Abstract
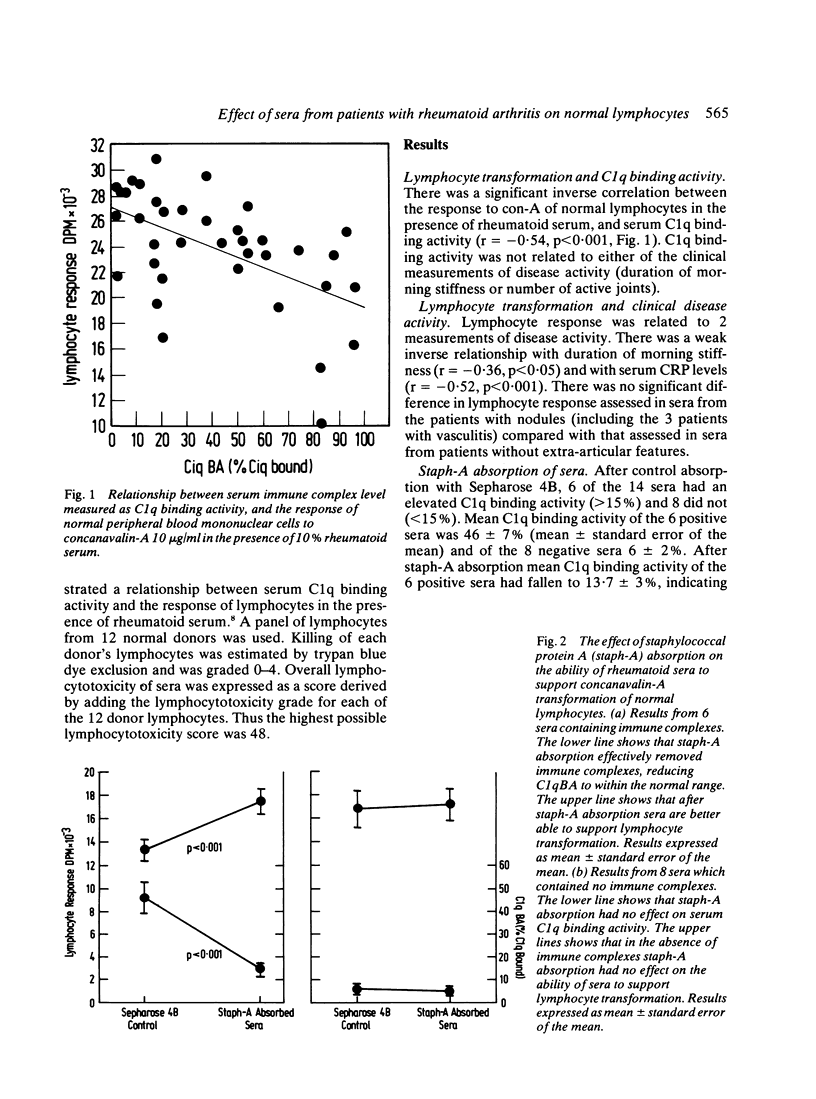
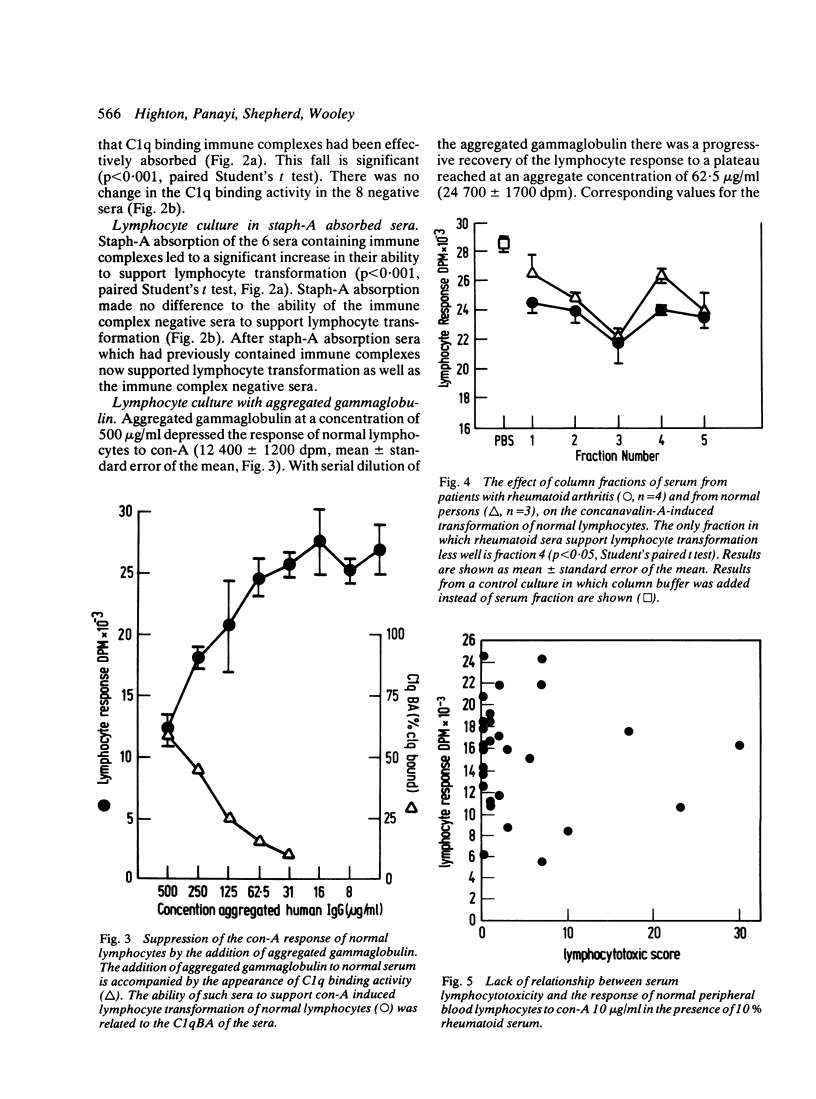
The ability of rheumatoid sera to support concanavalin-A transformation of normal lymphocytes was inversely related to serum C1q binding activity. When C1q binding activity of the sera was removed by absorption with staphylococcal protein A, subsequent lymphocyte response increased to the level found in immune-complex negative sera. Gel filtration of a small number of sera suggested that the suppressive material had a molecular weight in the range 1.8-4.9 x 10(5) daltons. Aggregated human gammaglobulin suppressed con-A transformation of normal lymphocytes in a dose-dependent fashion. These results suggest that immune complexes present in rheumatoid sera can suppress lymphocyte responsiveness. The relevance of this observation to be clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antel J. P., Medof M. E., Oger J. J., Kuo H. H., Arnason B. G. Generation of suppressor cells by aggregated human globulin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Feb;43(2):351–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgren J., Klockars M., Weber T., Wangel A., Linström B., Stenstrand K., Pettersson T., Riska H., Kajander A., Wegelius O. Extracorporeal irradiation of thoracic duct lymph as immunosuppressive treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1976;5(2):108–112. doi: 10.3109/03009747609099900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highton J., Panayi G. S., Shepherd P., Faith A., Griffin J., Gibson T. Fall in immune complex levels during gold treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Dec;40(6):575–579. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.6.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highton J., Panayi G. S., Shepherd P., Griffin J., Gibson T. Changes in immune function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis following treatment with sodium aurothiomalate. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):254–262. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KULKA J. P., BOCKING D., ROPES M. W., BAUER W. Early joint lesions of rheumatoid arthritis; report of eight cases, with knee biopsies of lesions of less than one year's duration. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Feb;59(2):129–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley T. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Katz S. I., Theofilopoulos A. N., Chused T. M., Frank M. M. Demonstration of circulating immune complexes in Sjögren's syndrome. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1382–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Redecha P. B., Inman R. D., Christian C. L. Binding of immunoglobulin G aggregates and immune complexes in human sera to Staphylococci containing protein A. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):627–636. doi: 10.1172/JCI109345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Mickey M. R., Singal D. P., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. 18. Refinement of microdroplet lymphocyte cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1968 Nov;6(8):913–927. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. M., Paulus H. E., Machleder H. I. The role of the lymphocyte and its products in the propagation of joint disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:150–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Jr Synovial membrane and fluid morphologic alterations in early rheumatoid arthritis: microvascular injury and virus-like particles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:39–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Kitridou R. C. Synovitis of recent onset. A clinicopathologic study during the first month of disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Sep-Oct;15(5):465–485. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Moritoh T., Azuma T., Horiuchi Y. Detection of IgG rheumatoid factor by concanavalin A treatment and complement fixation with IgG rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Jun;35(3):240–245. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.3.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Mottironi V. D., Barnett E. V. Cytotoxins in disease. Autocytotoxins in lupus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):724–728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traycoff R. B., Pascual E., Schumacher H. R., Jr Mononuclear cells in human synovial fluid. Identification of lymphoblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jul-Aug;19(4):743–748. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197607/08)19:4<743::aid-art1780190414>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren C., Whicher J., Kohn J. The use of concanavalin A to measure acute phase proteins by laser nephelometry. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Panayi G. S., Batchelor J. R. Lymphocytotoxins in rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence, lymphocyte specificity, and HLA-DR antigens. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Apr;40(2):154–156. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.2.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue R., Tackaberry E., McAvoy D., Shustik C., Broder I. Studies into the occurrence of soluble antigen-antibody complexes in disease. VIII. Fractionation of rheumatoid samples containing immune complex-like material. J Rheumatol. 1978 Fall;5(3):252–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



