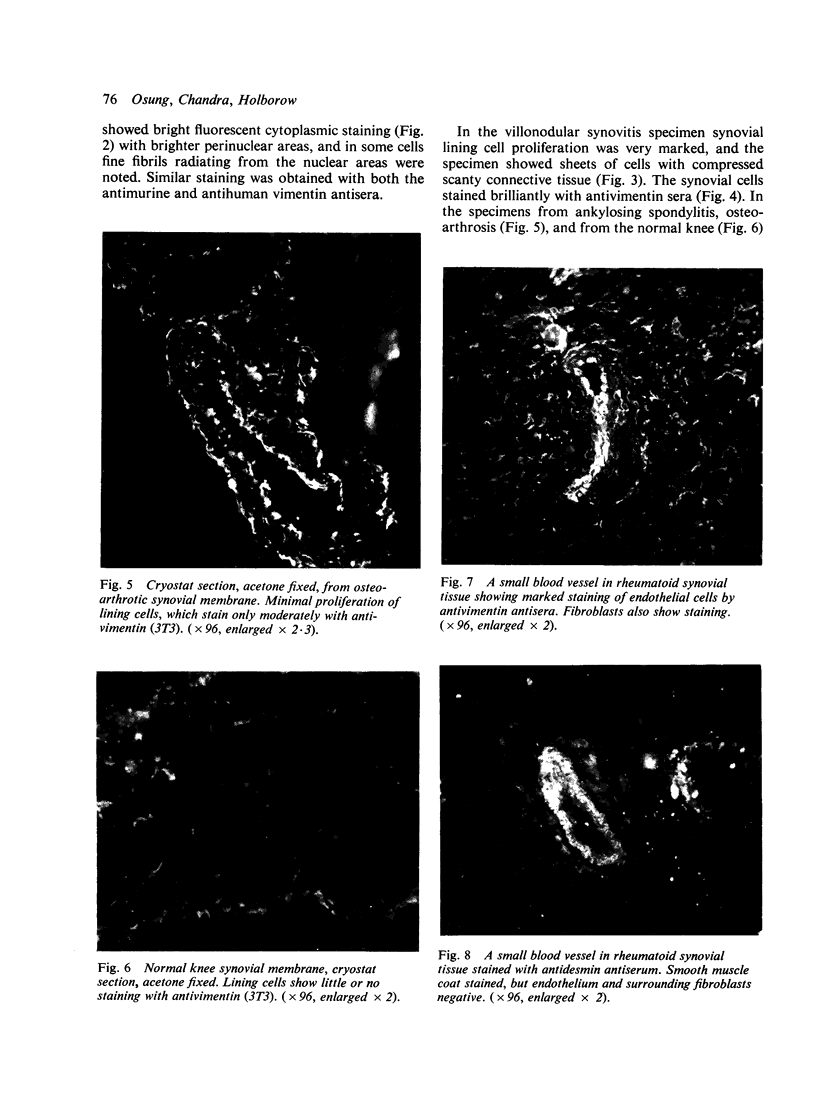
Cryostat section of synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthrosis, pigmented villonodular synovitis, and from a normal knee were studied by indirect immunofluorescence with guinea-pig antibodies to the intermediate filament proteins prekeratin, vimentin, and desmin. Staining for vimentin, but absence of prekeratin and desmin, was demonstrated in synovial lining cells. Antivimentin antibody also stained synovial tissue fibroblasts and vascular endothelial lining cells. The intensity of fluorescent staining for vimentin broadly correlated with cellular proliferative activity at these 3 sites.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. The intermediate-sized filaments in rat kangaroo PtK2 cells. II. Structure and composition of isolated filaments. Cytobiologie. 1978 Aug;17(2):392–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially F. N., Roy S. Ultrastructure of synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1967 Sep;26(5):426–443. doi: 10.1136/ard.26.5.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Fyrand O., Brath H. K., Olsen E. Oligoclonal immunoglobulins and smooth muscle antibodies in arthritic joints. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):103–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Sobieszek A. Studies on the function and composition of the 10-NM(100-A) filaments of vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Sci. 1977 Feb;23:243–268. doi: 10.1242/jcs.23.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]